
In the diagram of T.S. of the spinal cord given above, certain parts have been indicated by alphabets; choose the answer in which these alphabets have been correctly matched with the parts of which they indicate.
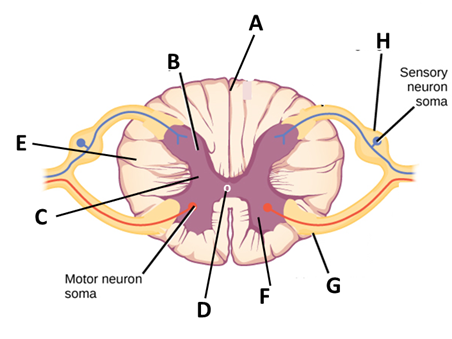
(A) A- Dorsal septum, B- Dorsal horn, C- Grey matter, D- Central cavity, E- White matter, F- Ventral horn, G- Ventral root, H- Dorsal root and ganglion
(B) A- Dorsal septum, B- Dorsal horn, C- Central cavity, D- Grey matter, E- Ventral horn, F- White matter, G- Dorsal root and ganglion, H- Ventral root
(C) A- Dorsal septum, B- Dorsal horn, C- Grey matter, D- White matter, E- Central cavity, F- Ventral root, G- Dorsal root and ganglion
(D) A- Dorsal septum, B- Dorsal horn, C- Central cavity, D- Grey matter, E- Ventral horn, F- Ventral root, G- Dorsal root and ganglion, H- White matter

Answer
572.7k+ views
Hint:-The spinal cord, a unique feature of vertebrates, is a thin, long, tubular structure consisting of nervous tissue. It begins from the medulla oblongata in the brain stem and extends until the lumbar region. It is a connective pathway to transmit information from the peripheral nervous system to the brain.
Complete Answer:-The spinal cord is approximately 43cm long in females and 45cm long in males. It has 31 segments in it with one pair of motor nerve roots and one pair of sensory nerve roots. The segments are ovoid in shape as seen from the picture. Now let us look at the structure and function of each part given in the options to find the answer.
Dorsal septum – The spinal cord and its segments are bilaterally symmetrical which means when it is cut into two halves, both are identical to each other. Both the halves are separated by a median fissure on the ventral side and by median septum in the dorsal side. So dorsal septum is part A.
White matter – It is present in the peripheral region containing many motor and sensory myelinated axons. Since it is myelinated, it appears whiter in colour. The presence of myelin around the axon helps in passing the information quickly. Part E shows the white matter.
Grey matter – This is located inside the posterior region distributed in three grey columns in shape of a butterfly. It consists of interneurons, nerve cell bodies and few myelinated axons. This is at part C in the figure.
Dorsal and ventral horn – These are a part of grey matter. As I mentioned earlier, the grey matter is shaped like a butterfly. The two arms at the back are the dorsal horns, which contains the sensory neuron’s cell bodies. Similarly, the two arms in the front are the ventral horns, containing the cell bodies of motor neurons. Part B and F are dorsal and ventral horns respectively.
Dorsal root and ganglia – It is a bundle of axons. Their primary purpose is to receive sensory information from visceral organs, skin and muscle and pass it to the brain. Dorsal root ganglia is where the dorsal root terminates. Part H is where dorsal root and ganglia is located.
Ventral root – They are made of efferent fibres and carry information for motor neurons. The cell bodies of these neurons are located in the ventral horns. It is located at part G.
Central cavity – It is also known as the central canal and is filled with cerebrospinal fluid. It provides the nutrients to the spinal cord and protects it by cushioning when there is a sudden force. Part D indicates the central cavity.
Thus, the correct answer is option (A).
Note:- The spinal cord is a complex structure with a number of neurons. It is protected by meninges, which is of three layers: dura mater (outermost layer), arachnoid mater (middle layer) and pia mater (adheres to the surface of the spine).
Complete Answer:-The spinal cord is approximately 43cm long in females and 45cm long in males. It has 31 segments in it with one pair of motor nerve roots and one pair of sensory nerve roots. The segments are ovoid in shape as seen from the picture. Now let us look at the structure and function of each part given in the options to find the answer.
Dorsal septum – The spinal cord and its segments are bilaterally symmetrical which means when it is cut into two halves, both are identical to each other. Both the halves are separated by a median fissure on the ventral side and by median septum in the dorsal side. So dorsal septum is part A.
White matter – It is present in the peripheral region containing many motor and sensory myelinated axons. Since it is myelinated, it appears whiter in colour. The presence of myelin around the axon helps in passing the information quickly. Part E shows the white matter.
Grey matter – This is located inside the posterior region distributed in three grey columns in shape of a butterfly. It consists of interneurons, nerve cell bodies and few myelinated axons. This is at part C in the figure.
Dorsal and ventral horn – These are a part of grey matter. As I mentioned earlier, the grey matter is shaped like a butterfly. The two arms at the back are the dorsal horns, which contains the sensory neuron’s cell bodies. Similarly, the two arms in the front are the ventral horns, containing the cell bodies of motor neurons. Part B and F are dorsal and ventral horns respectively.
Dorsal root and ganglia – It is a bundle of axons. Their primary purpose is to receive sensory information from visceral organs, skin and muscle and pass it to the brain. Dorsal root ganglia is where the dorsal root terminates. Part H is where dorsal root and ganglia is located.
Ventral root – They are made of efferent fibres and carry information for motor neurons. The cell bodies of these neurons are located in the ventral horns. It is located at part G.
Central cavity – It is also known as the central canal and is filled with cerebrospinal fluid. It provides the nutrients to the spinal cord and protects it by cushioning when there is a sudden force. Part D indicates the central cavity.
Thus, the correct answer is option (A).
Note:- The spinal cord is a complex structure with a number of neurons. It is protected by meninges, which is of three layers: dura mater (outermost layer), arachnoid mater (middle layer) and pia mater (adheres to the surface of the spine).
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




