
In the following circuit, the current through the resistor R (=2$\Omega $) is I amperes. The value of I is:
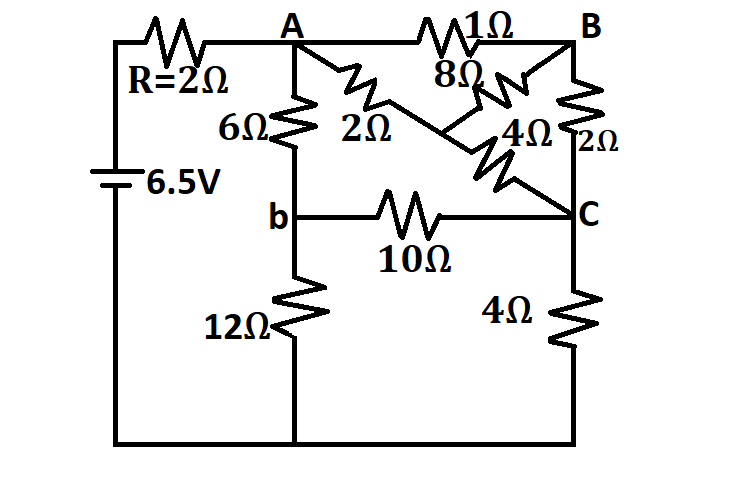

Answer
542.1k+ views
Hint: It is advisable to solve the question by taking one part of the circuit at a time. By doing so we can simplify this complex circuit. It is also observable that the circuit can be simplified into the balanced Wheatstone bridge. The Wheatstone bridge can be analysed clearly as two series of strings in parallel when balanced. In our Resistors in Series tutorial, we saw that as a result of the current flowing through it as described by Ohms Law, each resistor inside the series chain causes an IR drop, or voltage drop through itself. We can solve a balanced Wheatstone bridge easily as the resistance at the junction can be neglected in this case.
Complete answer:
Let us solve the question part by part.
If we observe the network, we can see that it is a case of a balanced Wheatstone bridge. (Refer to the diagram to find the balanced Wheatstone bridge)
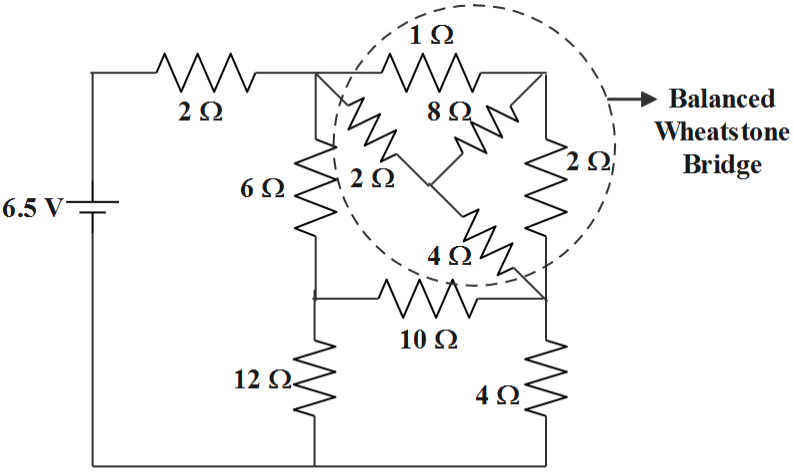
So, now
The equivalent resistance of balanced Wheatstone bridge is
$\dfrac{1}{{{R}_{eq}}}=\dfrac{1}{2+1}+\dfrac{1}{2+4}$
$\Rightarrow \dfrac{1}{{{R}_{eq}}}=\dfrac{1}{3}+\dfrac{1}{6}$
\[\Rightarrow \dfrac{1}{{{R}_{eq}}}=\dfrac{2+1}{6}\]
\[\Rightarrow \dfrac{1}{{{R}_{eq}}}=\dfrac{1}{2}\]
\[\Rightarrow {{R}_{eq}}=2\Omega \]
Now,
The new circuit will look like
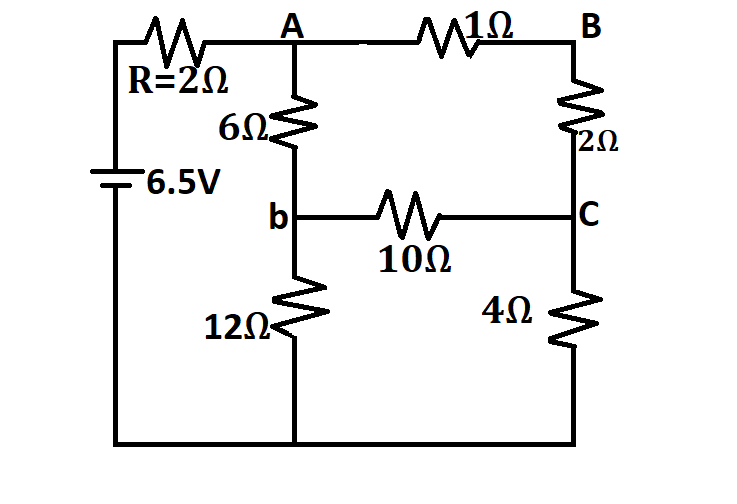
Now, In this new circuit we can see a new balanced Wheatstone Bridge again
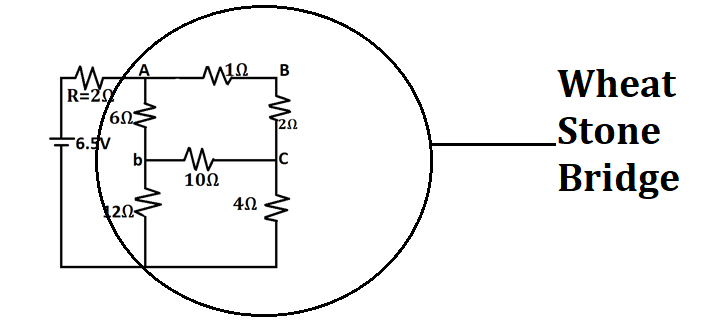
Again, The equivalent resistance of balanced Wheatstone bridge is
$\dfrac{1}{{{R}_{eq}}}=\dfrac{1}{12+6}+\dfrac{1}{2+4}$
$\Rightarrow \dfrac{1}{{{R}_{eq}}}=\dfrac{1}{18}+\dfrac{1}{6}$
\[\Rightarrow \dfrac{1}{{{R}_{eq}}}=\dfrac{1+3}{18}\]
\[\Rightarrow \dfrac{1}{{{R}_{eq}}}=\dfrac{2}{9}\]
\[\Rightarrow {{R}_{eq}}=\dfrac{9}{2}\Omega \]
Now, the total resistance of the circuit will be
\[\Rightarrow {{R}_{eq}}=(2+4.5)\Omega \]
\[\Rightarrow {{R}_{eq}}=6.5\Omega \]
Therefore,
By ohm’s law
We have,
V = IR
So,
$I=\dfrac{V}{R}$
Here,
V = 6.5 V
And R = \[6.5\Omega \]
So, using the values we have
$\Rightarrow I=\dfrac{6.5}{6.5}$
$\Rightarrow I=1A$
So, the value of I in the given circuit will be 1A
Note:
While solving such a question, remember that it is easier to simplify the circuit first. Try taking out the resistances which are useless such as in this case the ones that were rejected due to the balancing of the Wheatstone bridge. Sometimes, the fuses in the circuit are fuse ones which can also be neglected.
Complete answer:
Let us solve the question part by part.
If we observe the network, we can see that it is a case of a balanced Wheatstone bridge. (Refer to the diagram to find the balanced Wheatstone bridge)

So, now
The equivalent resistance of balanced Wheatstone bridge is
$\dfrac{1}{{{R}_{eq}}}=\dfrac{1}{2+1}+\dfrac{1}{2+4}$
$\Rightarrow \dfrac{1}{{{R}_{eq}}}=\dfrac{1}{3}+\dfrac{1}{6}$
\[\Rightarrow \dfrac{1}{{{R}_{eq}}}=\dfrac{2+1}{6}\]
\[\Rightarrow \dfrac{1}{{{R}_{eq}}}=\dfrac{1}{2}\]
\[\Rightarrow {{R}_{eq}}=2\Omega \]
Now,
The new circuit will look like

Now, In this new circuit we can see a new balanced Wheatstone Bridge again

Again, The equivalent resistance of balanced Wheatstone bridge is
$\dfrac{1}{{{R}_{eq}}}=\dfrac{1}{12+6}+\dfrac{1}{2+4}$
$\Rightarrow \dfrac{1}{{{R}_{eq}}}=\dfrac{1}{18}+\dfrac{1}{6}$
\[\Rightarrow \dfrac{1}{{{R}_{eq}}}=\dfrac{1+3}{18}\]
\[\Rightarrow \dfrac{1}{{{R}_{eq}}}=\dfrac{2}{9}\]
\[\Rightarrow {{R}_{eq}}=\dfrac{9}{2}\Omega \]
Now, the total resistance of the circuit will be
\[\Rightarrow {{R}_{eq}}=(2+4.5)\Omega \]
\[\Rightarrow {{R}_{eq}}=6.5\Omega \]
Therefore,
By ohm’s law
We have,
V = IR
So,
$I=\dfrac{V}{R}$
Here,
V = 6.5 V
And R = \[6.5\Omega \]
So, using the values we have
$\Rightarrow I=\dfrac{6.5}{6.5}$
$\Rightarrow I=1A$
So, the value of I in the given circuit will be 1A
Note:
While solving such a question, remember that it is easier to simplify the circuit first. Try taking out the resistances which are useless such as in this case the ones that were rejected due to the balancing of the Wheatstone bridge. Sometimes, the fuses in the circuit are fuse ones which can also be neglected.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




