
In the formation of alkene when alcoholic $KOH$ reacts with $C{H_3}C{H_2}Cl$ . What is the attacking species in the reaction?
A.${C_2}{H_5}{O^ - }$
B.$O{H^ - }$
C.${H_3}{O^ + }$
D.${K^ + }$
Answer
570k+ views
Hint:
Dehydrohalogenation are those types of elimination reactions in which hydrogen and a halogen are eliminated. Attacking species include electrophile, nucleophile and free radicals.
Complete step by step answer:
When alkyl halides are heated in the presence of alcoholic potash (alcoholic potash is when potassium hydroxide is dissolved in alcohol), the product we get is an alkene.
In this one molecule of halogen is eliminated to give alkene.
This type of reaction is also known as dehydrohalogenation reaction.
This type of reaction is an example of $\beta - $ elimination reaction where hydrogen from the $\beta - $carbon is eliminated and halogen from $\alpha - $ carbon is eliminated.
The general reaction of dehydrohalogenation is given as follows:
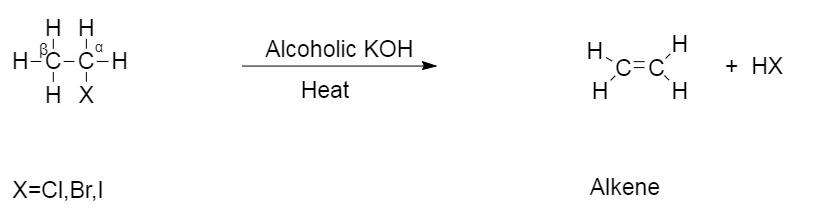
This is the reaction of chloroethane reacting in the presence of alcoholic $KOH$ .
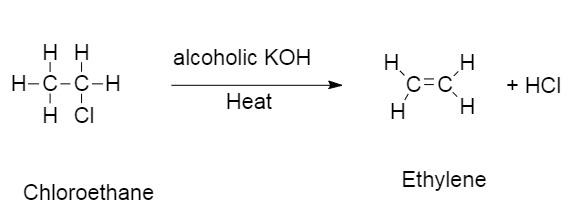
In this reaction chloroethane reacts with alcoholic $KOH$ to give ethylene and $HCl$ .
The hydrogen from the $\beta - $ carbon and a halogen is displaced from chloroethane to give ethylene and hydrochloric acid.
The alcoholic $KOH$ solution consists of alkoxide ion $\left( {R{O^ - }} \right)$ which is a strong base. When alcohol $KOH$ reacts with alkyl halide , the alkoxide easily abstracts hydrogen from the $\beta - $carbon atom and forms alkene by eliminating the molecule of hydrogen halide.
The attacking species that is present in this reaction is ${C_2}{H_5}{O^ - }$ .
So the correct answer is option a) ${C_2}{H_5}{O^ - }$ .
Note:If we use aqueous $KOH$ in this reaction then the attacking species here will be $O{H^ - }$ ion which is a weak base because it becomes weaker as it is highly solvated in aqueous solution. Thus it cannot abstract hydrogen from $\beta - $ carbon atom easily. Therefore, $O{H^ - }$ is a weaker base as compared to alkoxide ion.
Dehydrohalogenation are those types of elimination reactions in which hydrogen and a halogen are eliminated. Attacking species include electrophile, nucleophile and free radicals.
Complete step by step answer:
When alkyl halides are heated in the presence of alcoholic potash (alcoholic potash is when potassium hydroxide is dissolved in alcohol), the product we get is an alkene.
In this one molecule of halogen is eliminated to give alkene.
This type of reaction is also known as dehydrohalogenation reaction.
This type of reaction is an example of $\beta - $ elimination reaction where hydrogen from the $\beta - $carbon is eliminated and halogen from $\alpha - $ carbon is eliminated.
The general reaction of dehydrohalogenation is given as follows:

This is the reaction of chloroethane reacting in the presence of alcoholic $KOH$ .

In this reaction chloroethane reacts with alcoholic $KOH$ to give ethylene and $HCl$ .
The hydrogen from the $\beta - $ carbon and a halogen is displaced from chloroethane to give ethylene and hydrochloric acid.
The alcoholic $KOH$ solution consists of alkoxide ion $\left( {R{O^ - }} \right)$ which is a strong base. When alcohol $KOH$ reacts with alkyl halide , the alkoxide easily abstracts hydrogen from the $\beta - $carbon atom and forms alkene by eliminating the molecule of hydrogen halide.
The attacking species that is present in this reaction is ${C_2}{H_5}{O^ - }$ .
So the correct answer is option a) ${C_2}{H_5}{O^ - }$ .
Note:If we use aqueous $KOH$ in this reaction then the attacking species here will be $O{H^ - }$ ion which is a weak base because it becomes weaker as it is highly solvated in aqueous solution. Thus it cannot abstract hydrogen from $\beta - $ carbon atom easily. Therefore, $O{H^ - }$ is a weaker base as compared to alkoxide ion.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE

In a human foetus the limbs and digits develop after class 12 biology CBSE

AABbCc genotype forms how many types of gametes a 4 class 12 biology CBSE

The correct structure of ethylenediaminetetraacetic class 12 chemistry CBSE




