
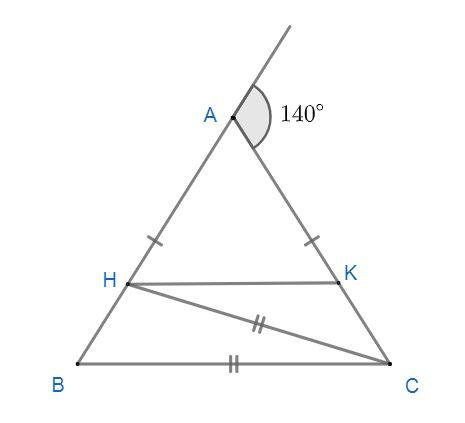
In the given figure, if \[AB = AC\], $CH = CB$ and $HK||BC$, then the value of $\angle HCK$ is
A) $30^\circ $
B) $35^\circ $
C) $40^\circ $
D) $45^\circ $

Answer
586.5k+ views
Hint: First find the value of the angle $\angle BAC$ using the fact that of supplementary angles and then use the property that if the sides of the triangle are same then their corresponding angles are also the same. Then use the given data that $HK||BC$, to approach the desired result.
Complete step by step answer:
We have given that \[AB = AC\], $CH = CB$, exterior angle $\angle A = 140^\circ $ and $HK||BC$ in the adjoint figure.
The goal of the problem is to find the measure of the angle $\angle HCK$.
As we have an exterior angle $\angle A = 140^\circ $, and $\angle BAC$ and $\angle A$ are supplementary angles. So, we can write
$\angle BAC = 180 - \angle A$
$\angle BAC = 180^\circ - 140^\circ $
$\angle BAC = 40^\circ $
Now, we have given that$AB = AC$, it means that the given triangle ABC is an isosceles trinagle so their base angles are same, therefore
$\angle ACB = \angle ABC$
In a triangle$\Delta ABC$, we have
$\angle BAC = 40^\circ $and $\angle ACB = \angle ABC$
We know that the sum of the angles in a triangle is $180^\circ $then we can write
$\angle ABC + \angle ACB + \angle BAC = 180^\circ $
Substitute the value of the angles $\angle BAC = 40^\circ $and $\angle ACB = \angle ABC$ then we have
$\angle ABC + \angle ABC + 40^\circ = 180^\circ $
$ \Rightarrow 2\angle ABC = 180^\circ - 40^\circ $
$ \Rightarrow \angle ABC = \dfrac{{140^\circ }}{2}$
$ \Rightarrow \angle ABC = 70^\circ $
Then we also have:
$\angle ACB = \angle ABC = 70^\circ $
It is also given that the transversal lines $HK$ is parallel to the $BC$, then using the property of transversal lines, we have:
$\angle ACB = \angle ABC = \angle AHK = \angle AKH$
$\Rightarrow \angle AHK = \angle AKH = 70^\circ $
We can see that $\angle AKH$ and $\angle HKC$ are supplementary angles, so we have
$\angle AKH + \angle HKC = 180$
Substituting the values $\angle AKH = 70^\circ $, then
$70^\circ + \angle HKC = 180$
$\angle HKC = 180^\circ - 70^\circ $
$\angle HKC = 110^\circ $
We also have given that $CH = CB$, then the corresponding angles are also same, that is
$\angle HBC = \angle BHC$
The angle $\angle HBC$ is equal to the angle $\angle ABC$. So, we can write as
$\Rightarrow \angle HBC = \angle BHC = 70^\circ $
We can see in the figure that,
$\Rightarrow \angle AHK + \angle KHC + \angle BHC = 180^\circ $
Substitute the values $\angle AHK = 70^\circ $ and $\angle BHC = 70^\circ $ into the equation
$70^\circ + \angle KHC + 70^\circ = 180^\circ $
$ \Rightarrow \angle KHC = 180^\circ - 140^\circ $
$ \Rightarrow \angle KHC = 40^\circ $
Now, in the triangles $\Delta KHC$, we have
\[\Rightarrow \angle KHC = 40^\circ \] and $\angle HKC = 110^\circ $
We know that the sum of the angles of the triangle is $180^\circ $, so we can write
\[\Rightarrow \angle KHC + \angle HKC + \angle HCK = 180^\circ \]
Substituting the values \[\angle KHC = 40^\circ \] and $\angle HKC = 110^\circ $ into the equation,
\[\Rightarrow 40^\circ + 110^\circ + \angle HCK = 180^\circ \]
\[ \Rightarrow \angle HCK = 180^\circ - 150^\circ \]
\[ \Rightarrow \angle HCK = 30^\circ \]
Therefore, the required measurement of the angle has the value \[\angle HCK = 30^\circ \].
Note:
If the sum of two angles is $180^\circ $then these angles are said as supplementary angles and of the sum of two angles is $90^\circ $, then these angles are called complementary angles.
Complete step by step answer:
We have given that \[AB = AC\], $CH = CB$, exterior angle $\angle A = 140^\circ $ and $HK||BC$ in the adjoint figure.
The goal of the problem is to find the measure of the angle $\angle HCK$.
As we have an exterior angle $\angle A = 140^\circ $, and $\angle BAC$ and $\angle A$ are supplementary angles. So, we can write
$\angle BAC = 180 - \angle A$
$\angle BAC = 180^\circ - 140^\circ $
$\angle BAC = 40^\circ $
Now, we have given that$AB = AC$, it means that the given triangle ABC is an isosceles trinagle so their base angles are same, therefore
$\angle ACB = \angle ABC$
In a triangle$\Delta ABC$, we have
$\angle BAC = 40^\circ $and $\angle ACB = \angle ABC$
We know that the sum of the angles in a triangle is $180^\circ $then we can write
$\angle ABC + \angle ACB + \angle BAC = 180^\circ $
Substitute the value of the angles $\angle BAC = 40^\circ $and $\angle ACB = \angle ABC$ then we have
$\angle ABC + \angle ABC + 40^\circ = 180^\circ $
$ \Rightarrow 2\angle ABC = 180^\circ - 40^\circ $
$ \Rightarrow \angle ABC = \dfrac{{140^\circ }}{2}$
$ \Rightarrow \angle ABC = 70^\circ $
Then we also have:
$\angle ACB = \angle ABC = 70^\circ $
It is also given that the transversal lines $HK$ is parallel to the $BC$, then using the property of transversal lines, we have:
$\angle ACB = \angle ABC = \angle AHK = \angle AKH$
$\Rightarrow \angle AHK = \angle AKH = 70^\circ $
We can see that $\angle AKH$ and $\angle HKC$ are supplementary angles, so we have
$\angle AKH + \angle HKC = 180$
Substituting the values $\angle AKH = 70^\circ $, then
$70^\circ + \angle HKC = 180$
$\angle HKC = 180^\circ - 70^\circ $
$\angle HKC = 110^\circ $
We also have given that $CH = CB$, then the corresponding angles are also same, that is
$\angle HBC = \angle BHC$
The angle $\angle HBC$ is equal to the angle $\angle ABC$. So, we can write as
$\Rightarrow \angle HBC = \angle BHC = 70^\circ $
We can see in the figure that,
$\Rightarrow \angle AHK + \angle KHC + \angle BHC = 180^\circ $
Substitute the values $\angle AHK = 70^\circ $ and $\angle BHC = 70^\circ $ into the equation
$70^\circ + \angle KHC + 70^\circ = 180^\circ $
$ \Rightarrow \angle KHC = 180^\circ - 140^\circ $
$ \Rightarrow \angle KHC = 40^\circ $
Now, in the triangles $\Delta KHC$, we have
\[\Rightarrow \angle KHC = 40^\circ \] and $\angle HKC = 110^\circ $
We know that the sum of the angles of the triangle is $180^\circ $, so we can write
\[\Rightarrow \angle KHC + \angle HKC + \angle HCK = 180^\circ \]
Substituting the values \[\angle KHC = 40^\circ \] and $\angle HKC = 110^\circ $ into the equation,
\[\Rightarrow 40^\circ + 110^\circ + \angle HCK = 180^\circ \]
\[ \Rightarrow \angle HCK = 180^\circ - 150^\circ \]
\[ \Rightarrow \angle HCK = 30^\circ \]
Therefore, the required measurement of the angle has the value \[\angle HCK = 30^\circ \].
Note:
If the sum of two angles is $180^\circ $then these angles are said as supplementary angles and of the sum of two angles is $90^\circ $, then these angles are called complementary angles.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 7 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 7 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 7 Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Class 7 Question and Answer - Your Ultimate Solutions Guide

Master Class 9 General Knowledge: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 9 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
The value of 6 more than 7 is A 1 B 1 C 13 D 13 class 7 maths CBSE

Convert 200 Million dollars in rupees class 7 maths CBSE

List of coprime numbers from 1 to 100 class 7 maths CBSE

AIM To prepare stained temporary mount of onion peel class 7 biology CBSE

The plural of Chief is Chieves A True B False class 7 english CBSE

Write a letter to the editor of the national daily class 7 english CBSE





