
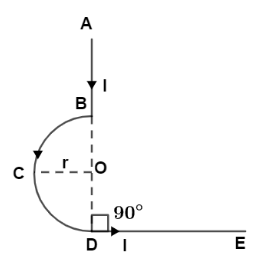
In the given figure, the magnetic induction at the point $O$ is
A. $\dfrac{{{\mu _0}I}}{{4\pi r}}$
B. $\dfrac{{{\mu _0}I}}{{2\pi r}} + \dfrac{{{\mu _0}I}}{{4r}}$
C. $\dfrac{{{\mu _0}I}}{{4\pi r}} + \dfrac{{{\mu _0}I}}{{4r}}$
D. $ - \dfrac{{{\mu _0}I}}{{4\pi r}} + \dfrac{{{\mu _0}I}}{{4r}}$

Answer
508.8k+ views
Hint: In magnetism, magnetic field is the space around an accelerated charge or current carrying conductor where magnetic force can be experienced, in order to find net magnetic induction at point O we will use the general formula of finding magnetic field due to current carrying wire.
Formula used:
Magnetic field due to semicircular arc of wire at centre having current $I$ and radius $r$ is calculated as,
${B_{centre}} = \dfrac{{{\mu _0}I}}{{4r}}$
Magnetic field due to wire at one end perpendicular to the wire at a distance of $r$ is calculated by,
${B_{end}} = \dfrac{{{\mu _0}I}}{{4\pi r}}$
Magnetic field due to wire at a point on the line of wire at any distance through it on any end is always zero.
Complete step by step answer:
According to the given diagram, we can see that the part of wire AB having current I and point O lies on the line of wire AB hence the magnetic field due to this part will be zero.
${B_{AB}} = 0$
Now, part of wire BCD is a semi-circular arc having radius of r and current I and centre at O then by using the formula ${B_{centre}} = \dfrac{{{\mu _0}I}}{{4r}}$ the magnetic field at point O will be
${B_{BCD}} = \dfrac{{{\mu _0}I}}{{4r}}$
Now, the part of wire DE having current I, point O lies perpendicular to the wire at one end and having at a distance of r will have magnetic field according to the formula ${B_{end}} = \dfrac{{{\mu _0}I}}{{4\pi r}}$ so,
${B_{DE}} = \dfrac{{{\mu _0}I}}{{4\pi r}}$
Since magnetic field due to each individual part is same hence, total magnetic field at point O can be written as
${B_{net}} = {B_{BCD}} + {B_{DE}} + {B_{AB}}$
On putting the values we get,
$\therefore {B_{net}} = \dfrac{{{\mu _0}I}}{{4\pi r}} + \dfrac{{{\mu _0}I}}{{4r}}$
Hence, the correct option is C.
Note: It should be remembered that, if the current in the wire is moving in anticlockwise direction then direction of magnetic field will be out of the plane and if current were flowing in clockwise direction then magnetic field direction would be into the plane.${\mu _0}$ Is known as the permeability of free space.
Formula used:
Magnetic field due to semicircular arc of wire at centre having current $I$ and radius $r$ is calculated as,
${B_{centre}} = \dfrac{{{\mu _0}I}}{{4r}}$
Magnetic field due to wire at one end perpendicular to the wire at a distance of $r$ is calculated by,
${B_{end}} = \dfrac{{{\mu _0}I}}{{4\pi r}}$
Magnetic field due to wire at a point on the line of wire at any distance through it on any end is always zero.
Complete step by step answer:
According to the given diagram, we can see that the part of wire AB having current I and point O lies on the line of wire AB hence the magnetic field due to this part will be zero.
${B_{AB}} = 0$
Now, part of wire BCD is a semi-circular arc having radius of r and current I and centre at O then by using the formula ${B_{centre}} = \dfrac{{{\mu _0}I}}{{4r}}$ the magnetic field at point O will be
${B_{BCD}} = \dfrac{{{\mu _0}I}}{{4r}}$
Now, the part of wire DE having current I, point O lies perpendicular to the wire at one end and having at a distance of r will have magnetic field according to the formula ${B_{end}} = \dfrac{{{\mu _0}I}}{{4\pi r}}$ so,
${B_{DE}} = \dfrac{{{\mu _0}I}}{{4\pi r}}$
Since magnetic field due to each individual part is same hence, total magnetic field at point O can be written as
${B_{net}} = {B_{BCD}} + {B_{DE}} + {B_{AB}}$
On putting the values we get,
$\therefore {B_{net}} = \dfrac{{{\mu _0}I}}{{4\pi r}} + \dfrac{{{\mu _0}I}}{{4r}}$
Hence, the correct option is C.
Note: It should be remembered that, if the current in the wire is moving in anticlockwise direction then direction of magnetic field will be out of the plane and if current were flowing in clockwise direction then magnetic field direction would be into the plane.${\mu _0}$ Is known as the permeability of free space.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




