
In the half wave rectifier circuit operating with 5Hz mains frequency. The fundamental frequency in the ripple will be:
(A) \[100\,{\text{Hz}}\]
(B) \[20\,{\text{Hz}}\]
(C) \[50\,{\text{Hz}}\]
(D) \[25\,{\text{Hz}}\]
Answer
576k+ views
Hint: First of all, we will see that in a half wave rectifier circuit, we only get the half of a wave i.e. the positive part followed by elimination of the negative part. In a full wave rectifier circuit, the ripple frequency is twice that of the main frequency.
Complete answer:
-Let us discuss a bit about a rectifier circuit and a half rectifier circuit. Before that let us discuss a bit about the element rectifier to have better understanding. A rectifier is an electrical device consisting of one or even more diodes which allow only one direction of current flow. Essentially, alternating current is converted into direct current. As required, rectifiers can be moulded in several forms, such as semiconductor diodes, SCRs (silicon-controlled rectifiers), vacuum tube diodes, mercury arc valves, etc.
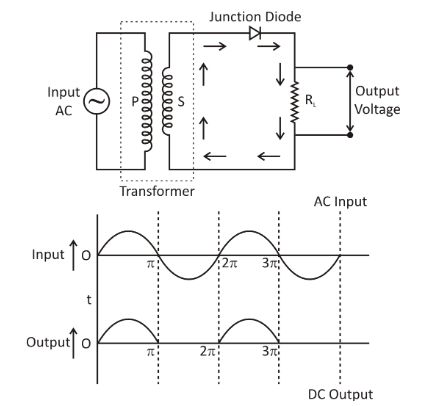
-Only one half of the input sine wave (either positive or negative) passes through the half wave rectifier and rejects the other half. Pulsating DC is the output of the half wave rectifier. Using the filtration system, the ripple in the output waveform can be reduced.
-We understand that, for the full wave rectifier, the fundamental frequency of the ripple voltage is twice, but for the half wave rectifier, the basic frequency of the ripple voltage is equal to the supply frequency.Hence, the basic frequency in the ripple would then be the same as the main frequency in a half wave rectifier circuit working from the \[50\,{\text{Hz}}\] main frequency.
The correct option is C.
Note:While answering this question, we should remember that full-wave rectification rectifies the input voltage negative portion to a positive voltage, then transforms it using a diode bridge configuration into DC (pulse current). In comparison, before switching to DC, half-wave rectification eliminates only the negative voltage portion using a single diode.
Complete answer:
-Let us discuss a bit about a rectifier circuit and a half rectifier circuit. Before that let us discuss a bit about the element rectifier to have better understanding. A rectifier is an electrical device consisting of one or even more diodes which allow only one direction of current flow. Essentially, alternating current is converted into direct current. As required, rectifiers can be moulded in several forms, such as semiconductor diodes, SCRs (silicon-controlled rectifiers), vacuum tube diodes, mercury arc valves, etc.

-Only one half of the input sine wave (either positive or negative) passes through the half wave rectifier and rejects the other half. Pulsating DC is the output of the half wave rectifier. Using the filtration system, the ripple in the output waveform can be reduced.
-We understand that, for the full wave rectifier, the fundamental frequency of the ripple voltage is twice, but for the half wave rectifier, the basic frequency of the ripple voltage is equal to the supply frequency.Hence, the basic frequency in the ripple would then be the same as the main frequency in a half wave rectifier circuit working from the \[50\,{\text{Hz}}\] main frequency.
The correct option is C.
Note:While answering this question, we should remember that full-wave rectification rectifies the input voltage negative portion to a positive voltage, then transforms it using a diode bridge configuration into DC (pulse current). In comparison, before switching to DC, half-wave rectification eliminates only the negative voltage portion using a single diode.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




