
In the hydroboration-oxidation reaction of propene with diborane, ${H_2}{O_2}$ and NaOH, the organic compound formed is:
(A) $C{H_3}C{H_2}OH$
(B) $C{H_3}CH(OH)C{H_3}$
(C) $C{H_3}C{H_2}C{H_2}OH$
(D) ${(C{H_3})_3}COH$
Answer
593.7k+ views
Hint: In this reaction alkenes are converted into primary alcohols and the addition of alcohol takes place according to anti markovnikov rule.
Complete answer:
-The hydroboration-oxidation reaction is a two step hydration reaction which converts an alkene into an alcohol. There occurs addition of water (hydrogen and hydroxyl group) along the double bond, and the stoichiometry of the product is cis.
It is also an anti-markovnikov reaction and thus the hydroxyl group attaches to the carbon atom which is least substituted.
According to the anti-markovnikov rule the substituent is bonded to the least substituted carbon atom or the carbon atom having the most number of hydrogen atoms.
The solvent used for hydroboration is THF (Tetrahydrofuran).
-In this reaction the propene molecule reacts with diborane (${B_2}{H_6}$,${H_2}{O_2}$) and NaOH to give a final product of propan-1-ol ($C{H_3}C{H_2}C{H_2}OH$). This reaction occurs in two steps:
1) Hydroboration step: $B{H_3}$ reacts with the double bond and transfers one of the hydrogen atoms to the C atom adjacent to the one that bonds with the B atom. This step is repeated two more times until 3 alkyl groups are bonded with the B atom to form${R_3}B$. In case of propene the product formed here is: ${\left( {C{H_3}C{H_2}C{H_2}} \right)_3}B$
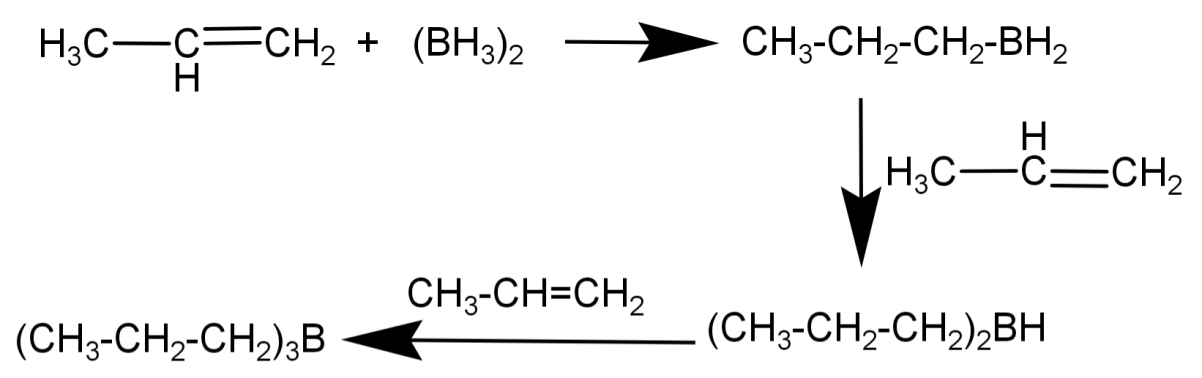
2) Oxidation step: Now the boron atom is attacked by the hydrogen peroxide ion which acts as a nucleophile and sodium hydroxide (${H_2}{O_2}/O{H^ - }$) and produces primary alcohol (R-OH). In case of propene the product formed will be ($C{H_3}C{H_2}C{H_2}OH$).
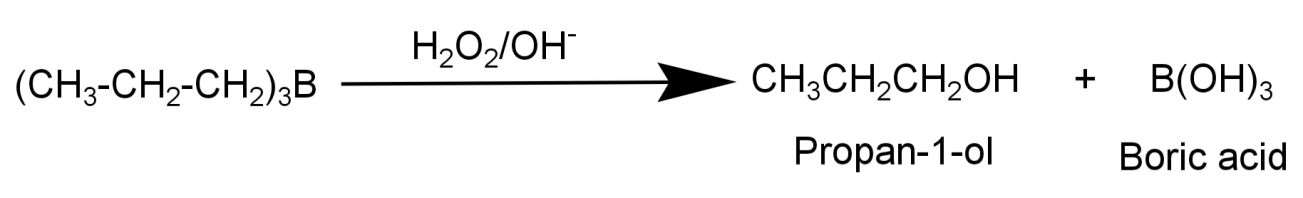
The final product formed is propan-1-ol ($C{H_3}C{H_2}C{H_2}OH$).
So, the correct option is: (C) $C{H_3}C{H_2}C{H_2}OH$
So, the correct answer is “Option C”.
Note: In this reaction the product formed is a cis product because the addition of hydroxyl group (-OH) and the hydrogen ion takes place on the same side of the double bond which means syn addition occurs.
Complete answer:
-The hydroboration-oxidation reaction is a two step hydration reaction which converts an alkene into an alcohol. There occurs addition of water (hydrogen and hydroxyl group) along the double bond, and the stoichiometry of the product is cis.
It is also an anti-markovnikov reaction and thus the hydroxyl group attaches to the carbon atom which is least substituted.
According to the anti-markovnikov rule the substituent is bonded to the least substituted carbon atom or the carbon atom having the most number of hydrogen atoms.
The solvent used for hydroboration is THF (Tetrahydrofuran).
-In this reaction the propene molecule reacts with diborane (${B_2}{H_6}$,${H_2}{O_2}$) and NaOH to give a final product of propan-1-ol ($C{H_3}C{H_2}C{H_2}OH$). This reaction occurs in two steps:
1) Hydroboration step: $B{H_3}$ reacts with the double bond and transfers one of the hydrogen atoms to the C atom adjacent to the one that bonds with the B atom. This step is repeated two more times until 3 alkyl groups are bonded with the B atom to form${R_3}B$. In case of propene the product formed here is: ${\left( {C{H_3}C{H_2}C{H_2}} \right)_3}B$

2) Oxidation step: Now the boron atom is attacked by the hydrogen peroxide ion which acts as a nucleophile and sodium hydroxide (${H_2}{O_2}/O{H^ - }$) and produces primary alcohol (R-OH). In case of propene the product formed will be ($C{H_3}C{H_2}C{H_2}OH$).

The final product formed is propan-1-ol ($C{H_3}C{H_2}C{H_2}OH$).
So, the correct option is: (C) $C{H_3}C{H_2}C{H_2}OH$
So, the correct answer is “Option C”.
Note: In this reaction the product formed is a cis product because the addition of hydroxyl group (-OH) and the hydrogen ion takes place on the same side of the double bond which means syn addition occurs.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




