
In the Lewis structure of $S{O_3}$. What is the formal charge on the atom $O$?
Answer
504.3k+ views
Hint: The Lewis structure is also called an electron dot structure which determines the number of valence electrons present in an atom. Moreover, they also describe how these valence electrons are participating in the bond formation to form a molecule.
Complete answer:
According to octet rule, the maximum number of electrons that can be filled within a valence shell is eight. When there are less than eight electrons only then an atom undergoes a bond formation either by accepting or donating electrons to achieve a stable condition like noble gases.
The sulfur trioxide is a tetra atomic chemical molecule where both the sulfur and three oxygen molecules bond with an equal number of valence electrons. The total number of valence electrons in a single sulfur trioxide molecule is $24$. Six electrons are needed to complete the octet in the $S{O_3}$ molecule, where both sulfur and oxygen atoms need two valence electrons to stabilize their atom.
In the molecule of sulfur trioxide there are three double covalent bond between sulfur and oxygen atom each. The structure of sulfur trioxide is trigonal pyramidal, as the double bond is formed there are no lone pair exists on the central atom sulfur. Sulfur trioxide does not have a charge and the oxygen atoms are so electronegative that sulfur surrenders its electron to them, because sulfur is weak compared to oxygen.
To calculate formal charge on oxygen, using the following equation:
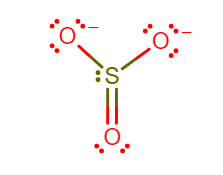
Formal charge= (Number of valence electrons in free atom) $ - $ (Number of Lone-pair electrons) $ - $ ($\dfrac{1}{2}$ number of pair electrons)
Formal charge on Oxygen atom= $(6) - (6) - (\dfrac{1}{2} \times 2)$
Therefore, formal charge on oxygen is $ - 1$
Note:
The common arrangement of oxygen that has formal charge of zero is when the oxygen atom has two bonds and two lone pairs. Oxygen can also exist as a radical, such as where an oxygen atom has one bond, two lone pairs, and one unpaired electron, giving it a formal charge of zero.
Complete answer:
According to octet rule, the maximum number of electrons that can be filled within a valence shell is eight. When there are less than eight electrons only then an atom undergoes a bond formation either by accepting or donating electrons to achieve a stable condition like noble gases.
The sulfur trioxide is a tetra atomic chemical molecule where both the sulfur and three oxygen molecules bond with an equal number of valence electrons. The total number of valence electrons in a single sulfur trioxide molecule is $24$. Six electrons are needed to complete the octet in the $S{O_3}$ molecule, where both sulfur and oxygen atoms need two valence electrons to stabilize their atom.
In the molecule of sulfur trioxide there are three double covalent bond between sulfur and oxygen atom each. The structure of sulfur trioxide is trigonal pyramidal, as the double bond is formed there are no lone pair exists on the central atom sulfur. Sulfur trioxide does not have a charge and the oxygen atoms are so electronegative that sulfur surrenders its electron to them, because sulfur is weak compared to oxygen.
To calculate formal charge on oxygen, using the following equation:

Formal charge= (Number of valence electrons in free atom) $ - $ (Number of Lone-pair electrons) $ - $ ($\dfrac{1}{2}$ number of pair electrons)
Formal charge on Oxygen atom= $(6) - (6) - (\dfrac{1}{2} \times 2)$
Therefore, formal charge on oxygen is $ - 1$
Note:
The common arrangement of oxygen that has formal charge of zero is when the oxygen atom has two bonds and two lone pairs. Oxygen can also exist as a radical, such as where an oxygen atom has one bond, two lone pairs, and one unpaired electron, giving it a formal charge of zero.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

What is a transformer Explain the principle construction class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE




