
In which of the following compounds, all the monosaccharide units are not joined by only ${{C}_{1}}-O-{{C}_{4}}$ chain?
(A) Lactose
(B) Maltose
(C) Cellulose
(D) Amylopectin
Answer
578.1k+ views
Hint: Hint: Monosaccharides are also known as simple sugars as it is the simplest form of sugar and most basic unit of carbohydrates which cannot be further hydrolyzed to any other simpler chemical compounds.
Complete Step by step explanation: Carbohydrate is a biomolecule which consists of carbon, oxygen and hydrogen atoms. In biochemistry carbohydrates are known by the name saccharides which have sugar, starch and cellulose. The saccharides can be further divided into four groups known by monosaccharides, disaccharides, polysaccharides and oligosaccharides. Monosaccharides and disaccharides are the smallest carbohydrates which correspond to sugar. Monosaccharides generally ended with the suffix ose.
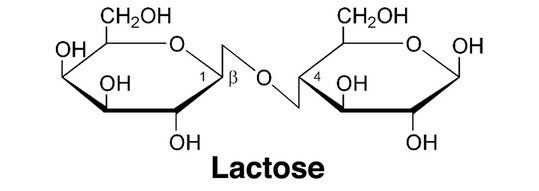
Lactose: It is generally made up of two units of glucose called galactose and glucose having molecular formula${{C}_{12}}{{H}_{22}}{{O}_{11}}$. It is formed by $\beta -1\to 4$ glycosidic linkage i.e. monosaccharides are joined by ${{C}_{1}}-O-{{C}_{4}}$ chain shown as:
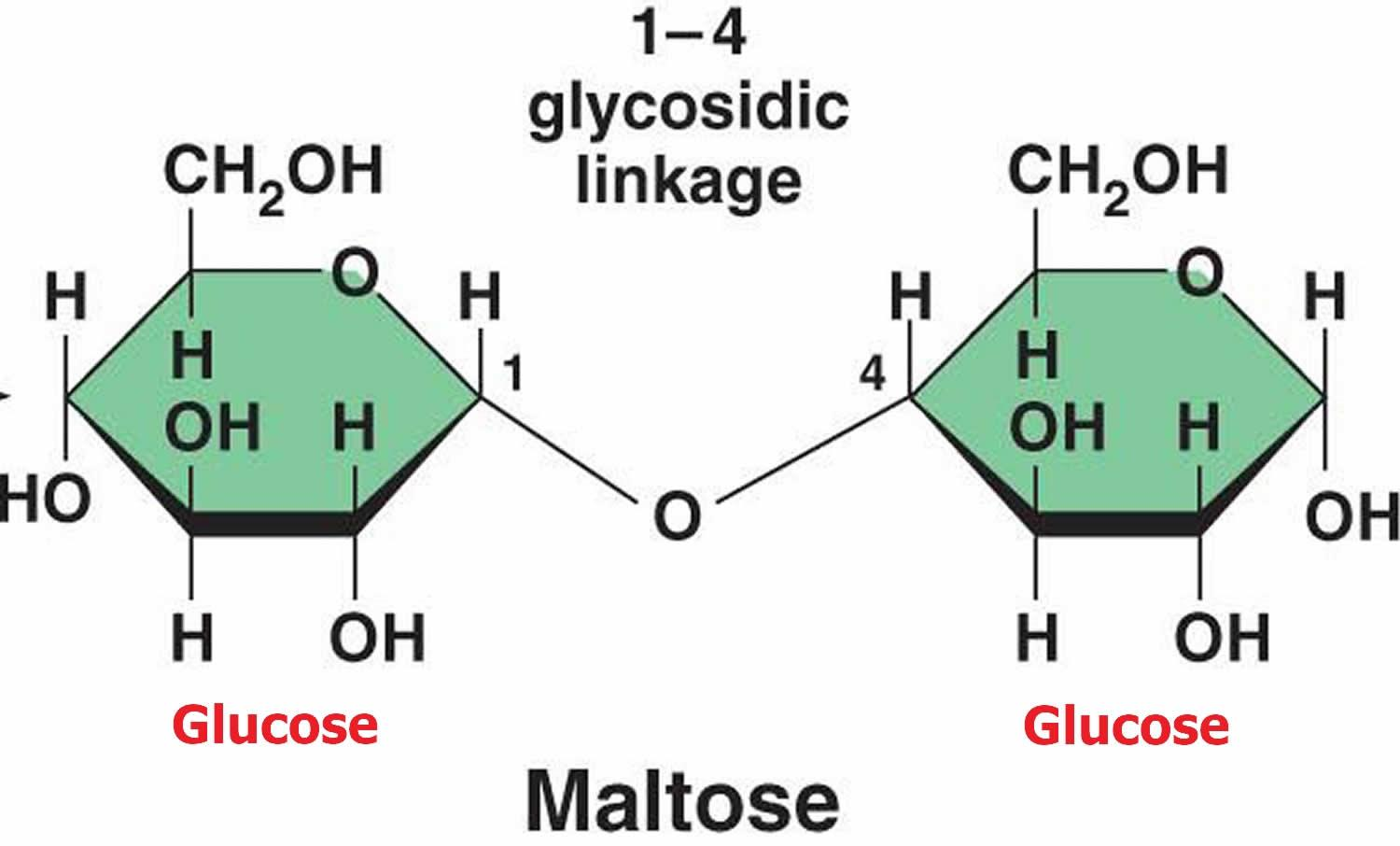
Maltose: Maltose is also known by maltobiose or malt sugar. It is formed from two glucose units joined by $\alpha -1\to 4$ bonds.
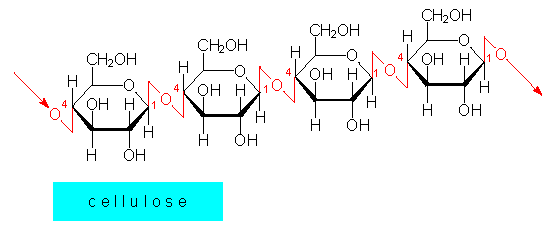
Cellulose: Cellulose is an organic compound having molecular formula${{({{C}_{6}}{{H}_{10}}{{O}_{5}})}_{n}}$. It consists of $\beta -1\to 4$ linked glucose units.
Amylopectin: It is a branched chain polymer of \[\alpha -D-glu\cos e\] units in which the chain is formed by two types of linkages i.e.${{C}_{1}}-{{C}_{4}}$ glycosidic linkage, whereas branching occurs by ${{C}_{1}}-{{C}_{6}}$ glycosidic linkage.
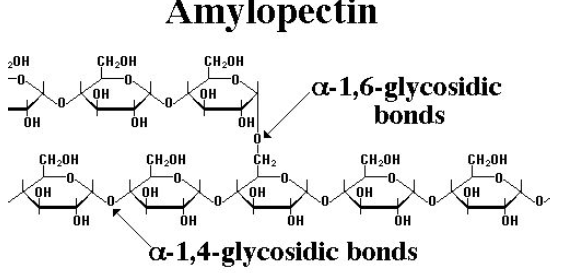
Thus, amylopectin consists of two types of linkages so we can say that option d is correct.
Note: Glycosidic linkage is a type of covalent bond that joins a carbohydrate molecule to another group which may or may not be carbohydrate.
Complete Step by step explanation: Carbohydrate is a biomolecule which consists of carbon, oxygen and hydrogen atoms. In biochemistry carbohydrates are known by the name saccharides which have sugar, starch and cellulose. The saccharides can be further divided into four groups known by monosaccharides, disaccharides, polysaccharides and oligosaccharides. Monosaccharides and disaccharides are the smallest carbohydrates which correspond to sugar. Monosaccharides generally ended with the suffix ose.
Lactose: It is generally made up of two units of glucose called galactose and glucose having molecular formula${{C}_{12}}{{H}_{22}}{{O}_{11}}$. It is formed by $\beta -1\to 4$ glycosidic linkage i.e. monosaccharides are joined by ${{C}_{1}}-O-{{C}_{4}}$ chain shown as:

Maltose: Maltose is also known by maltobiose or malt sugar. It is formed from two glucose units joined by $\alpha -1\to 4$ bonds.

Cellulose: Cellulose is an organic compound having molecular formula${{({{C}_{6}}{{H}_{10}}{{O}_{5}})}_{n}}$. It consists of $\beta -1\to 4$ linked glucose units.

Amylopectin: It is a branched chain polymer of \[\alpha -D-glu\cos e\] units in which the chain is formed by two types of linkages i.e.${{C}_{1}}-{{C}_{4}}$ glycosidic linkage, whereas branching occurs by ${{C}_{1}}-{{C}_{6}}$ glycosidic linkage.

Thus, amylopectin consists of two types of linkages so we can say that option d is correct.
Note: Glycosidic linkage is a type of covalent bond that joins a carbohydrate molecule to another group which may or may not be carbohydrate.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

What is a transformer Explain the principle construction class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE




