
What is the increasing order of acidic strength among the following?
i. para-methoxy phenol
ii. para-methyl phenol
iii. para-nitro phenol
A) ii$<$iii$<$i
B) iii$<$ii$<$i
C) i$<$ii$<$iii
D) i$<$iii$<$ii
Answer
600k+ views
Hint: The question is dealing with different types of phenols. The pH of phenol is around 10 (in water) so; the pH of all the above species will be either above 10 or below 10.
Complete step by step answer:
First we need to understand the structures of all these phenols.
Given Below are the structures of the different phenols.
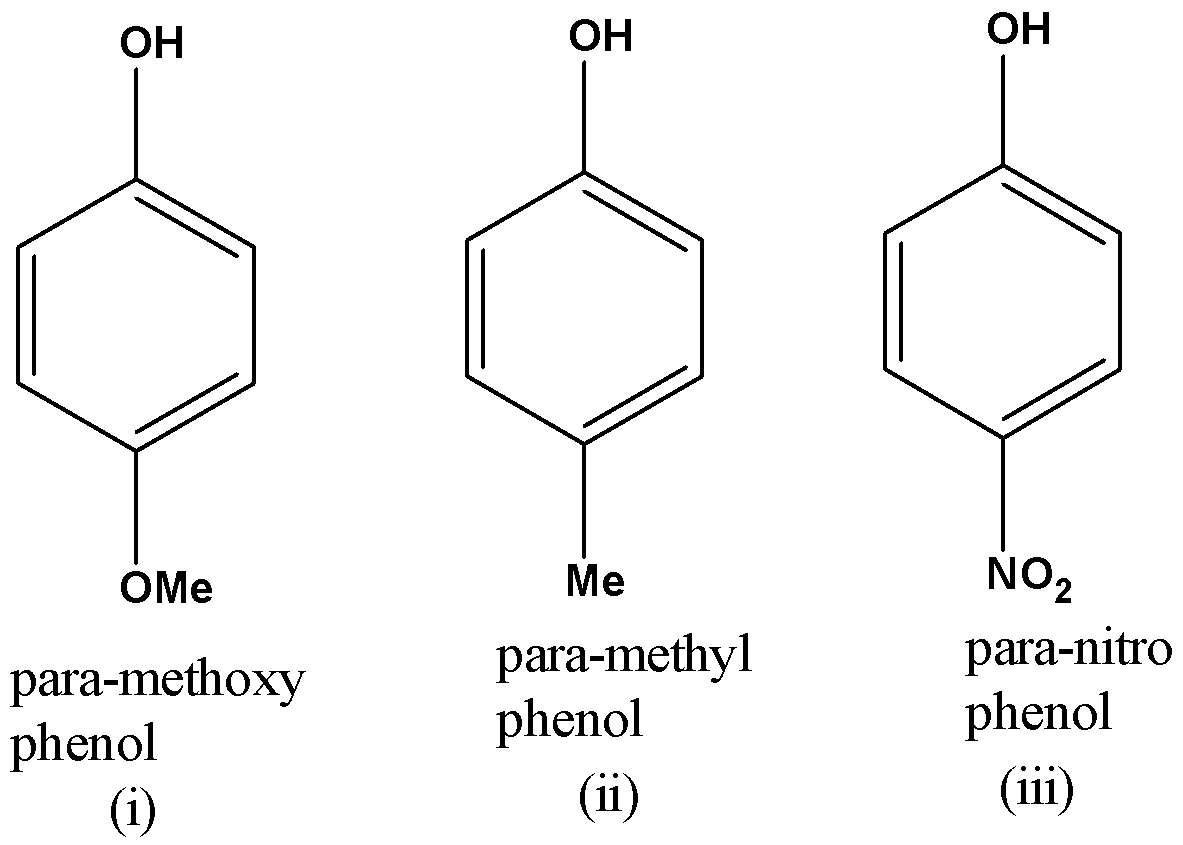
Phenols are more acidic than saturated alcohols due to the stabilisation of the negative charge on the phenolate ion over the benzene ring. For example Phenol is far more acidic than methanol since the methoxide ion is highly unstable whereas the phenoxide ion is stabilized due to resonance.
In the above question all are a type of phenol but with different substituents present at the para position.
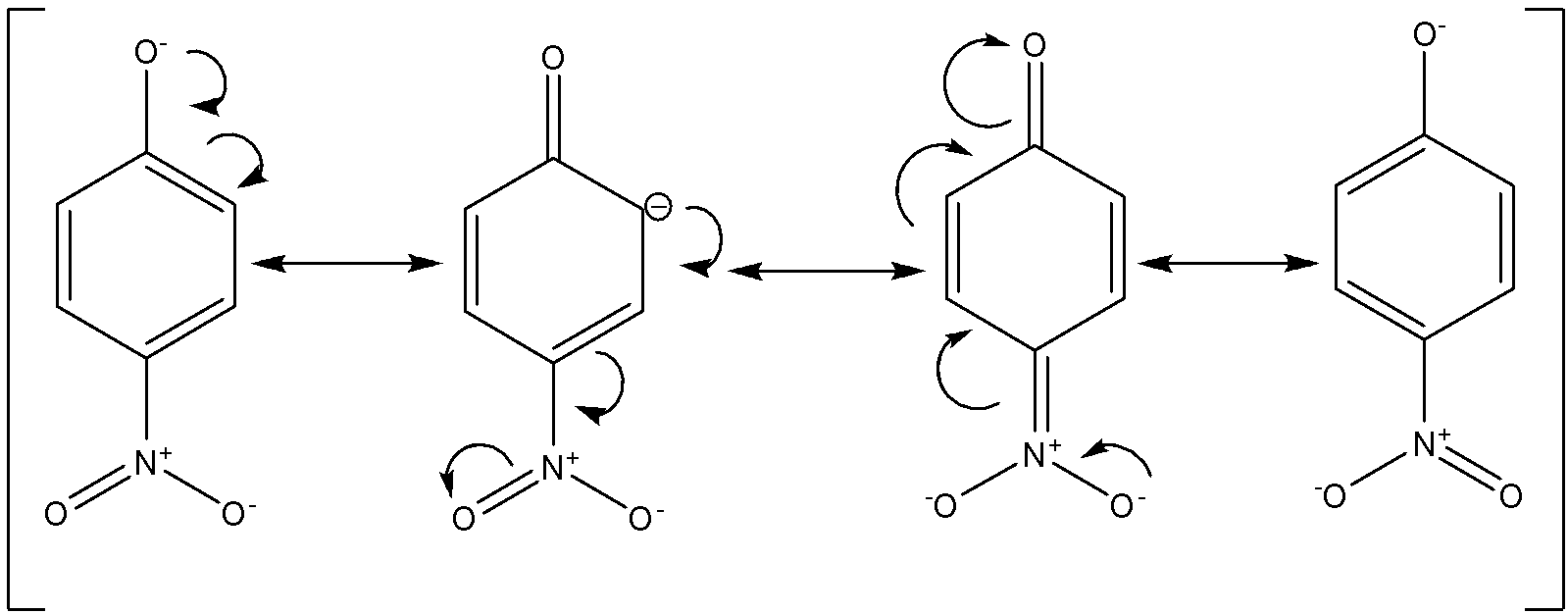
Out of all these, para-nitro phenol will be the most acidic. This is because the nitro group has –R effect (electron withdrawing group) due to which the negative charge on the phenoxide conjugate base will get stabilised. Given below are the different resonance structures for the said phenoxide ion.
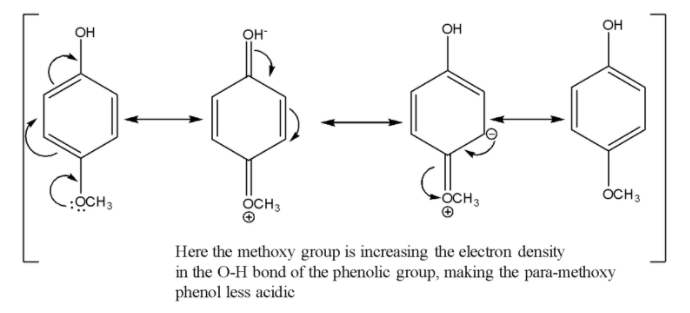
Out of para-methyl phenol and para-methoxy phenol, para-methyl phenol is more acidic since the methyl group has a weak +R effect whereas the methoxy group has a strong +R effect which will make the corresponding phenoxide conjugate base less stable. Given below are the resonance structures for the para-methoxy phenol.
Therefore the increasing order of acidity is option C) that is i$ < $ii$ < $iii
Note: Whenever a question regarding the acidic strength is asked, always remember that the acid which will have a more stable conjugate base will be more acidic. So always compare the stability of the conjugate bases in order to determine the acidity of different acids.
Complete step by step answer:
First we need to understand the structures of all these phenols.
Given Below are the structures of the different phenols.

Phenols are more acidic than saturated alcohols due to the stabilisation of the negative charge on the phenolate ion over the benzene ring. For example Phenol is far more acidic than methanol since the methoxide ion is highly unstable whereas the phenoxide ion is stabilized due to resonance.
In the above question all are a type of phenol but with different substituents present at the para position.
Out of all these, para-nitro phenol will be the most acidic. This is because the nitro group has –R effect (electron withdrawing group) due to which the negative charge on the phenoxide conjugate base will get stabilised. Given below are the different resonance structures for the said phenoxide ion.

Out of para-methyl phenol and para-methoxy phenol, para-methyl phenol is more acidic since the methyl group has a weak +R effect whereas the methoxy group has a strong +R effect which will make the corresponding phenoxide conjugate base less stable. Given below are the resonance structures for the para-methoxy phenol.

Therefore the increasing order of acidity is option C) that is i$ < $ii$ < $iii
Note: Whenever a question regarding the acidic strength is asked, always remember that the acid which will have a more stable conjugate base will be more acidic. So always compare the stability of the conjugate bases in order to determine the acidity of different acids.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




