
Infections of Ascaris usually occurs by
(a) Drinking water containing eggs of ascaris
(b) Eating imperfectly cooked port
(c) Tse- tse fly
(d) Mosquito
Answer
582.6k+ views
Hint: Infections of Ascaris occur during rainy months, tropical and subtropical countries. Indiscriminate defecation particularly near areas of habitation seeds the soil. Children become infected by ingesting soil or putting soiled items in their mouth.
Complete step by step answer:
Largest nematode to infect the human intestine. A common cream colored roundworm which is parasitic in the intestines of humans. The eggs may contaminate unwashed vegetables and water supplies. Eggs can also be carried by cockroaches, flies, wind, and even on money. Eggs can survive for longer periods as long as they are kept warm, in shade, and moist conditions are provided. Modes of transmission by mainly via ingestion of water or food (raw vegetables or fruit in particular) contaminated with A. lumbricoides eggs.
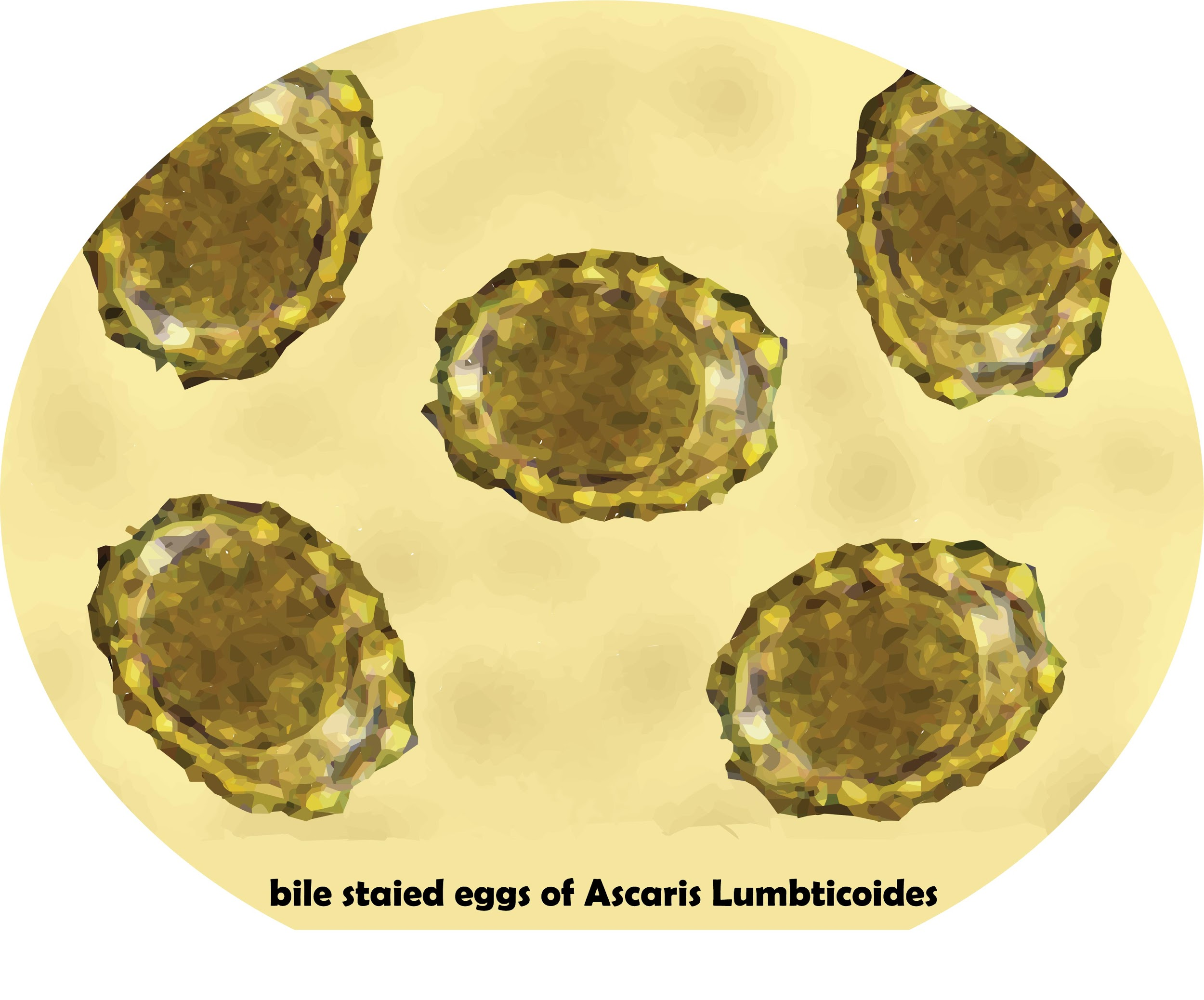
Additional Information:
- Some larvae migrate to ectopic sites and depend upon number and location, causing various inflammatory responses, leading to very severe allergic reactions.
- In the lungs worms destroy capillaries in the lungs which can cause hemorrhage.
- Migration of white blood cells leads to more congestion which is a condition known as Ascaris pneumonitis than in Loeffler's pneumonia lung tissue destroyed and bacterial infections occur, may be fatal.
- In innate Immune Response is caused by macrophages, neutrophils and most importantly eosinophils where the worms would be coated with IgG or IgE which would increase the release of eosinophil granules.
- In adaptive Immune Response causes high IL- 4 production, high levels of IgE, eosinophilia and mastocytosis but prior infection does not confer protective immunity.
So, the correct answer is ‘Drinking water containing eggs of ascaris.’
Note:
- Washing hands properly with soap and water before eating food.
- Good sanitation practise is needed to prevent fecal contamination of soil.
- Wash properly, peel or cook all raw vegetables and fruits before eating.
- Prevention of reinfection poses a substantial problem as this parasite is abundant in soil. - Treatment is albendazole: a single oral dose of 400 mg and mebendazole: 100 mg orally and twice daily for 3 days.
Complete step by step answer:
Largest nematode to infect the human intestine. A common cream colored roundworm which is parasitic in the intestines of humans. The eggs may contaminate unwashed vegetables and water supplies. Eggs can also be carried by cockroaches, flies, wind, and even on money. Eggs can survive for longer periods as long as they are kept warm, in shade, and moist conditions are provided. Modes of transmission by mainly via ingestion of water or food (raw vegetables or fruit in particular) contaminated with A. lumbricoides eggs.

Additional Information:
- Some larvae migrate to ectopic sites and depend upon number and location, causing various inflammatory responses, leading to very severe allergic reactions.
- In the lungs worms destroy capillaries in the lungs which can cause hemorrhage.
- Migration of white blood cells leads to more congestion which is a condition known as Ascaris pneumonitis than in Loeffler's pneumonia lung tissue destroyed and bacterial infections occur, may be fatal.
- In innate Immune Response is caused by macrophages, neutrophils and most importantly eosinophils where the worms would be coated with IgG or IgE which would increase the release of eosinophil granules.
- In adaptive Immune Response causes high IL- 4 production, high levels of IgE, eosinophilia and mastocytosis but prior infection does not confer protective immunity.
So, the correct answer is ‘Drinking water containing eggs of ascaris.’
Note:
- Washing hands properly with soap and water before eating food.
- Good sanitation practise is needed to prevent fecal contamination of soil.
- Wash properly, peel or cook all raw vegetables and fruits before eating.
- Prevention of reinfection poses a substantial problem as this parasite is abundant in soil. - Treatment is albendazole: a single oral dose of 400 mg and mebendazole: 100 mg orally and twice daily for 3 days.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




