
Insect tolerant gene from Bacillus thuringiensis is introduced using Ti plasmid of
(a) Escherichia coli
(b) Haemophilus influenzae
(c) Agrobacterium tumefaciens
(d) Arabidopsis thaliana
Answer
579.6k+ views
Hint: It is a Gram-negative, non-sporing, motile, rod-shaped bacterium, closely related to Rhizobium which forms nitrogen-fixing nodules on clover and other leguminous plants. Commonly, it is found around the root surfaces, it is the region called the rhizosphere where it appears to survive due by utilizing nutrients that spills from the root tissues.
Complete step by step answer:
By the help of Ti plasmid of Agrobacterium tumefaciens the Bacillus thuringiensis is introduced and it have a great effect in producing pest-resistant plant and it is widely used in cotton called as Bt cotton that assists with shielding cotton plants from insect-like coleopterans, lepidopterans, and dipterans.
So the correct answer is ‘Agrobacterium tumefaciens’.
Additional information: Agrobacterium tumefaciens causes crown gall infection of a wide scope of dicotyledonous plants, particularly individuals from the rose family, for example, apple, pear, peach, cherry, almond, raspberry, and roses. A different strain, named biovar 3, causes the crown nerve of the grapevine.
The ailment picks up its name from the huge tumor-like swellings that ordinarily happen at the crown of the plant, simply above soil level. Despite the fact that it diminishes the marketability of nursery stock, it generally doesn't make genuine harm to more established plants. In any case, this disease is one of the most broadly known, on account of its noteworthy science. Generally, a small portion of DNA is incorporated into the plant genome that results in the formation of tumors and leads to a change in metabolism.
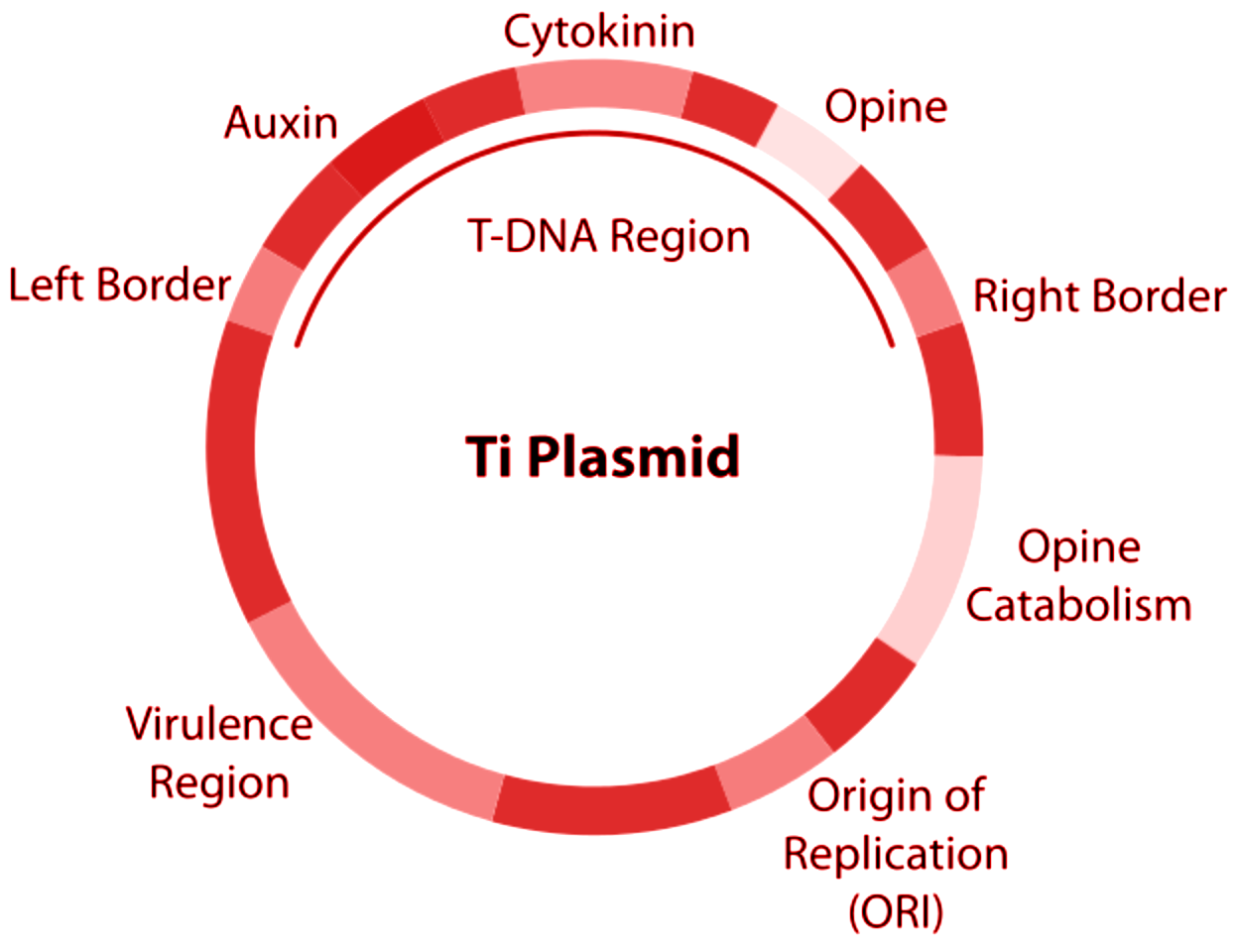
Note: The A. tumefaciens interceded plant genetic transformation measure requires the presence of two genetic segments situated on the bacterial Ti-plasmid.Basically, the main basic part is the T-DNA, which is characterized by conserved 25-base pair imperfect repeats at the closures of the T-region known as a border sequence. The second is the virulence (vir) region, which is made out of in any event seven significant loci (virA, virB, virC, virD, virE, virF, and virG) encoding parts of the bacterial protein machinery which is mediating the T-DNA processing and transfer.
Complete step by step answer:
By the help of Ti plasmid of Agrobacterium tumefaciens the Bacillus thuringiensis is introduced and it have a great effect in producing pest-resistant plant and it is widely used in cotton called as Bt cotton that assists with shielding cotton plants from insect-like coleopterans, lepidopterans, and dipterans.

So the correct answer is ‘Agrobacterium tumefaciens’.
Additional information: Agrobacterium tumefaciens causes crown gall infection of a wide scope of dicotyledonous plants, particularly individuals from the rose family, for example, apple, pear, peach, cherry, almond, raspberry, and roses. A different strain, named biovar 3, causes the crown nerve of the grapevine.
The ailment picks up its name from the huge tumor-like swellings that ordinarily happen at the crown of the plant, simply above soil level. Despite the fact that it diminishes the marketability of nursery stock, it generally doesn't make genuine harm to more established plants. In any case, this disease is one of the most broadly known, on account of its noteworthy science. Generally, a small portion of DNA is incorporated into the plant genome that results in the formation of tumors and leads to a change in metabolism.
Note: The A. tumefaciens interceded plant genetic transformation measure requires the presence of two genetic segments situated on the bacterial Ti-plasmid.Basically, the main basic part is the T-DNA, which is characterized by conserved 25-base pair imperfect repeats at the closures of the T-region known as a border sequence. The second is the virulence (vir) region, which is made out of in any event seven significant loci (virA, virB, virC, virD, virE, virF, and virG) encoding parts of the bacterial protein machinery which is mediating the T-DNA processing and transfer.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE

In a human foetus the limbs and digits develop after class 12 biology CBSE

AABbCc genotype forms how many types of gametes a 4 class 12 biology CBSE

The correct structure of ethylenediaminetetraacetic class 12 chemistry CBSE




