
What is irreversible enzyme inhibition? Give an example.
Answer
480.6k+ views
Hint: Enzyme inhibition is the process in which an inhibitor molecule binds to the enzyme and decreases or even stops its activity. Few molecules permanently bind to the enzymes and stop their activity. This activity cannot be regained even after changing conditions. The irreversible inhibition is also called covalent inhibition.
Complete answer:
The inhibitors are the substances that bind to the active site of the enzyme and block the enzyme-substrate binding which further prevents the formation of the product. This inhibition may be reversed by changing the substrate concentration. There are certain inhibitions in which the substance permanently binds to the enzymes and does not yield the product. This type of inhibition is known as irreversible inhibition.
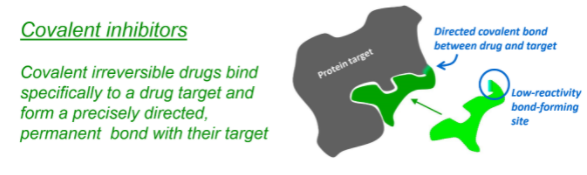
The irreversible inhibitors react with the enzyme and change the structural and functional conformation of the enzyme. As the enzyme and the inhibitors involve covalent binding with each other, the enzyme action cannot be re-established even after the removal of the inhibitor. This type of inhibition takes place in certain drugs like penicillin, aspirin etc.
In the case of cancer treatment, irreversible inhibitors are used which blocks several
enzymes that are required for the growth and survival of cells. Hence without necessary enzymes, the cells can kill themselves.
Note: The enzymes are the biomolecules that catalyse the biochemical reaction and increases its rate. The substrate binds to the active site of the enzyme and brings about product formation. The enzymes are substrate-specific and work at optimum conditions. The enzyme is not used up in a biochemical reaction. After the product formation, the enzyme is removed.
Complete answer:
The inhibitors are the substances that bind to the active site of the enzyme and block the enzyme-substrate binding which further prevents the formation of the product. This inhibition may be reversed by changing the substrate concentration. There are certain inhibitions in which the substance permanently binds to the enzymes and does not yield the product. This type of inhibition is known as irreversible inhibition.

The irreversible inhibitors react with the enzyme and change the structural and functional conformation of the enzyme. As the enzyme and the inhibitors involve covalent binding with each other, the enzyme action cannot be re-established even after the removal of the inhibitor. This type of inhibition takes place in certain drugs like penicillin, aspirin etc.
In the case of cancer treatment, irreversible inhibitors are used which blocks several
enzymes that are required for the growth and survival of cells. Hence without necessary enzymes, the cells can kill themselves.
Note: The enzymes are the biomolecules that catalyse the biochemical reaction and increases its rate. The substrate binds to the active site of the enzyme and brings about product formation. The enzymes are substrate-specific and work at optimum conditions. The enzyme is not used up in a biochemical reaction. After the product formation, the enzyme is removed.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




