
Is Nitrogen gas inert?
Answer
503.4k+ views
Hint: Nitrogen was discovered by Rutherford and A. Lavoisier in $1772$ . The atomic number assigned to the atomic nitrogen is $7$ because of presences of $7$ electrons in total to it. The atomic mass of the nitrogen was calculated to be $14.0067\,u$ . The nitrogen gas or dinitrogen or the ${N_2}$ accounts for the $78\% $ of the volume of earth’s atmosphere.
Complete answer:
Nitrogen is an essential element of the periodic table. It is present in minute essential organic groups like amino acids to other important day to day useful things. Though ${N_2}$ accounts for the $78\% $ of the volume of earth’s atmosphere, still the raw ${N_2}$ is very rare on the earth's surface.
The electronic configuration of $N$ is as follows: $1{s^2},\,2{s^2}2{p^3}$ . Thus, required only three more electrons to attain the nearest next noble gas configuration of $Ne$ i.e., neon.
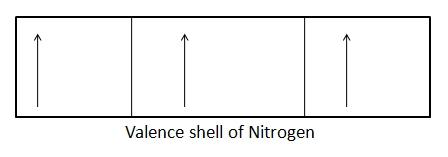
Thus by getting three more electrons, the nitrogen will be stabilized. Molecular nitrogen reacts with hydrogen to produce ammonia. It also reacts with oxygen to produce various products like dinitrogen oxide, nitrogen monoxide, dinitrogen trioxide, nitrogen dioxide, dinitrogen tetroxide, dinitrogen pentoxide. Reacts with both oxygen and hydrogen to produce nitric acid.
However if an atomic nitrogen forms a triple bond with another atomic nitrogen which then leads to dinitrogen gas or commonly called nitrogen gas. This nitrogen gas is inert because of fully filled valence shell of the nitrogen, which is as shown below
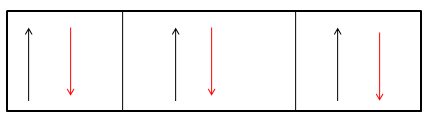
As one can see a fully filled valence shell, thus this means that the nitrogen attains the nearest noble gas configuration and attains the stability.
Note:
Dinitrogen is converted to ammonia by Haber’s process. While filling electrons to any sub shell one revise all the laws or the rules of the configuration namely aufbau rule ( electrons are filled in various subshell in the increasing order of the energy of the subshell ), hund's rule ( pairing of electrons will takes place ), pauli exclusion principle ( opposite spin of the electrons ) and the bohr bury rule.
Complete answer:
Nitrogen is an essential element of the periodic table. It is present in minute essential organic groups like amino acids to other important day to day useful things. Though ${N_2}$ accounts for the $78\% $ of the volume of earth’s atmosphere, still the raw ${N_2}$ is very rare on the earth's surface.
The electronic configuration of $N$ is as follows: $1{s^2},\,2{s^2}2{p^3}$ . Thus, required only three more electrons to attain the nearest next noble gas configuration of $Ne$ i.e., neon.

Thus by getting three more electrons, the nitrogen will be stabilized. Molecular nitrogen reacts with hydrogen to produce ammonia. It also reacts with oxygen to produce various products like dinitrogen oxide, nitrogen monoxide, dinitrogen trioxide, nitrogen dioxide, dinitrogen tetroxide, dinitrogen pentoxide. Reacts with both oxygen and hydrogen to produce nitric acid.
However if an atomic nitrogen forms a triple bond with another atomic nitrogen which then leads to dinitrogen gas or commonly called nitrogen gas. This nitrogen gas is inert because of fully filled valence shell of the nitrogen, which is as shown below

As one can see a fully filled valence shell, thus this means that the nitrogen attains the nearest noble gas configuration and attains the stability.
Note:
Dinitrogen is converted to ammonia by Haber’s process. While filling electrons to any sub shell one revise all the laws or the rules of the configuration namely aufbau rule ( electrons are filled in various subshell in the increasing order of the energy of the subshell ), hund's rule ( pairing of electrons will takes place ), pauli exclusion principle ( opposite spin of the electrons ) and the bohr bury rule.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




