
Is pyrrole aromatic?
Answer
495.6k+ views
Hint: Aromatic compounds are chemical compounds that feature conjugated planar ring systems with delocalized pi electron clouds rather than distinct alternating single and double bonds. Aromatics and arenes are other names for them. Benzene is the most well-known aromatic chemical. In nature, they are unsaturated molecules that are stable.
Complete answer:
When the total number of pi electrons belonging to a ring-shaped cyclic molecule can be equivalent to formula ‘4n + 2', where n can be any integer with a positive value, the molecule is said to obey the Huckel rule (including zero). Only for values of ‘n' ranging from zero to six have examples of molecules obeying Huckel's rule been found. The total number of pi electrons in the benzene molecule shown below is 6, following the 4n+2 electron rule with n=1.
Due to the resonance energy or the delocalized electron cloud, aromatic compounds are often highly stable. The following requirements must be satisfied by a molecule in order for it to have aromatic properties.
In a system of linked p orbitals (where the electrons are delocalized) belonging to the molecule, there must be \[(4n\text{ }+\text{ }2)\pi \]electrons.
To fulfil the first criterion, the molecule must have an essentially planar structure with more or less parallel p orbitals and the capacity to interact with one another.
The molecule must have a cyclic structure with a ring of p orbitals that is devoid of \[s{{p}^{3}}\] hybridised atoms.
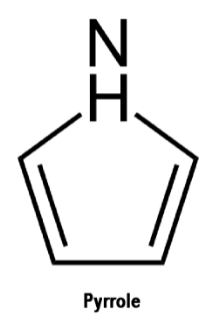
Pyrrole is a cyclic, conjugated compound (that lone pair on nitrogen can contribute to the pi-system). The pi system consists of two pi bonds and one lone pair of electrons. This gives us a total of 6 pi electrons, which is a Huckel number (i.e., 4n+2). As a result, it has a pleasant fragrance.
Note:
Aromaticity is a characteristic of cyclic (ring-shaped), planar (flat) structures with pi bonds in resonance (those containing delocalized electrons) that provides more stability than alternative geometric or connective arrangements with the same set of atoms in chemistry. Aromatic rings are extremely stable and do not easily break apart. Aliphatic compounds are organic compounds that are not aromatic; they may be cyclic, but only aromatic rings have increased stability.
Complete answer:
When the total number of pi electrons belonging to a ring-shaped cyclic molecule can be equivalent to formula ‘4n + 2', where n can be any integer with a positive value, the molecule is said to obey the Huckel rule (including zero). Only for values of ‘n' ranging from zero to six have examples of molecules obeying Huckel's rule been found. The total number of pi electrons in the benzene molecule shown below is 6, following the 4n+2 electron rule with n=1.
Due to the resonance energy or the delocalized electron cloud, aromatic compounds are often highly stable. The following requirements must be satisfied by a molecule in order for it to have aromatic properties.
In a system of linked p orbitals (where the electrons are delocalized) belonging to the molecule, there must be \[(4n\text{ }+\text{ }2)\pi \]electrons.
To fulfil the first criterion, the molecule must have an essentially planar structure with more or less parallel p orbitals and the capacity to interact with one another.
The molecule must have a cyclic structure with a ring of p orbitals that is devoid of \[s{{p}^{3}}\] hybridised atoms.

Pyrrole is a cyclic, conjugated compound (that lone pair on nitrogen can contribute to the pi-system). The pi system consists of two pi bonds and one lone pair of electrons. This gives us a total of 6 pi electrons, which is a Huckel number (i.e., 4n+2). As a result, it has a pleasant fragrance.
Note:
Aromaticity is a characteristic of cyclic (ring-shaped), planar (flat) structures with pi bonds in resonance (those containing delocalized electrons) that provides more stability than alternative geometric or connective arrangements with the same set of atoms in chemistry. Aromatic rings are extremely stable and do not easily break apart. Aliphatic compounds are organic compounds that are not aromatic; they may be cyclic, but only aromatic rings have increased stability.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




