
How many isomeric pentynes $\left( {{C_5}{H_8}} \right)$ are possible:
A. $3$
B. $4$
C. $5$
D. $6$
Given: The formula of the organic compound, pentynes is: $\left( {{C_5}{H_8}} \right)$
Answer
583.2k+ views
Hint:
We can write the structures of different isomers by using different carbon skeletons keeping the same formula.
Complete step by step solution:
We know that isomers are those compounds that have the same molecular formula but different properties. In organic compounds, we have basically two types of isomerism: structural isomers and stereo-isomers. Here, we will discuss the structural isomerism that arises with difference in the structure. We can further classify structural isomers as follows:
- Chain isomers: these have different carbon skeletons
- Position isomers: these have functional group/substituent positioned differently
- Functional group isomers: these have different functional groups
- Metamers: these have different alkyl chains at the sides of a functional group
We are given the organic compound, pentyne whose chemical formula is \[{C_5}{H_8}\]. let’s try to draw structural isomers with formula \[{C_5}{H_8}\] as follows:
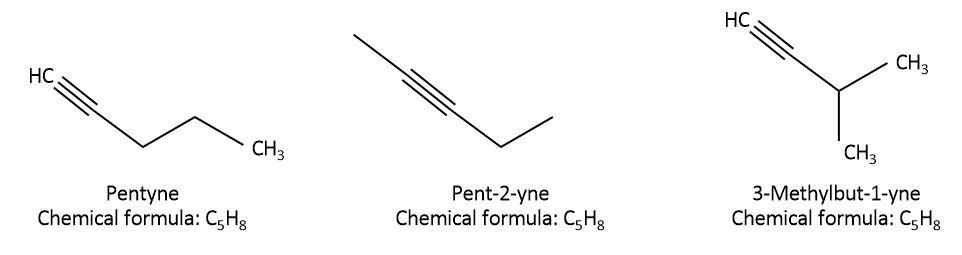
As we can see that in pentyne, all the $5$ carbons are attached in a straight chain and the triple bond is between the first and second carbon. This can also be called n-pentyne or $pent - 1 - yne$. In the second isomer, $pent - 2 - yne$, all the $5$ carbons are attached in a straight chain but the triple bond is between second and third carbon. In the last isomer, \[{\rm{3 - methylbut - 1 - yne}}\] , only $4$ carbons are attached in a straight chain, triple bond is between first and second carbon and there is one methyl group present as a substituent on the third carbon. So, all the three isomers have different structures but the molecular formula is the same for all of them.
Hence, the correct option is A.
Note:
We can see that positioning the triple bond between third and fourth or fourth and fifth carbons would have the same structure as that of $pent - 2 - yne$ and $pent - 1 - yne$ respectively.
We can write the structures of different isomers by using different carbon skeletons keeping the same formula.
Complete step by step solution:
We know that isomers are those compounds that have the same molecular formula but different properties. In organic compounds, we have basically two types of isomerism: structural isomers and stereo-isomers. Here, we will discuss the structural isomerism that arises with difference in the structure. We can further classify structural isomers as follows:
- Chain isomers: these have different carbon skeletons
- Position isomers: these have functional group/substituent positioned differently
- Functional group isomers: these have different functional groups
- Metamers: these have different alkyl chains at the sides of a functional group
We are given the organic compound, pentyne whose chemical formula is \[{C_5}{H_8}\]. let’s try to draw structural isomers with formula \[{C_5}{H_8}\] as follows:

As we can see that in pentyne, all the $5$ carbons are attached in a straight chain and the triple bond is between the first and second carbon. This can also be called n-pentyne or $pent - 1 - yne$. In the second isomer, $pent - 2 - yne$, all the $5$ carbons are attached in a straight chain but the triple bond is between second and third carbon. In the last isomer, \[{\rm{3 - methylbut - 1 - yne}}\] , only $4$ carbons are attached in a straight chain, triple bond is between first and second carbon and there is one methyl group present as a substituent on the third carbon. So, all the three isomers have different structures but the molecular formula is the same for all of them.
Hence, the correct option is A.
Note:
We can see that positioning the triple bond between third and fourth or fourth and fifth carbons would have the same structure as that of $pent - 2 - yne$ and $pent - 1 - yne$ respectively.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

10 examples of friction in our daily life




