
Isopropyl methyl ether when treated with cold hydrogen iodide gives:
(a) isopropyl iodide and methyl iodide
(b) isopropyl alcohol and methyl iodide
(c) isopropyl alcohol and methyl alcohol
(d) isopropyl iodide and methyl alcohol
Answer
592.5k+ views
Hint: Some reactions follow substitution reactions while others are - addition reactions. Substitution reaction is where a functional group is substituted with another functional group and we get substituted products.
Complete step by step answer:
Isopropyl methyl ether when treated with cold hydrogen iodide gives substituted products of isopropyl alcohol and methyl iodide. The reaction is as follows
\[{{(C{{H}_{3}})}_{2}}CH-O-C{{H}_{3}}+HI\to {{(C{{H}_{3}})}_{2}}CH-OH+C{{H}_{3}}I\]
In this reaction the ether bonds break and to \[{{(C{{H}_{3}})}_{2}}CH-O-\] hydrogen ion from the HI gets bonded and to \[C{{H}_{3}}-\] the iodide ion from the HI is bonded. The mechanism is shown below:
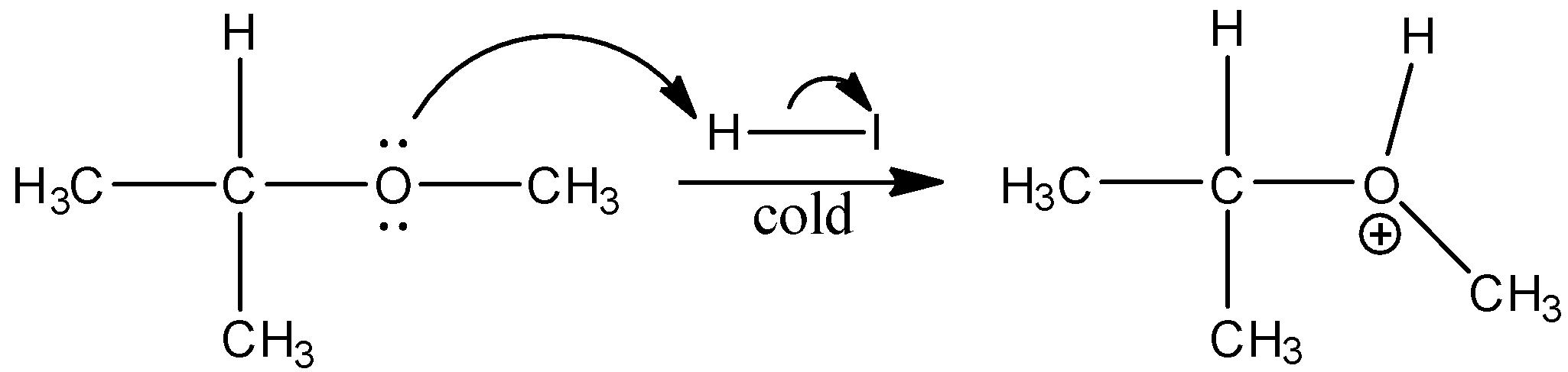

Thus, when isopropyl methyl ether is treated with cold hydrogen iodide we get option (b)isopropyl alcohol and methyl iodide.
Additional Information:
When a functional group is replaced by another functional group in a chemical reaction is called substitution reaction. It is a very important reaction in organic chemistry. It is classified into electrophilic substitution and nucleophilic substitution reactions. The above given reaction is a nucleophilic substitution reaction or \[SN\] reaction. In such a reaction a nucleophile is present which drives the reaction to occur. These nucleophiles attack the positive or partially positive charge on atoms or a group of atoms. It replaces a weaker nucleophile which becomes the leaving group. The remaining positive or partially positive atom is known as electrophile. The electrophile and the leaving group together in a molecular entity are usually called substrates. The general form of this reaction is
Nu: + R-LG → R-Nu + LG:
Where Nu: is the nucleophile and LG is the leaving group.
Note: The above reaction only occurs when the cold HI is used. When hot HI is used the products formed are isopropyl iodide and methyl iodide along with water as product. The reaction can proceed further as one molecule of HI reacts with isopropyl alcohol giving rise to isopropyl iodide and water.
Complete step by step answer:
Isopropyl methyl ether when treated with cold hydrogen iodide gives substituted products of isopropyl alcohol and methyl iodide. The reaction is as follows
\[{{(C{{H}_{3}})}_{2}}CH-O-C{{H}_{3}}+HI\to {{(C{{H}_{3}})}_{2}}CH-OH+C{{H}_{3}}I\]
In this reaction the ether bonds break and to \[{{(C{{H}_{3}})}_{2}}CH-O-\] hydrogen ion from the HI gets bonded and to \[C{{H}_{3}}-\] the iodide ion from the HI is bonded. The mechanism is shown below:


Thus, when isopropyl methyl ether is treated with cold hydrogen iodide we get option (b)isopropyl alcohol and methyl iodide.
Additional Information:
When a functional group is replaced by another functional group in a chemical reaction is called substitution reaction. It is a very important reaction in organic chemistry. It is classified into electrophilic substitution and nucleophilic substitution reactions. The above given reaction is a nucleophilic substitution reaction or \[SN\] reaction. In such a reaction a nucleophile is present which drives the reaction to occur. These nucleophiles attack the positive or partially positive charge on atoms or a group of atoms. It replaces a weaker nucleophile which becomes the leaving group. The remaining positive or partially positive atom is known as electrophile. The electrophile and the leaving group together in a molecular entity are usually called substrates. The general form of this reaction is
Nu: + R-LG → R-Nu + LG:
Where Nu: is the nucleophile and LG is the leaving group.
Note: The above reaction only occurs when the cold HI is used. When hot HI is used the products formed are isopropyl iodide and methyl iodide along with water as product. The reaction can proceed further as one molecule of HI reacts with isopropyl alcohol giving rise to isopropyl iodide and water.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




