
IUPAC name of diethyl ether is:
(A)- Ethoxy ether
(B)- diethyl ether
(C)- ethoxyethane
(D)- none of these
Answer
585.6k+ views
Hint: While naming of ether compounds, we use the prefix- alkoxy for the bigger alkyl group and the other alkyl group forms the parent alkane chain.
Complete step-by-step answer:
Ether is the class of organic compounds that contains an oxygen atom bonded to the two alkyl or aryl groups. The oxygen atom being $s{{p}^{3}}$ hybridised has two bond pairs and two lone pairs of electrons in a tetrahedral arrangement.
Thus, it has a general formula $R-\,O-\,R'$ , where $R$ and $R'$represent the alkyl or aryl groups.
Depending on the type of alkyl groups attached to the oxygen atom it can be classified into two types as:
- Symmetrical ether where the oxygen atom has the same alkyl group on either side, $R=R'$.
- Unsymmetrical ethers if two different alkyl groups are attached to oxygen atoms.
According to the IUPAC nomenclature, ethers are named as alkoxy alkane, where the oxygen atom is taken along with the smaller alkyl group, being referred as alkoxy substituent and the bigger alkyl group forms the part of the base alkane chain.
Thus, the IUPAC name the diethyl ether compound, ${{C}_{2}}{{H}_{5}}-O-{{C}_{2}}{{H}_{5}}$ is ethoxy ethane. Due to the presence of the same ethyl- alkyl group on both sides of the oxygen atom, it is an example of symmetrical ether.
Therefore, the correct option is (C).
Additional information:
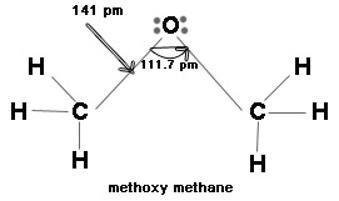
The $R-O-R'$ bond angle is more than the tetrahedral angle, as the two bulky alkyl groups interact among themselves causing the angle to increase from ${{109}^{\circ }}\,to\,\,{{111.7}^{\circ }}$.

Note: Diethyl ether is the common name of ethers where the alkyl groups are simply named by the alphabetical order and suffix as -ether at the end.
Complete step-by-step answer:
Ether is the class of organic compounds that contains an oxygen atom bonded to the two alkyl or aryl groups. The oxygen atom being $s{{p}^{3}}$ hybridised has two bond pairs and two lone pairs of electrons in a tetrahedral arrangement.
Thus, it has a general formula $R-\,O-\,R'$ , where $R$ and $R'$represent the alkyl or aryl groups.
Depending on the type of alkyl groups attached to the oxygen atom it can be classified into two types as:
- Symmetrical ether where the oxygen atom has the same alkyl group on either side, $R=R'$.
- Unsymmetrical ethers if two different alkyl groups are attached to oxygen atoms.
According to the IUPAC nomenclature, ethers are named as alkoxy alkane, where the oxygen atom is taken along with the smaller alkyl group, being referred as alkoxy substituent and the bigger alkyl group forms the part of the base alkane chain.
Thus, the IUPAC name the diethyl ether compound, ${{C}_{2}}{{H}_{5}}-O-{{C}_{2}}{{H}_{5}}$ is ethoxy ethane. Due to the presence of the same ethyl- alkyl group on both sides of the oxygen atom, it is an example of symmetrical ether.
Therefore, the correct option is (C).
Additional information:
The $R-O-R'$ bond angle is more than the tetrahedral angle, as the two bulky alkyl groups interact among themselves causing the angle to increase from ${{109}^{\circ }}\,to\,\,{{111.7}^{\circ }}$.


Note: Diethyl ether is the common name of ethers where the alkyl groups are simply named by the alphabetical order and suffix as -ether at the end.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




