
What is the IUPAC nomenclature of $Ni{\left( {CO} \right)_4}$ ?
(A) Tetracarbonyl Nickel (I)
(B) Tetracarboxy Nickel (0)
(C) Tetracarbonyl Nickel (0)
(D) None of these
Answer
600.3k+ views
Hint: A coordination complex has a central metal atom or ion and a number of ions or molecules, known as ligands, attached to it. Naming of the complex can be possible by determining the oxidation state of the central metal and identifying types of ligands and the number of ligands of the complex.
Complete answer:
$Ni{\left( {CO} \right)_4}$ is a coordination complex. Every coordination complex has a central metal atom or ion and other molecules or ions create bonds with the central metal. These bonds are called coordination bonds. The molecules or ions that create coordination bonds with the central metal atom or ion are known as ligands.
Ligands can be neutral in nature (when a molecule creates a complex) or a charged particle (when an ion, mostly anion, creates a complex).
In this mentioned complex, the central metal atom is nickel (Ni) and 4 carbon monoxide molecules have created bonds with the central metal atom, nickel. Hence, there are 4 ligands in this complex.
Again, the overall complex can be either neutral or charged. It depends upon the charge of the central metal and what type of ligands are being used to form the complex and how many of those are being used.
For example, this complex ($Ni{\left( {CO} \right)_4}$) is neutral as the central metal atom is neutral and all the ligands are neutral as well.
The structure of $Ni{\left( {CO} \right)_4}$ is given below:
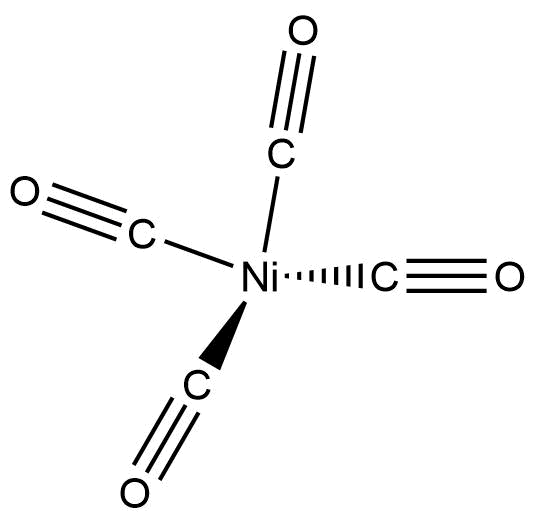
Now, to name such complexes, a number of rules are followed:
1. First, you have to identify the oxidation number of the central metal atom or ion. This can be determined from the overall charge, the charge of the ligands and the number of ligands of the complex.
2. Now, you have to count the number of ligands there in the complex.
3. You have to start naming the complex by putting the number in the chemical nomenclature form (for example: mono for 1, bi for 2, tri for 3, tetra for 4 etc.).
4. Then you have to write the ligand name (if more than one ligand is used, then you have to mention all the ligands along with their numbers as mentioned in point 3).
5. Then you have to mention the central metal atom’s name along with its oxidation state mentioned in the first bracket.
So, let’s apply all the rules to find out the name of this complex:
* Central metal atom: nickel (Ni)
* Oxidation state: 0 (entire complex is neutral; ligands are neutral too).
* Ligands: carbonyl (CO), when carbon monoxide is used as ligand, then it takes the name carbonyl.
* Number of ligands: 4 (tetra).
Hence, the name of the complex will be tetracarbonyl Nickel (0).
Let’s look at the answer options available:
* Oxidation state of nickel is not 1. Hence, option A cannot be true.
* The ligand’s name is carbonyl not carboxy. Hence, option B cannot be true.
Hence, option C is the correct answer to this question.
Note: It is important to mention the proper oxidation state of the central metal atom or ion. Without this, the nomenclature will not be correct. So, students should calculate the oxidation state of the central metal correctly.
Complete answer:
$Ni{\left( {CO} \right)_4}$ is a coordination complex. Every coordination complex has a central metal atom or ion and other molecules or ions create bonds with the central metal. These bonds are called coordination bonds. The molecules or ions that create coordination bonds with the central metal atom or ion are known as ligands.
Ligands can be neutral in nature (when a molecule creates a complex) or a charged particle (when an ion, mostly anion, creates a complex).
In this mentioned complex, the central metal atom is nickel (Ni) and 4 carbon monoxide molecules have created bonds with the central metal atom, nickel. Hence, there are 4 ligands in this complex.
Again, the overall complex can be either neutral or charged. It depends upon the charge of the central metal and what type of ligands are being used to form the complex and how many of those are being used.
For example, this complex ($Ni{\left( {CO} \right)_4}$) is neutral as the central metal atom is neutral and all the ligands are neutral as well.
The structure of $Ni{\left( {CO} \right)_4}$ is given below:

Now, to name such complexes, a number of rules are followed:
1. First, you have to identify the oxidation number of the central metal atom or ion. This can be determined from the overall charge, the charge of the ligands and the number of ligands of the complex.
2. Now, you have to count the number of ligands there in the complex.
3. You have to start naming the complex by putting the number in the chemical nomenclature form (for example: mono for 1, bi for 2, tri for 3, tetra for 4 etc.).
4. Then you have to write the ligand name (if more than one ligand is used, then you have to mention all the ligands along with their numbers as mentioned in point 3).
5. Then you have to mention the central metal atom’s name along with its oxidation state mentioned in the first bracket.
So, let’s apply all the rules to find out the name of this complex:
* Central metal atom: nickel (Ni)
* Oxidation state: 0 (entire complex is neutral; ligands are neutral too).
* Ligands: carbonyl (CO), when carbon monoxide is used as ligand, then it takes the name carbonyl.
* Number of ligands: 4 (tetra).
Hence, the name of the complex will be tetracarbonyl Nickel (0).
Let’s look at the answer options available:
* Oxidation state of nickel is not 1. Hence, option A cannot be true.
* The ligand’s name is carbonyl not carboxy. Hence, option B cannot be true.
Hence, option C is the correct answer to this question.
Note: It is important to mention the proper oxidation state of the central metal atom or ion. Without this, the nomenclature will not be correct. So, students should calculate the oxidation state of the central metal correctly.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




