
Ketones react with Mg-Hg over water and give:
(A) Alcohols
(B) pinacolones
(C) pinacols
(D) None of the above
Answer
569.7k+ views
Hint: Ketone is a carbonyl group; it reacts with Mg-Hg over water then that type of reaction is a free radical reaction. In this reaction the reducing agent is the Magnesium group or mercury group.
Complete answer:
The reaction in which the Ketones react with Mg-Hg over water is known as Pinacol coupling reaction. Pinacol coupling reaction is a type of free radical process. In this process carbon-carbon bonds are formed between Carbonyl groups of ketones or aldehydes. This reaction can take place in presence of an electron donor. The product formed in this reaction is vicinal diols, which is also known as pinacols.
The first step in the reaction mechanism is the reduction of the carbonyl group to ketyl radical species, in presence of reducing agent such as Magnesium. Again, one more carbonyl group is added. Two ketyl groups will react in the coupling reaction to give pinacol with both the hydroxyl groups being deprotonated. Addition of the water molecule will give the diols.
The mechanism of the pinacol coupling reaction is given below:
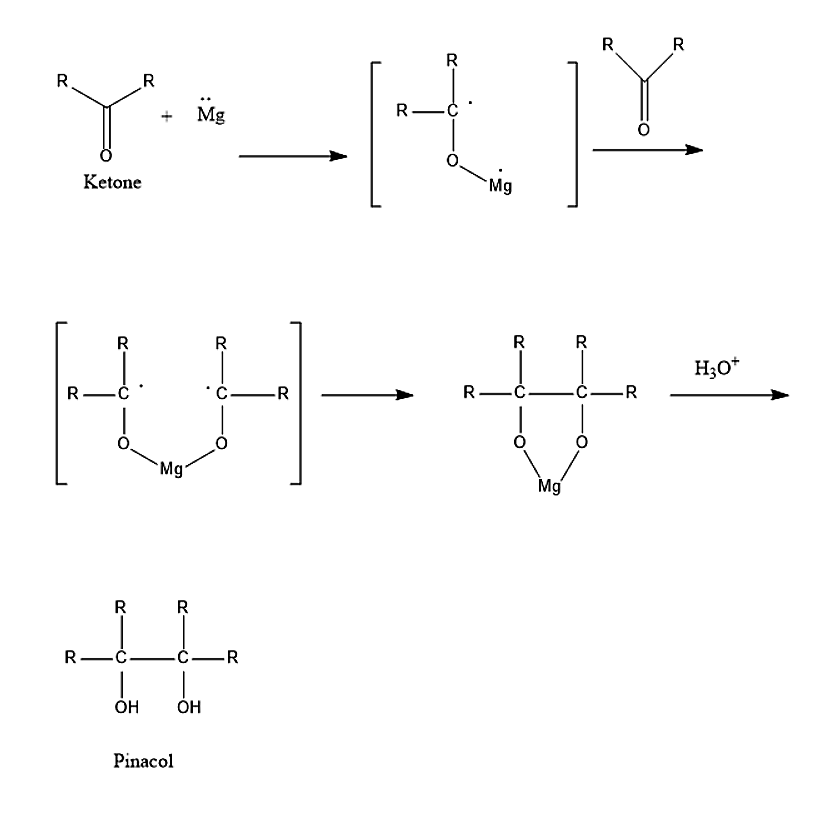
Therefore, the correct answer is option(C) pinacols.
Additional information:
- Pinacol is present as white solid organic compound.
- Pinacol will undergo pinacol rearrangement when heated with dilute sulphuric acid to form pinacolone.
- Pinacol can be treated with Borane and Boron trichloride to produce synthetic intermediates such as pinacol borane, pinacol chloroborane and bis(pinacolato) diboron.
Note:
- Pinacol coupling reaction between unsymmetrical ketones such as acetone and p-chloroacetophenone will produce Phenaglycodol
- Benzaldehyde will undergo pinacol coupling reaction by using the catalyst such as Vanadium (III) chloride and Aluminium metal as the stoichiometric reductant.
Complete answer:
The reaction in which the Ketones react with Mg-Hg over water is known as Pinacol coupling reaction. Pinacol coupling reaction is a type of free radical process. In this process carbon-carbon bonds are formed between Carbonyl groups of ketones or aldehydes. This reaction can take place in presence of an electron donor. The product formed in this reaction is vicinal diols, which is also known as pinacols.
The first step in the reaction mechanism is the reduction of the carbonyl group to ketyl radical species, in presence of reducing agent such as Magnesium. Again, one more carbonyl group is added. Two ketyl groups will react in the coupling reaction to give pinacol with both the hydroxyl groups being deprotonated. Addition of the water molecule will give the diols.
The mechanism of the pinacol coupling reaction is given below:

Therefore, the correct answer is option(C) pinacols.
Additional information:
- Pinacol is present as white solid organic compound.
- Pinacol will undergo pinacol rearrangement when heated with dilute sulphuric acid to form pinacolone.
- Pinacol can be treated with Borane and Boron trichloride to produce synthetic intermediates such as pinacol borane, pinacol chloroborane and bis(pinacolato) diboron.
Note:
- Pinacol coupling reaction between unsymmetrical ketones such as acetone and p-chloroacetophenone will produce Phenaglycodol
- Benzaldehyde will undergo pinacol coupling reaction by using the catalyst such as Vanadium (III) chloride and Aluminium metal as the stoichiometric reductant.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




