
Kirchhoff’s voltage law states that the algebraic sum of the product of resistance and current in each part of any closed circuit is the algebraic sum of the emfs in that closed circuit. State which law is this
A. Kirchhoff’s voltage law
B. Kirchhoff’s current law
C. newton’s law of gravitation
D. Ampere’s law
Answer
587.7k+ views
Hint: According to Kirchhoff’s second law around any closed loop or network, the algebraic sum of the changes in potential must be zero. Or the algebraic sum of the emfs in a closed loop of a circuit is equal to the sum of products of currents and resistance.
Complete answer:
Kirchhoff gave two laws to calculate the current and voltage across a meshed network. The first Kirchhoff’s law states the current entering at a junction is equal to current leaving at that junction. Which obeys law of conservation of charge. Kirchhoff's voltage law states that the algebraic sum of the product of resistance and current in each part of any closed circuit is the algebraic sum of the emfs in that closed circuit. Which obey’s the conservation of energy.
So, the correct answer is “Option A”.
Additional Information:
Applying Kirchhoff’s voltage law to a meshed network.
(i) We can take any direction, clockwise or anti-clockwise as the direction of the loop.
(ii) The emf of the cell is taken as positive if the direction of the loop is from its negative to positive terminal of the battery.
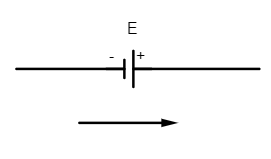
Here if the emf of cell is E then the potential across the cell is $V=+E$ (positive emf)
(iii) ) The emf of the cell is taken as negative if the direction of the loop is from its positive to negative terminal of the battery.
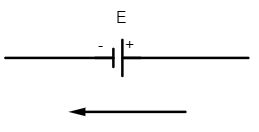
Here if the emf of cell is E then the potential across the cell is $V=-E$ (negative emf)
(iv) The current-resistance $\left( IR \right)$ product is taken as positive if the resistance is travelled in the same direction as the assumed loop.
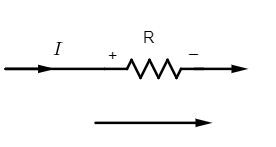
Here potential drop across the resistance R is $V=+IR$ (positive potential drop)
(v) The current-resistance $\left( IR \right)$ product is taken as negative if the resistance is travelled in the opposite direction as that of the assumed loop.
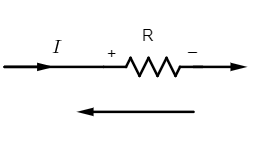
Here potential drop across the resistance R is $V=-IR$ (negative potential drop)
Note:
Kirchhoff's second law or Kirchhoff’s voltage law is based on the principle of conservation of energy. This is because of the conservative nature of electrostatic force. As the electrostatic force is conservative the total work done by it along any closed path must be zero.
Complete answer:
Kirchhoff gave two laws to calculate the current and voltage across a meshed network. The first Kirchhoff’s law states the current entering at a junction is equal to current leaving at that junction. Which obeys law of conservation of charge. Kirchhoff's voltage law states that the algebraic sum of the product of resistance and current in each part of any closed circuit is the algebraic sum of the emfs in that closed circuit. Which obey’s the conservation of energy.
So, the correct answer is “Option A”.
Additional Information:
Applying Kirchhoff’s voltage law to a meshed network.
(i) We can take any direction, clockwise or anti-clockwise as the direction of the loop.
(ii) The emf of the cell is taken as positive if the direction of the loop is from its negative to positive terminal of the battery.

Here if the emf of cell is E then the potential across the cell is $V=+E$ (positive emf)
(iii) ) The emf of the cell is taken as negative if the direction of the loop is from its positive to negative terminal of the battery.

Here if the emf of cell is E then the potential across the cell is $V=-E$ (negative emf)
(iv) The current-resistance $\left( IR \right)$ product is taken as positive if the resistance is travelled in the same direction as the assumed loop.

Here potential drop across the resistance R is $V=+IR$ (positive potential drop)
(v) The current-resistance $\left( IR \right)$ product is taken as negative if the resistance is travelled in the opposite direction as that of the assumed loop.

Here potential drop across the resistance R is $V=-IR$ (negative potential drop)
Note:
Kirchhoff's second law or Kirchhoff’s voltage law is based on the principle of conservation of energy. This is because of the conservative nature of electrostatic force. As the electrostatic force is conservative the total work done by it along any closed path must be zero.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




