
What is the least radius through which an optical fiber of core diameter $ 0.05mm $ may be bent (as shown in figure) without serious loss of light? The refractive index of the core is $ 1.6 $ and that of cladding is $ 1.5 $
(A) $ 0.28mm $
(B) $ 0.78mm $
(C) $ 0.58mm $
(D) $ 1mm $

Answer
489.6k+ views
Hint: We start by making the necessary adjustments in the figure. For there to be no loss of light, we need the angle of incidence to be as small as possible. Then we take that ray that makes the smallest angle of incidence and constructs a triangle. We take the triangle and the sine function to get a relation between the ratio of refractive indices and sine value. We then equate them both and get a value for the unknown.
$ \sin \theta = \dfrac{{opposite}}{{hypotenuse}} $
$ \sin \theta = \dfrac{{{n_2}}}{{{n_1}}} $ (Modified Snell’s law. When theta is ninety degrees)
Complete Step By Step Answer:
Let us start by redrawing the diagram so that we have the necessary changes and information.
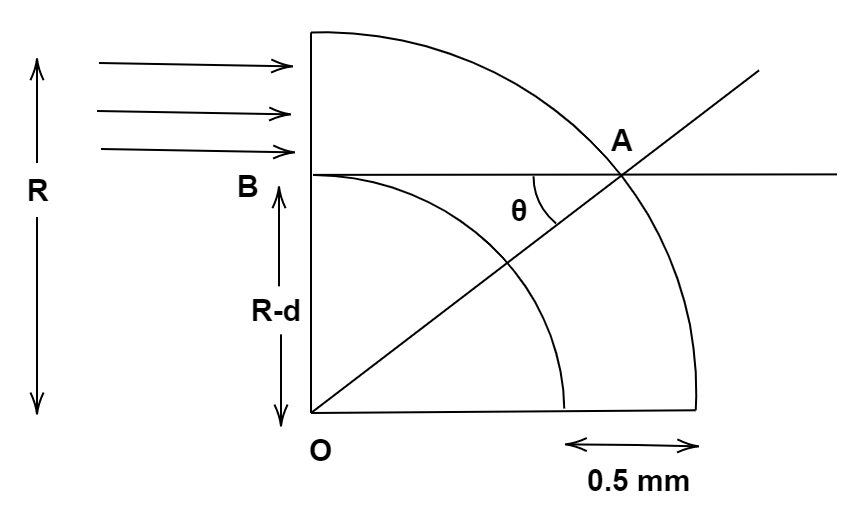
For there to be no escape of light, we take the smallest angle of incidence. That is shown in the figure making an angle theta with the line joining points O and A.
Taking the triangle OAB
$ \sin \theta = \dfrac{{R - d}}{R} $ value of OA is also $ R $
Now we remember Snell’s law $ {n_1}\sin {\theta _1} = {n_2}\sin {\theta _2} $
The angle the incident ray makes with the surface is normal. So we rewrite the above equation as,
$ {n_1}\sin \theta = {n_2}\sin 90 $
We simplify this to $ \sin \theta = \dfrac{{{n_2}}}{{{n_1}}} $
Now that we have two different equations for sine of theta, we can equate it to simplify and get the final answer.
$ \dfrac{{R - d}}{R} = \dfrac{{{n_2}}}{{{n_1}}} $
We have the values of refractive indices given in the question. We substitute and get
$ \dfrac{{R - d}}{R} = \dfrac{{1.5}}{{1.6}} $
We take $ R $ to the other side and bring the terms with the unknown to one side and get
$ 1.6R = 1.5R - 1.5d $
$ 0.1R = 1.5d $
Now we take the constant to the other side to get
$ R = \dfrac{{1.5 \times 0.05}}{{0.1}} = 0.75 $
In conclusion, the right answer is option (B) $ 0.78mm $ .
Note:
The phenomenon responsible for the fiber optic cable is the total internal reflection or TIR. Total internal reflection is the phenomenon in which the light rays moving from an optically denser medium to optically rarer medium will go back to the medium from where they are coming in case the incident angle is greater than or equal to the critical angle.
$ \sin \theta = \dfrac{{opposite}}{{hypotenuse}} $
$ \sin \theta = \dfrac{{{n_2}}}{{{n_1}}} $ (Modified Snell’s law. When theta is ninety degrees)
Complete Step By Step Answer:
Let us start by redrawing the diagram so that we have the necessary changes and information.

For there to be no escape of light, we take the smallest angle of incidence. That is shown in the figure making an angle theta with the line joining points O and A.
Taking the triangle OAB
$ \sin \theta = \dfrac{{R - d}}{R} $ value of OA is also $ R $
Now we remember Snell’s law $ {n_1}\sin {\theta _1} = {n_2}\sin {\theta _2} $
The angle the incident ray makes with the surface is normal. So we rewrite the above equation as,
$ {n_1}\sin \theta = {n_2}\sin 90 $
We simplify this to $ \sin \theta = \dfrac{{{n_2}}}{{{n_1}}} $
Now that we have two different equations for sine of theta, we can equate it to simplify and get the final answer.
$ \dfrac{{R - d}}{R} = \dfrac{{{n_2}}}{{{n_1}}} $
We have the values of refractive indices given in the question. We substitute and get
$ \dfrac{{R - d}}{R} = \dfrac{{1.5}}{{1.6}} $
We take $ R $ to the other side and bring the terms with the unknown to one side and get
$ 1.6R = 1.5R - 1.5d $
$ 0.1R = 1.5d $
Now we take the constant to the other side to get
$ R = \dfrac{{1.5 \times 0.05}}{{0.1}} = 0.75 $
In conclusion, the right answer is option (B) $ 0.78mm $ .
Note:
The phenomenon responsible for the fiber optic cable is the total internal reflection or TIR. Total internal reflection is the phenomenon in which the light rays moving from an optically denser medium to optically rarer medium will go back to the medium from where they are coming in case the incident angle is greater than or equal to the critical angle.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




