
LED stands for :
A . light emitting diode
B . loose emitting diode
C . light emission device
D . light emitting device
Answer
567k+ views
Hint: We know that LED is a semiconductor device. It has a p-n junction diode that emits light, when activated. The properties of LED are very important. We should know them before explaining LED.
Complete answer:
The answer to the question lies in the fact that, what is the purpose for which LED is used. Once we explain the purpose and working, the answer will be cleared.
When a p-n junction is forward biased electrons recombine with holes within the device releasing energy in the form of photons. Since, we are talking about junctions, then there has to be the mentioning of diodes. And considering the fact that photons are released, we can surely say that it emits light.
So, we can say that LEDs are known as light emitting diodes.
Therefore the correct answer is Option A.
Additional Information:
The symbol of LED is shown below:
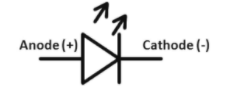
The working principle of a light emitting diode is that it is a two lead semiconductor light source. When a suitable voltage is applied to the leads, electrons are able to recombine with electron holes within the device releasing energy in the form of photons.
There are various advantages of the Light Emitting Diodes over the conventional incandescent, fluorescence and compact fluorescent lamps and lighting devices. The advantages include exceptionally longer lifespan, significantly lower energy consumption, reduced maintenance cost and higher safety.
Light Emitting Diodes are increasingly common in street lights, parking garage lighting, walkway and other outdoor areas, lighting refrigerated cases, modular lighting and task lighting.
Note:
The colour of the emitted light depends on the semiconductor material and composition. With LED we can say that it is generally classified into three wavelengths: ultraviolet, visible and infrared. The wavelength range of commercially available LEDs with single element output power of at least 5 mW is 360 to 950 nm.
Complete answer:
The answer to the question lies in the fact that, what is the purpose for which LED is used. Once we explain the purpose and working, the answer will be cleared.
When a p-n junction is forward biased electrons recombine with holes within the device releasing energy in the form of photons. Since, we are talking about junctions, then there has to be the mentioning of diodes. And considering the fact that photons are released, we can surely say that it emits light.
So, we can say that LEDs are known as light emitting diodes.
Therefore the correct answer is Option A.
Additional Information:
The symbol of LED is shown below:

The working principle of a light emitting diode is that it is a two lead semiconductor light source. When a suitable voltage is applied to the leads, electrons are able to recombine with electron holes within the device releasing energy in the form of photons.
There are various advantages of the Light Emitting Diodes over the conventional incandescent, fluorescence and compact fluorescent lamps and lighting devices. The advantages include exceptionally longer lifespan, significantly lower energy consumption, reduced maintenance cost and higher safety.
Light Emitting Diodes are increasingly common in street lights, parking garage lighting, walkway and other outdoor areas, lighting refrigerated cases, modular lighting and task lighting.
Note:
The colour of the emitted light depends on the semiconductor material and composition. With LED we can say that it is generally classified into three wavelengths: ultraviolet, visible and infrared. The wavelength range of commercially available LEDs with single element output power of at least 5 mW is 360 to 950 nm.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




