
Let ABC is a right-angled triangle with AB=3 cm and BC=4 cm and angle $\angle ABC = {90^ \circ }$. The three charges +15, +12 and -20 esu are placed on A, B and C respectively. The force acting on B will be-
A. Zero
B. 25 dynes
C. 30 dynes
D. 150 dynes
Answer
556.5k+ views
Hint: As both the forces on B charges are at right angles so use the resultant force formula to calculate the net force acting on the charge B.
Complete step by step answer:
Consider a system of three charges on the vertices of triangle ABC as shown.
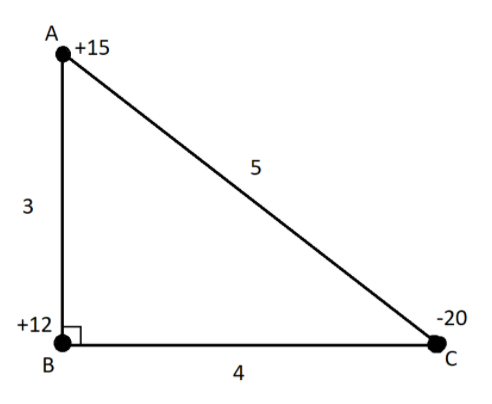
Step1:
In terms esu the force of attraction or repulsion between two charges is given by-
$F = \dfrac{{{q_1}{q_2}}}{{{r^2}}}$
Where r is the distance between charges,
For the force between B and A
${F_A} = \dfrac{{5 \times 12}}{{{3^2}}} = 20dynes$
Step2:
Now calculate the force between charges B and C
${F_C} = \dfrac{{20 \times 12}}{{{4^2}}} = 15dynes$
Step3: Now use the equation of resultant forces to calculate the net force at point B
${F_{net}} = \sqrt {F_A^2 + F_B^2} $
$ \Rightarrow {F_{net}} = \sqrt {{{20}^2} + {{15}^2}} = \sqrt {400 + 225} = \sqrt {625} $
$ \Rightarrow {F_{net}} = 25dynes$.
Hence, the correct answer is option (B).
Note: In this equation, we have used the formula of resultant force directly. However, the actual formula is –
${F_{net}} = \sqrt {F_A^2 + F_B^2 + 2{F_A}{F_B}\cos \theta } $
where $\cos \theta $ = angle between the two vectors. In this case, the angle between them is ${90^ \circ } \Rightarrow \cos {90^ \circ } = 0$
Hence, we can directly write,
${F_{net}} = \sqrt {F_A^2 + F_B^2} $
when the vectors are inclined at right angles to each other.
Complete step by step answer:
Consider a system of three charges on the vertices of triangle ABC as shown.

Step1:
In terms esu the force of attraction or repulsion between two charges is given by-
$F = \dfrac{{{q_1}{q_2}}}{{{r^2}}}$
Where r is the distance between charges,
For the force between B and A
${F_A} = \dfrac{{5 \times 12}}{{{3^2}}} = 20dynes$
Step2:
Now calculate the force between charges B and C
${F_C} = \dfrac{{20 \times 12}}{{{4^2}}} = 15dynes$
Step3: Now use the equation of resultant forces to calculate the net force at point B
${F_{net}} = \sqrt {F_A^2 + F_B^2} $
$ \Rightarrow {F_{net}} = \sqrt {{{20}^2} + {{15}^2}} = \sqrt {400 + 225} = \sqrt {625} $
$ \Rightarrow {F_{net}} = 25dynes$.
Hence, the correct answer is option (B).
Note: In this equation, we have used the formula of resultant force directly. However, the actual formula is –
${F_{net}} = \sqrt {F_A^2 + F_B^2 + 2{F_A}{F_B}\cos \theta } $
where $\cos \theta $ = angle between the two vectors. In this case, the angle between them is ${90^ \circ } \Rightarrow \cos {90^ \circ } = 0$
Hence, we can directly write,
${F_{net}} = \sqrt {F_A^2 + F_B^2} $
when the vectors are inclined at right angles to each other.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE

In a human foetus the limbs and digits develop after class 12 biology CBSE

AABbCc genotype forms how many types of gametes a 4 class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between homogeneous and heterogeneous class 12 chemistry CBSE

The correct structure of ethylenediaminetetraacetic class 12 chemistry CBSE




