
What is the Lewis dot structure of ${{\left( \text{C}{{\text{H}}_{\text{3}}} \right)}_{2}}\text{SeC}{{\text{l}}_{2}}$? What is the VSEPR class of the molecule?
Answer
524.4k+ views
Hint: Lewis dot structure is a symbolic representation of elements and compounds where the electrons present in the outermost shell of the atom, i.e. valence shell electrons are drawn as dots surrounding it, and lines are used to show bonding pairs of electrons between two atoms.
Complete answer:
Atoms either gain, lose, or share the electrons present in their outermost or valence orbital to achieve the most stable octet configuration in the valence shell. Lewis structures are used to show how these valence electrons are arranged around individual atoms in a molecule.
Electrons are represented as dots and sometimes a line is used to denote a bonding pair of electrons. Let us draw the Lewis dot structure of ${{\left( \text{C}{{\text{H}}_{\text{3}}} \right)}_{2}}\text{SeC}{{\text{l}}_{2}}$.
1 – First we need to determine the number of valence electrons each atom possesses in the molecule. Then, draw the Lewis dot structure of atoms as shown below.
\[\begin{align}
& \text{No}\text{. of valence electrons}: \\
& \text{Se}=6 \\
& \text{C}{{\text{H}}_{3}}=1 \\
& \text{Cl}=7 \\
\end{align}\]
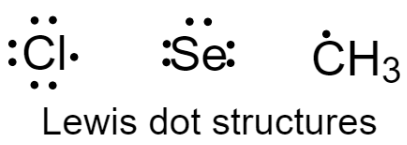
2 – Assign the central atom which is forming the greatest number of bonds. Here, selenium will be the central atom.

3 – Arrange electrons such that each atom contributes one electron and forms a single bond with another atom.
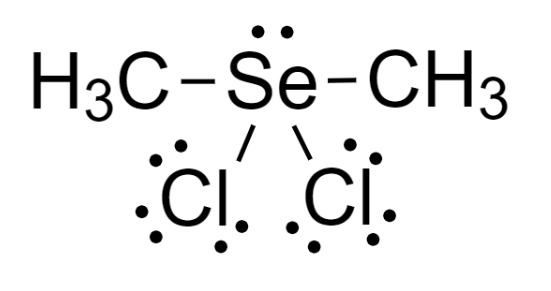
4 – Now, we can see the octet of each atom is complete and thus it is the required Lewis-dot structure.
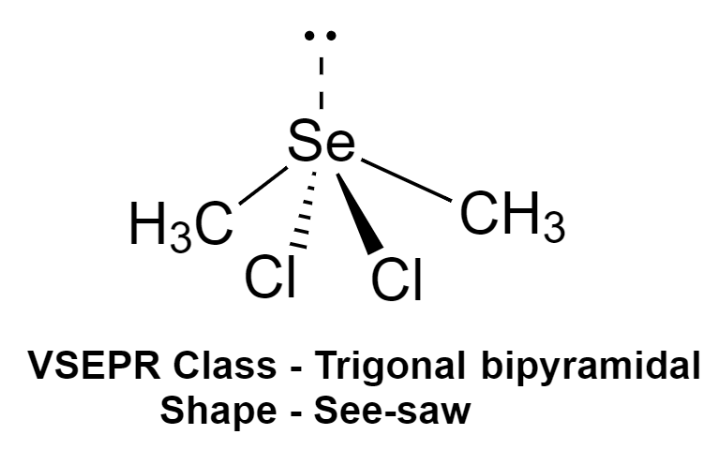
We can use the VSEPR model to predict the geometry of the molecule only by the number of electron pairs around the central atom. Now, this compound has a total of 5 electron pairs around the central atom out of which 4 are bonding pairs of electrons and one is lone pair.
Thus, the VSEPR class of this compound is trigonal bipyramidal in which lone pair is present at the axis. And hence the shape of the molecule will be see-saw.
Note:
Lewis's structure does not explain the geometry of molecules, or how the electrons are shared between the atoms. It is the simplest and most limited theory and that is why we have the VSEPR theory which helps to understand the geometry of any molecule, ion, or compound.
Complete answer:
Atoms either gain, lose, or share the electrons present in their outermost or valence orbital to achieve the most stable octet configuration in the valence shell. Lewis structures are used to show how these valence electrons are arranged around individual atoms in a molecule.
Electrons are represented as dots and sometimes a line is used to denote a bonding pair of electrons. Let us draw the Lewis dot structure of ${{\left( \text{C}{{\text{H}}_{\text{3}}} \right)}_{2}}\text{SeC}{{\text{l}}_{2}}$.
1 – First we need to determine the number of valence electrons each atom possesses in the molecule. Then, draw the Lewis dot structure of atoms as shown below.
\[\begin{align}
& \text{No}\text{. of valence electrons}: \\
& \text{Se}=6 \\
& \text{C}{{\text{H}}_{3}}=1 \\
& \text{Cl}=7 \\
\end{align}\]

2 – Assign the central atom which is forming the greatest number of bonds. Here, selenium will be the central atom.

3 – Arrange electrons such that each atom contributes one electron and forms a single bond with another atom.

4 – Now, we can see the octet of each atom is complete and thus it is the required Lewis-dot structure.
We can use the VSEPR model to predict the geometry of the molecule only by the number of electron pairs around the central atom. Now, this compound has a total of 5 electron pairs around the central atom out of which 4 are bonding pairs of electrons and one is lone pair.
Thus, the VSEPR class of this compound is trigonal bipyramidal in which lone pair is present at the axis. And hence the shape of the molecule will be see-saw.

Note:
Lewis's structure does not explain the geometry of molecules, or how the electrons are shared between the atoms. It is the simplest and most limited theory and that is why we have the VSEPR theory which helps to understand the geometry of any molecule, ion, or compound.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

10 examples of friction in our daily life




