
Lewis structure of ${\text{MgC}}{{\text{l}}_{\text{2}}}$ and ${\text{A}}{{\text{l}}_{\text{2}}}{{\text{O}}_{\text{3}}}$are:
A.

B.

C.Both A and B
D.None of the above


Answer
592.8k+ views
Hint: We have to calculate the total number of valence electrons of the compound by adding the number of valence electrons of all atoms in the molecule. A two-electron covalent bond is placed as a line between the atoms assuming that the atoms are bonded to each other. The remaining valence electrons are used as lone pairs about each atom so that the octet rule is satisfied.
Complete step by step answer:
We must know that the magnesium chloride $\left( {{\text{MgC}}{{\text{l}}_{\text{2}}}} \right)$ is an ionic compound and they show the presence of ionic bonding.
The valence electrons in magnesium are two.
The valence electrons in chlorine are fourteen.
The total number of valence electrons in magnesium chloride is sixteen.
The symbols of magnesium and chlorine are written as,
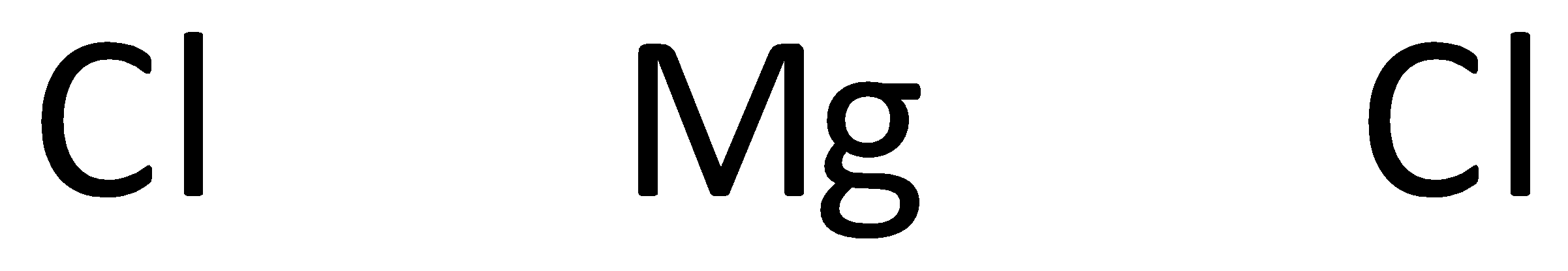
A covalent bond representing two electrons is placed as a line between chlorine and magnesium atoms.
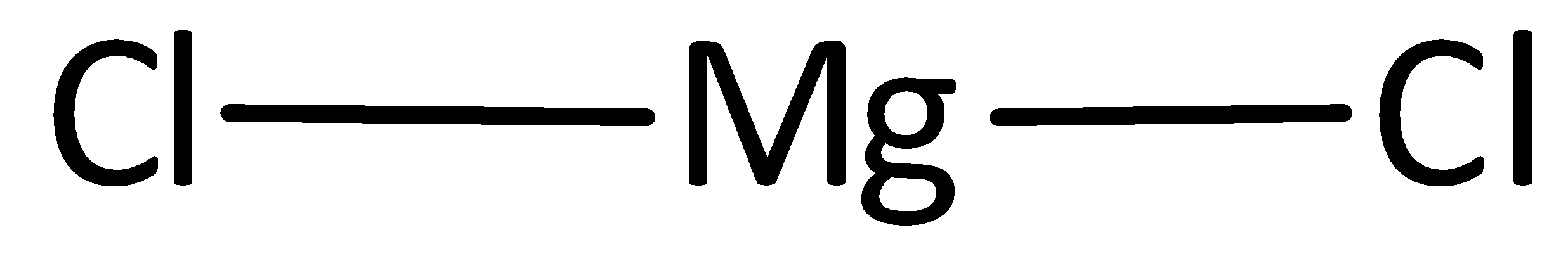
The remaining electrons are placed as lone pairs above the chlorine atom to satisfy the octet rule.
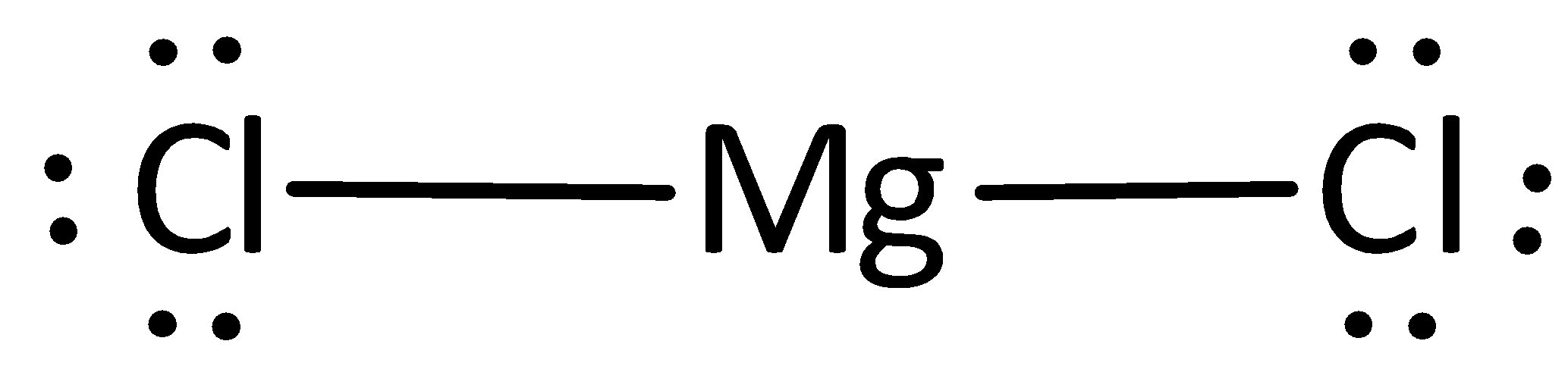
The Lewis structure of magnesium chloride is represented as,
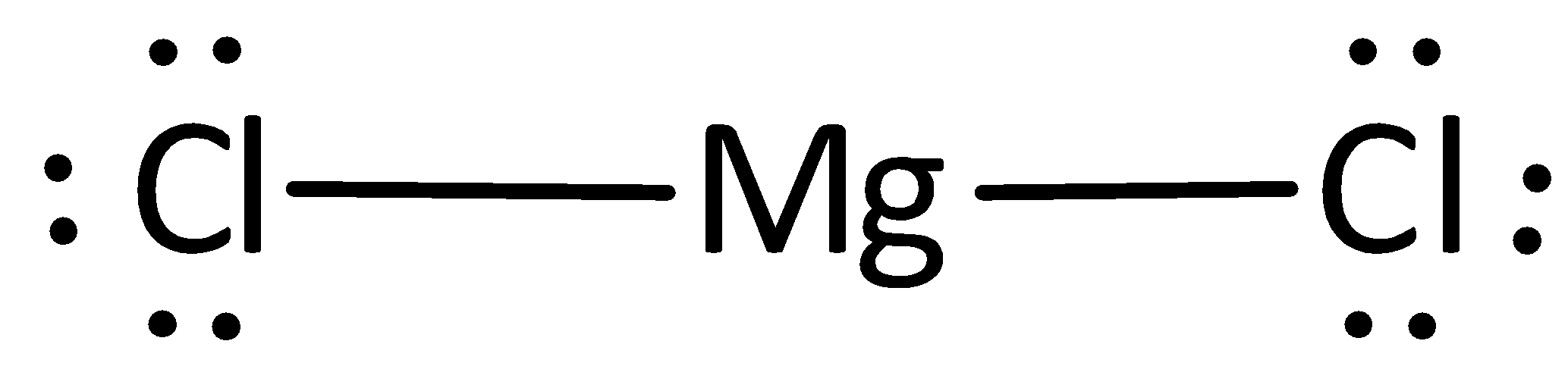
The Lewis structure can otherwise be given as,
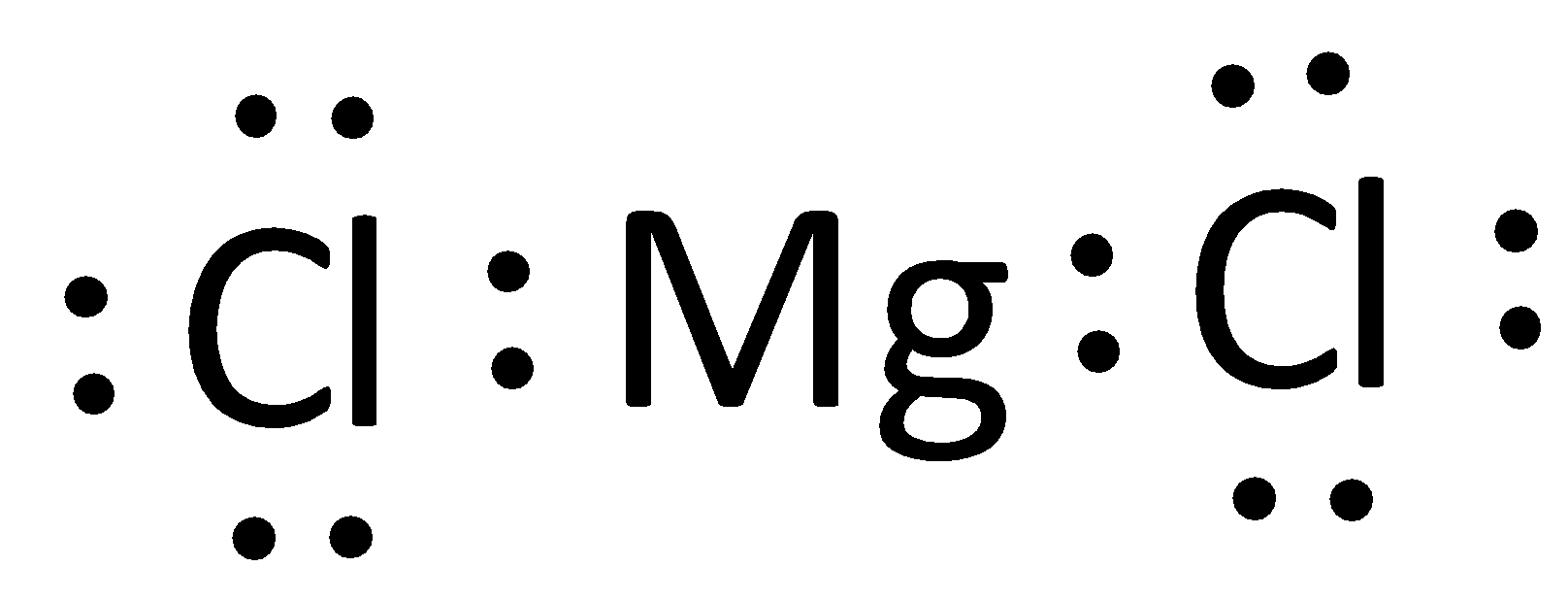
Aluminum oxide $\left( {{\text{A}}{{\text{l}}_{\text{2}}}{{\text{O}}_3}} \right)$ is an ionic compound and they show the presence of ionic bonding.
The valence electrons in aluminum are six.
The valence electrons in oxygen are eighteen.
The total number of valence electrons in aluminum oxide is twenty-four.
The symbols of aluminum and oxygen are written as,
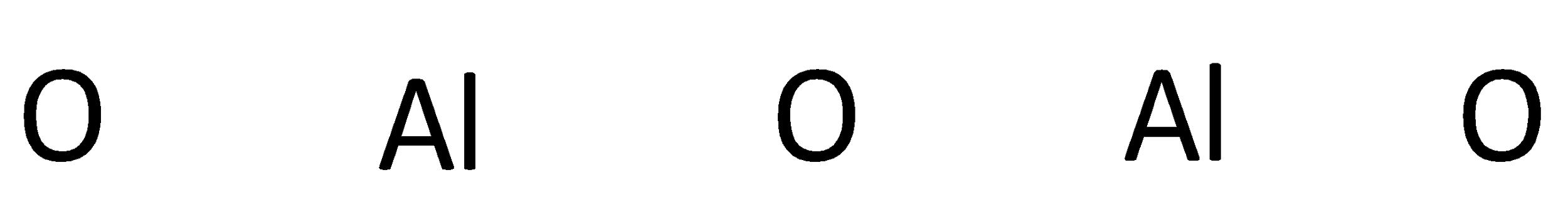
A covalent bond representing two electrons is placed as a line between aluminum and oxygen atoms.
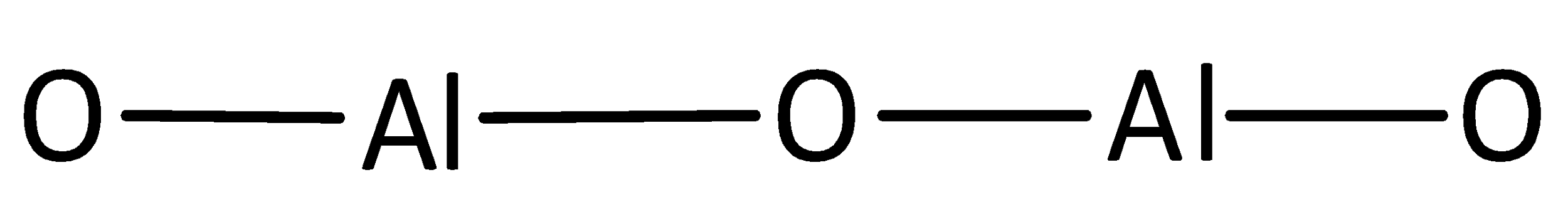
The remaining electrons are placed as lone pairs above the oxygen atoms to satisfy the octet rule.
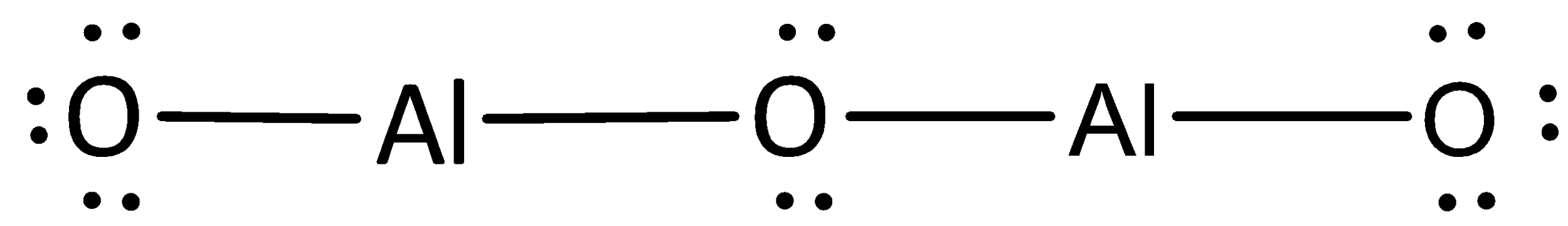
The Lewis structure of magnesium chloride is represented as,
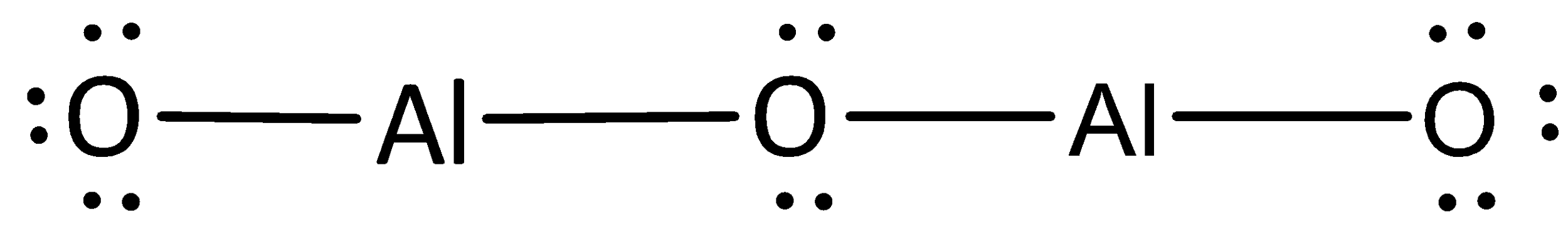
The Lewis structure can otherwise be given as,
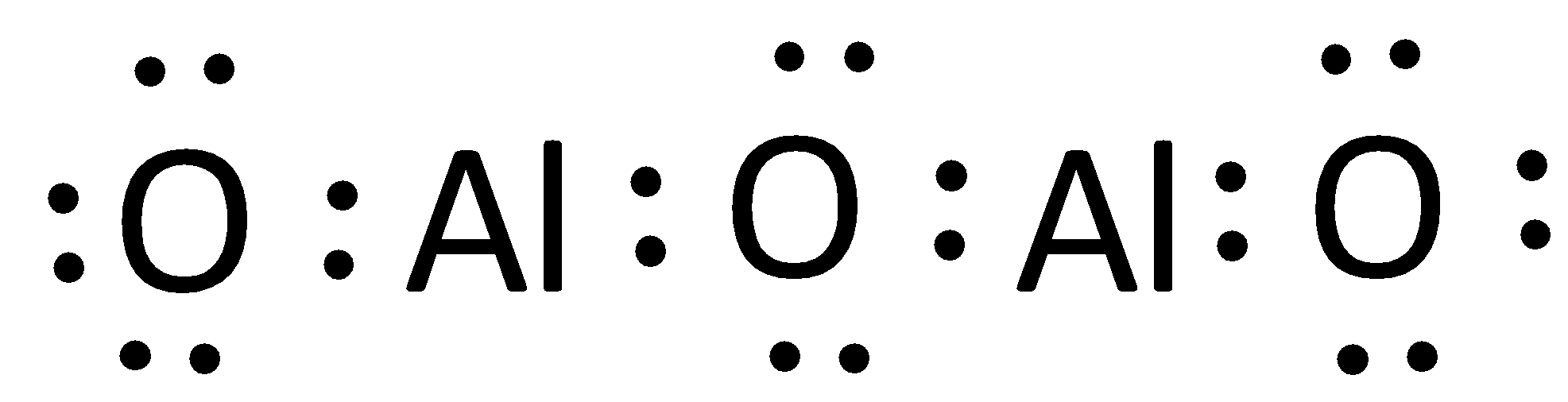
Hence, the correct option is (A).
And we must remember that the Lewis structure never includes charges in cation and anion.
Note:
We should know the number of valence electrons present in the element. While calculating the total valence electrons of an element, they should multiply the number of atoms present in the compound with the number of valence electrons.
Complete step by step answer:
We must know that the magnesium chloride $\left( {{\text{MgC}}{{\text{l}}_{\text{2}}}} \right)$ is an ionic compound and they show the presence of ionic bonding.
The valence electrons in magnesium are two.
The valence electrons in chlorine are fourteen.
The total number of valence electrons in magnesium chloride is sixteen.
The symbols of magnesium and chlorine are written as,
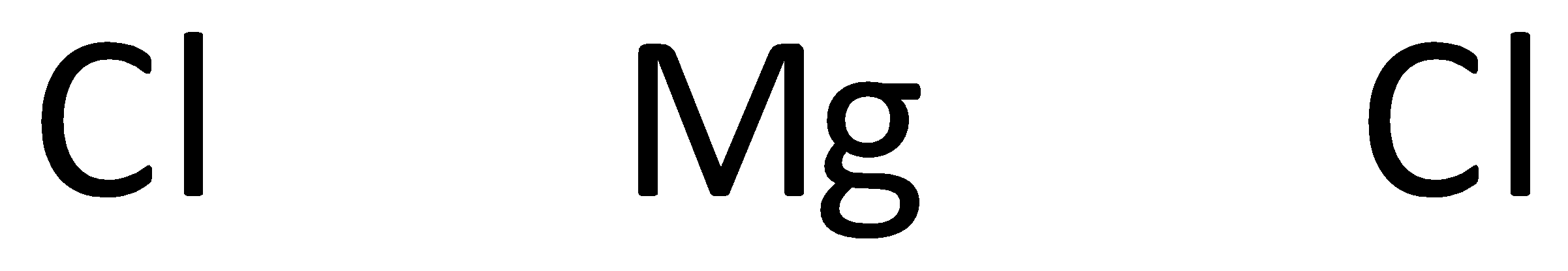
A covalent bond representing two electrons is placed as a line between chlorine and magnesium atoms.
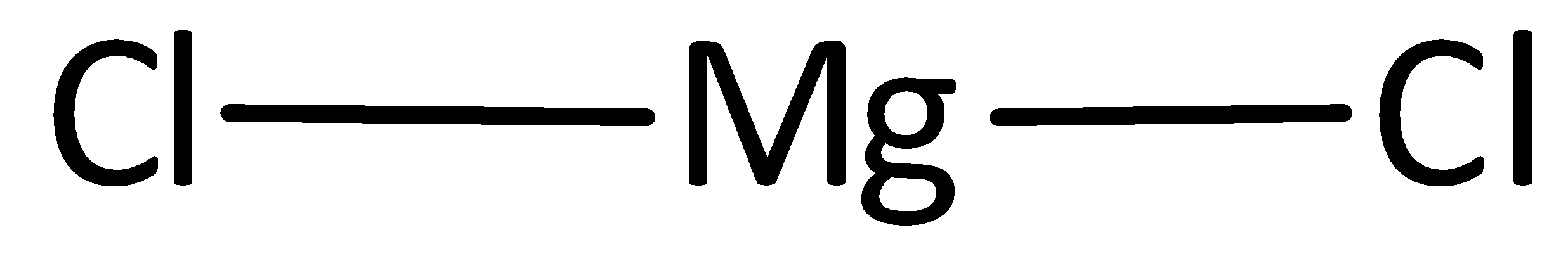
The remaining electrons are placed as lone pairs above the chlorine atom to satisfy the octet rule.
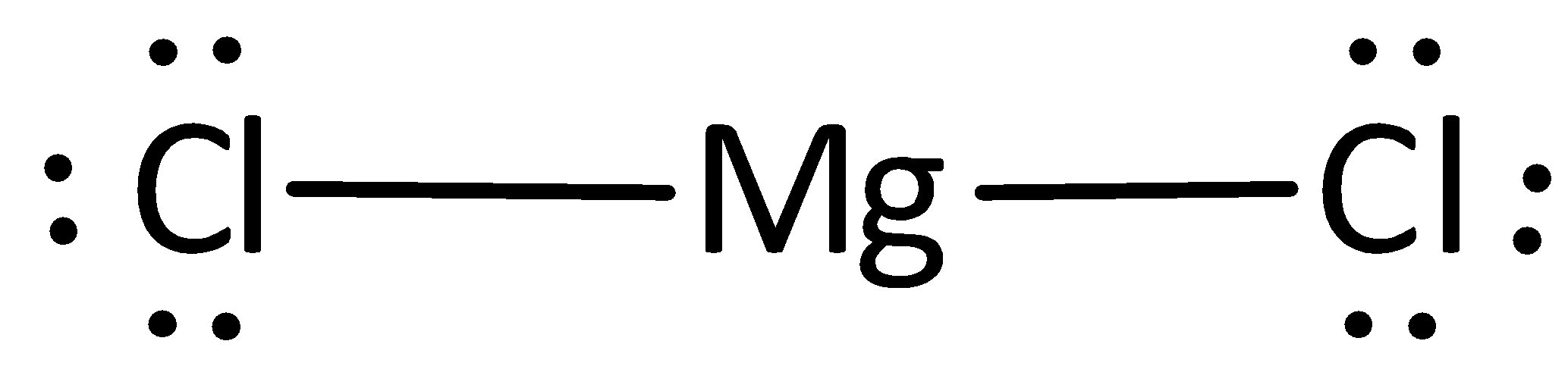
The Lewis structure of magnesium chloride is represented as,
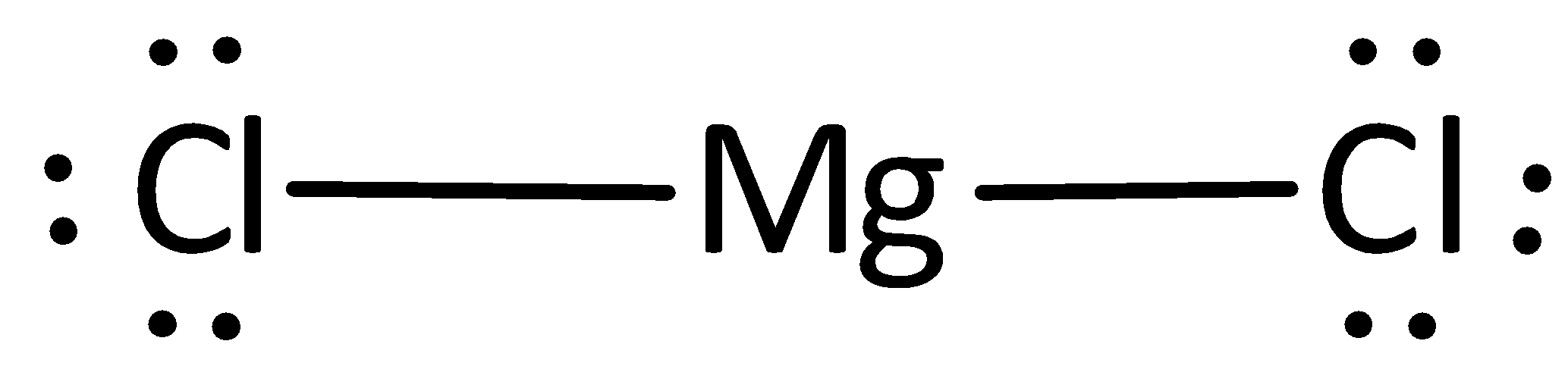
The Lewis structure can otherwise be given as,
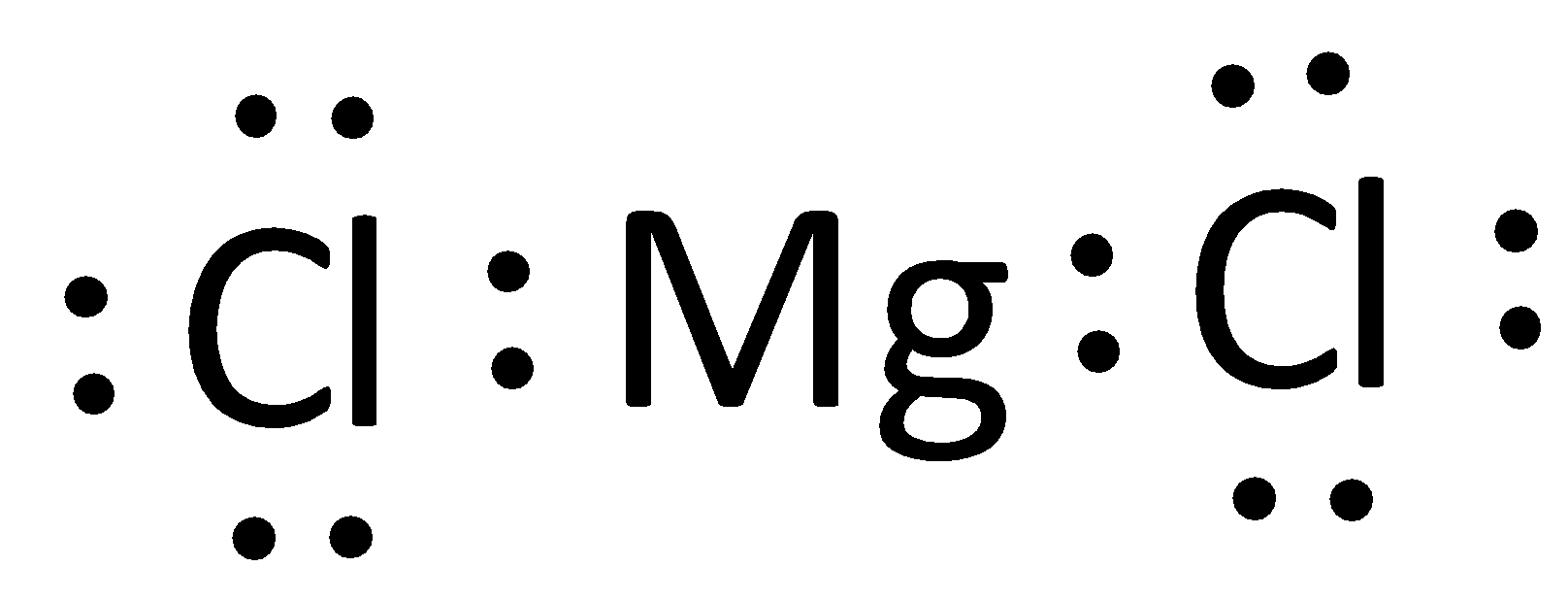
Aluminum oxide $\left( {{\text{A}}{{\text{l}}_{\text{2}}}{{\text{O}}_3}} \right)$ is an ionic compound and they show the presence of ionic bonding.
The valence electrons in aluminum are six.
The valence electrons in oxygen are eighteen.
The total number of valence electrons in aluminum oxide is twenty-four.
The symbols of aluminum and oxygen are written as,
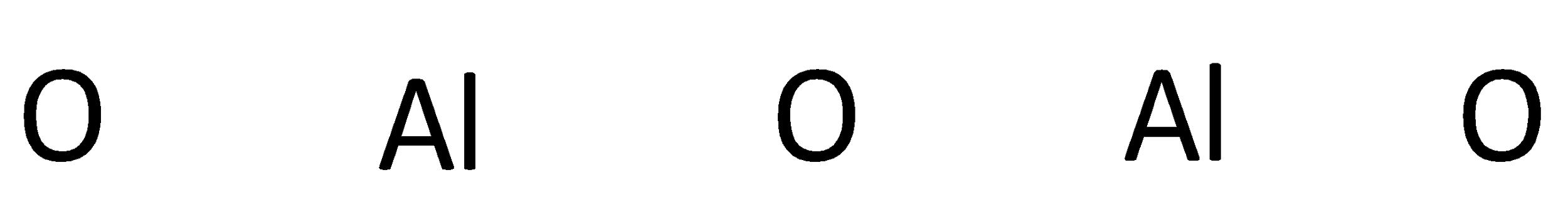
A covalent bond representing two electrons is placed as a line between aluminum and oxygen atoms.
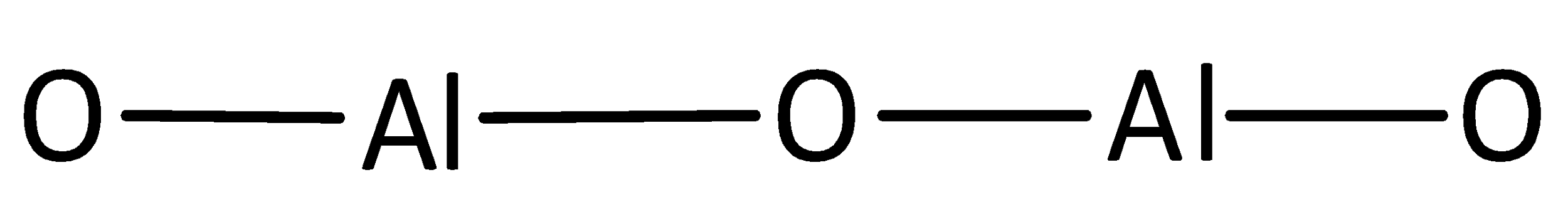
The remaining electrons are placed as lone pairs above the oxygen atoms to satisfy the octet rule.
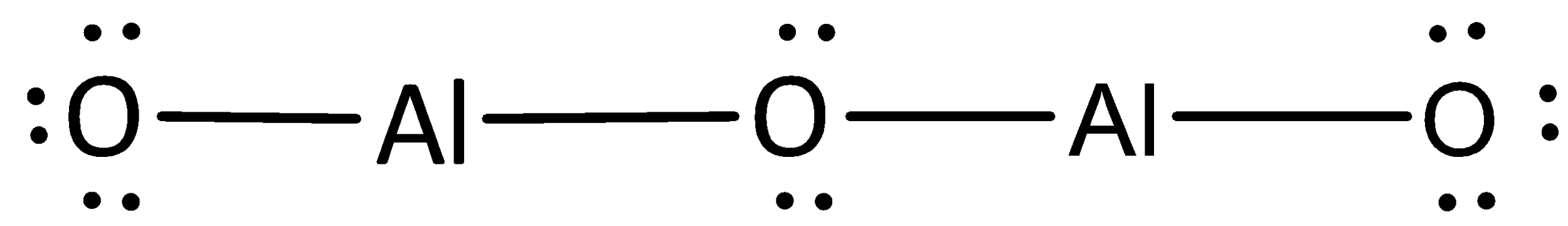
The Lewis structure of magnesium chloride is represented as,
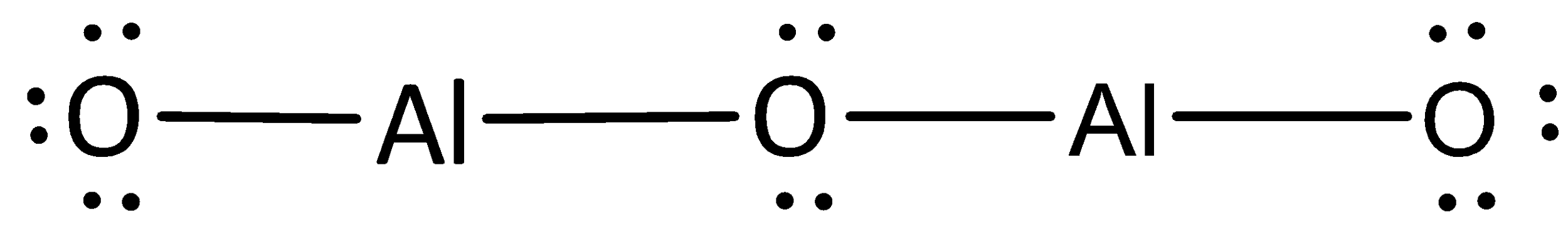
The Lewis structure can otherwise be given as,

Hence, the correct option is (A).
And we must remember that the Lewis structure never includes charges in cation and anion.
Note:
We should know the number of valence electrons present in the element. While calculating the total valence electrons of an element, they should multiply the number of atoms present in the compound with the number of valence electrons.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




