
List the different parts of the flower.
Answer
507.9k+ views
Hint: Sepals, petals, stamens, and carpels are the four primary components of most flowers. The stamens are the male component of the flower, while the carpels are the female part. The majority of flowers are hermaphrodites, meaning they have both male and female components. Others may be masculine or female and contain one of the two parts.
Complete answer:
Before moving on to the sections, familiarise yourself with the classification of flowers.
The flower's stalk is known as the peduncle.
The section of the flower to which the stem is attached is known as the receptacle. It is small and located in the centre of the flower's base.
Sepals: The little, leaf-like portions that sprout at the base of the petals are known as sepals. They make up the flower's outermost whorl. The calyx is the collective name for the sepals. The calyx and its sepals' primary role is to protect the flower before it blooms (in the bud stage).
Petals: Just above the sepal layer is the layer of petals. They are generally brightly coloured because their primary purpose is to attract pollinators to the flower, such as insects and butterflies. The corolla is the collective name for the petals.
The male portions of a flower are called stamens. The androecium is the collective name for a group of stamens. They are grouped into two sections structurally:
Filament: the long, slender portion that connects the anther to the flower.
Anthers: The anthers are the stamen's heads, and they're in charge of creating pollen, which is then transferred to the pistil or female portions of the same or another flower to fertilise it.
The female portions of a flower are formed by the pistil. The gynoecium is a group of pistils.
Pistils are made up of three major components:
1) the stigma, which is a sticky tip that collects pollen grains;
2) the style, which is a long neck that joins the stigma and the ovary; and
3) the ovary, which produces ovules.
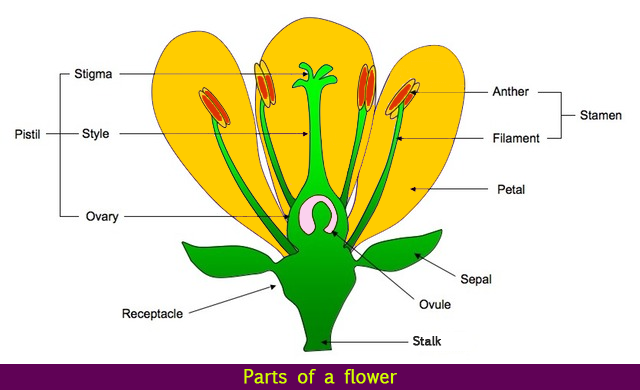
Note: A bisexual flower has all four whorls, including petals, sepals, male reproductive structure (stamen), and female reproductive structure (ovules) (pistil). As a result, it is often known as a perfect or entire flower.
Complete answer:
Before moving on to the sections, familiarise yourself with the classification of flowers.
The flower's stalk is known as the peduncle.
The section of the flower to which the stem is attached is known as the receptacle. It is small and located in the centre of the flower's base.
Sepals: The little, leaf-like portions that sprout at the base of the petals are known as sepals. They make up the flower's outermost whorl. The calyx is the collective name for the sepals. The calyx and its sepals' primary role is to protect the flower before it blooms (in the bud stage).
Petals: Just above the sepal layer is the layer of petals. They are generally brightly coloured because their primary purpose is to attract pollinators to the flower, such as insects and butterflies. The corolla is the collective name for the petals.
The male portions of a flower are called stamens. The androecium is the collective name for a group of stamens. They are grouped into two sections structurally:
Filament: the long, slender portion that connects the anther to the flower.
Anthers: The anthers are the stamen's heads, and they're in charge of creating pollen, which is then transferred to the pistil or female portions of the same or another flower to fertilise it.
The female portions of a flower are formed by the pistil. The gynoecium is a group of pistils.
Pistils are made up of three major components:
1) the stigma, which is a sticky tip that collects pollen grains;
2) the style, which is a long neck that joins the stigma and the ovary; and
3) the ovary, which produces ovules.

Note: A bisexual flower has all four whorls, including petals, sepals, male reproductive structure (stamen), and female reproductive structure (ovules) (pistil). As a result, it is often known as a perfect or entire flower.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




