
List the new Cartesian sign convention for reflection of light by spherical mirrors. Draw a diagram and apply these conventions for calculating the focal length and the nature of a spherical mirror which forms a $\dfrac{1}{3}$ times magnified the virtual image of an object placed 18cm in front of it.
Answer
579.6k+ views
Hint: In this question, after following sign convention (which we will discuss below in detail) it is easier to determine the nature of the spherical mirror. If the focal length of the mirror is positive it will be a convex mirror, if the focal length is negative then it is a concave mirror. Magnification of a mirror is given as the ratio of image height to the object height.
Complete step by step answer:
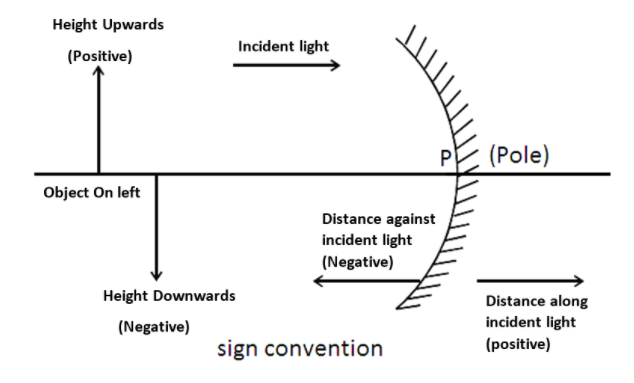
We must follow a set of sign conventions called the New Cartesian Sign convention while dealing with the reflection of light by spherical mirrors. Using this convention the pole(P) of the mirror is taken as the origin the principal axis of the mirror is taken as the x-axis of the coordinate system the convention are as follows-
a) The object is always placed to the left of the mirror this implies that the light from the object falls on the mirror from the left-hand side.
b) All distances parallel to the principal axis are measured from the pole of the mirror.
c) All the distances measured from the right of the origin (along +x axis) are taken as positive with those measured to the left of the origin (along x-axis) are taken as negative.
d) Distance measured perpendicular to and above the principal axis (along +y-axis) are taken as negative.
Focal Length: Focal length is the half of radius of curvature (R) of a spherical mirror.
There are two types of spherical mirror:
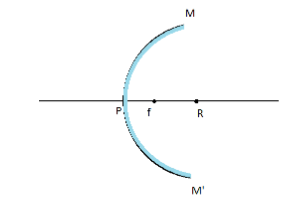
Convex mirror: Focal length of a convex mirror is positive (because it lies on the positive x-axis), an image formed by this mirror is virtual, erect, and small in size.
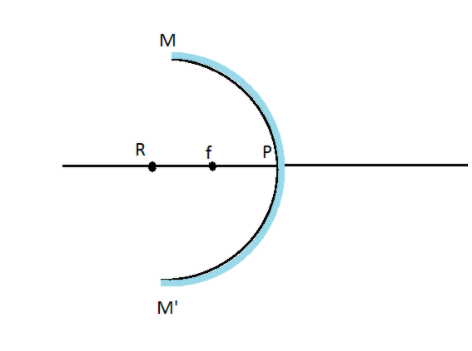
Concave Mirror: Focal length of a concave mirror is negative (because it lies on the negative x-axis). The image formed is real, inverted, and generally large. Only in one case, the image formed is virtual, erect is when the object is placed between focal length and pole of the mirror.
Magnification: It is the ratio of the height of the image to the height of the object $m=\dfrac{{{h}_{i}}}{{{h}_{o}}}$. It has some relation with the distance of image and the distance of object i.e. \[m=\dfrac{-v}{u}\] .
The distance of the object is represented by u and distance of image is represented by v.
In our question we are given with:
Magnification \[m=\dfrac{1}{3}\] .
Distance of the object \[u=-18cm\] .
\[\begin{align}
& m=\dfrac{-v}{u} \\
& \Rightarrow \dfrac{1}{3}=\dfrac{-v}{u} \\
& \Rightarrow u=-3v \\
& \Rightarrow -18=-3v \\
& \therefore v=+6cm \\
\end{align}\]
Now, we have to determine the image distance and focal length. Therefore applying the mirror formula,
\[\begin{align}
& \dfrac{1}{f}=\dfrac{1}{v}+\dfrac{1}{u} \\
& \Rightarrow \dfrac{1}{f}=\dfrac{1}{6}+\dfrac{1}{(-18)} \\
& \Rightarrow \dfrac{1}{f}=\dfrac{1}{6}-\dfrac{1}{18} \\
& \Rightarrow \dfrac{1}{f}=\dfrac{3-1}{18} \\
& \Rightarrow \dfrac{1}{f}=\dfrac{2}{18} \\
& \therefore f=+9cm \\
\end{align}\]
The positive focal length signifies the nature of the mirror as a convex mirror.
Note:
There is one more mirror called plane mirror which we use in our daily life that has an infinite focal length, this implies that the distance of the image from the mirror is the same as the distance of the object. This is an advice to the students to care about putting the right sign by following sign convention rules.
Complete step by step answer:
We must follow a set of sign conventions called the New Cartesian Sign convention while dealing with the reflection of light by spherical mirrors. Using this convention the pole(P) of the mirror is taken as the origin the principal axis of the mirror is taken as the x-axis of the coordinate system the convention are as follows-
a) The object is always placed to the left of the mirror this implies that the light from the object falls on the mirror from the left-hand side.
b) All distances parallel to the principal axis are measured from the pole of the mirror.
c) All the distances measured from the right of the origin (along +x axis) are taken as positive with those measured to the left of the origin (along x-axis) are taken as negative.
d) Distance measured perpendicular to and above the principal axis (along +y-axis) are taken as negative.

Focal Length: Focal length is the half of radius of curvature (R) of a spherical mirror.
There are two types of spherical mirror:
Convex mirror: Focal length of a convex mirror is positive (because it lies on the positive x-axis), an image formed by this mirror is virtual, erect, and small in size.

Concave Mirror: Focal length of a concave mirror is negative (because it lies on the negative x-axis). The image formed is real, inverted, and generally large. Only in one case, the image formed is virtual, erect is when the object is placed between focal length and pole of the mirror.

Magnification: It is the ratio of the height of the image to the height of the object $m=\dfrac{{{h}_{i}}}{{{h}_{o}}}$. It has some relation with the distance of image and the distance of object i.e. \[m=\dfrac{-v}{u}\] .
The distance of the object is represented by u and distance of image is represented by v.
In our question we are given with:
Magnification \[m=\dfrac{1}{3}\] .
Distance of the object \[u=-18cm\] .
\[\begin{align}
& m=\dfrac{-v}{u} \\
& \Rightarrow \dfrac{1}{3}=\dfrac{-v}{u} \\
& \Rightarrow u=-3v \\
& \Rightarrow -18=-3v \\
& \therefore v=+6cm \\
\end{align}\]
Now, we have to determine the image distance and focal length. Therefore applying the mirror formula,
\[\begin{align}
& \dfrac{1}{f}=\dfrac{1}{v}+\dfrac{1}{u} \\
& \Rightarrow \dfrac{1}{f}=\dfrac{1}{6}+\dfrac{1}{(-18)} \\
& \Rightarrow \dfrac{1}{f}=\dfrac{1}{6}-\dfrac{1}{18} \\
& \Rightarrow \dfrac{1}{f}=\dfrac{3-1}{18} \\
& \Rightarrow \dfrac{1}{f}=\dfrac{2}{18} \\
& \therefore f=+9cm \\
\end{align}\]
The positive focal length signifies the nature of the mirror as a convex mirror.
Note:
There is one more mirror called plane mirror which we use in our daily life that has an infinite focal length, this implies that the distance of the image from the mirror is the same as the distance of the object. This is an advice to the students to care about putting the right sign by following sign convention rules.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




