
How long is the oesophagus in the human digestive system?
Answer
497.1k+ views
Hint: Esophagus is a fibromuscular tube, which connects the throat or pharynx with the stomach. It is linked by a moist pink colored tissue referred to as mucosa. It runs behind the trachea or windpipe and the heart, but runs in front of the spine. It passes through the diaphragm and empties into the uppermost portion of the stomach. It aids in the passage of food from the pharynx to the stomach.
Complete answer
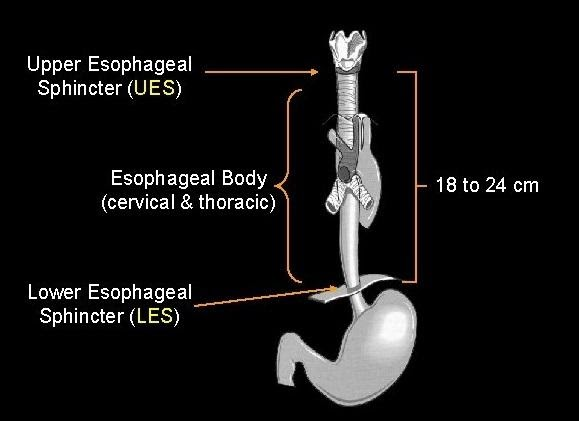
Figure: Anatomy of Esophagus
The length of the esophagus is eight inches. The length is also reported to be ten inches or twenty-five centimeters. A ring-like muscle existing at the end of the esophagus controls the flow of food into the stomach. It also helps in controlling the food from going up back into the esophagus.
There are two esophageal sphincters present in the esophageal region. The upper esophageal sphincter (UES), present at the top of the esophagus is constructed from a bundle of muscles. The muscles of UES are under conscious control, and are used during eating, breathing, vomiting and belching. The muscles prevent secretions and food from going down the windpipe.
The lower esophageal sphincter (LES), which exists at the lower end of the esophagus, where it meets the stomach is also composed of a bundle of muscles. During the closure of LES, it prevents acid and stomach contents from travelling backwards from the stomach. The muscles of LES are not voluntarily restrained.
Note:
The width of the esophagus varies from \[1.5\] to \[2\]cm. Their esophagus consists of four columns, mucosa, submucosa, muscularis and tunica adventitia. Mucosa is composed of stratified squamous epithelium containing mucosal glands. Submucosa is a thick fibrous layer. The inner layer is muscularis and the outer layer is tunica adventitia. Small intestine is the longest part of the human digestive system, which is seven metres long.
Complete answer

Figure: Anatomy of Esophagus
The length of the esophagus is eight inches. The length is also reported to be ten inches or twenty-five centimeters. A ring-like muscle existing at the end of the esophagus controls the flow of food into the stomach. It also helps in controlling the food from going up back into the esophagus.
There are two esophageal sphincters present in the esophageal region. The upper esophageal sphincter (UES), present at the top of the esophagus is constructed from a bundle of muscles. The muscles of UES are under conscious control, and are used during eating, breathing, vomiting and belching. The muscles prevent secretions and food from going down the windpipe.
The lower esophageal sphincter (LES), which exists at the lower end of the esophagus, where it meets the stomach is also composed of a bundle of muscles. During the closure of LES, it prevents acid and stomach contents from travelling backwards from the stomach. The muscles of LES are not voluntarily restrained.
Note:
The width of the esophagus varies from \[1.5\] to \[2\]cm. Their esophagus consists of four columns, mucosa, submucosa, muscularis and tunica adventitia. Mucosa is composed of stratified squamous epithelium containing mucosal glands. Submucosa is a thick fibrous layer. The inner layer is muscularis and the outer layer is tunica adventitia. Small intestine is the longest part of the human digestive system, which is seven metres long.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




