
Longest cell in the human body is
(a) Nerve cell
(b) Leg muscle cell
(c) Bone cell
(d) Heart muscle cell
Answer
590.7k+ views
Hint: The longest human body cell is composed of a cell body called soma, dendrites, and an axon. Dendrites and axons are fibers to the nerves. It is the nervous system’s structural and functional unit.
Complete answer:
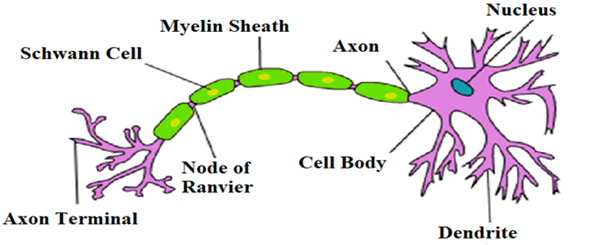
Neurons or nerve cells can be up to 3 feet long. Nerve cells have one to several small, fiber-like axons, and a cell body. Some nerve cells contain axons up to 1 meter long. The neuron which connects the central nervous system (brain and spinal cord) to other parts of the body is the longest cell in the human body. Nerve cells, also known as neurons, are the active portion of the nervous system.
A cell that carries electrical impulses is a neuron or nerve cell. Neurons are the central units of the nervous system. Each nerve cell consists of the nucleus, a large branching fiber (axon) , and numerous smaller branching fibers (dendrites) in the cell body. The myelin sheath is a fatty material that covers, insulates, and protects the brain and spinal cord nerves.
So, the correct answer is, ‘Nerve cell’.
Additional Information: Even though a very complex nervous system, nervous tissue consists of only two basic types of nerve cells: neurons and glial cells. They express electrical signals, which are called nerve impulses. Neurons are protected by Glial cells. They provide nutrients and other resources for the neurons.
The neurons are categorized according to the direction they bring nerve impulses in.
- Sensory neurons carry nerve impulses from the tissues and organs to the brain and spinal cord.
- The motor neurons bring nerve impulses to the muscles and glands from the brain and spinal cord.
- Interneurons bring back and forth nerve impulses between the sensory and motor neurons.
Note: Neurons are skilled in passing on information throughout the body. Neurons are equipped with a membrane for transmitting information to other cells. The neuron cell body includes the nucleus and other organelles of the cell. Dendrites detach from the body of the cell and receive nerve impulses from the neurons. The axon is a long line of the cell body transmitting nerve impulses to other cells. In the end, the axon branches out forming axon terminals. These are the points of communication between the neuron and other cells.
Complete answer:
Neurons or nerve cells can be up to 3 feet long. Nerve cells have one to several small, fiber-like axons, and a cell body. Some nerve cells contain axons up to 1 meter long. The neuron which connects the central nervous system (brain and spinal cord) to other parts of the body is the longest cell in the human body. Nerve cells, also known as neurons, are the active portion of the nervous system.
A cell that carries electrical impulses is a neuron or nerve cell. Neurons are the central units of the nervous system. Each nerve cell consists of the nucleus, a large branching fiber (axon) , and numerous smaller branching fibers (dendrites) in the cell body. The myelin sheath is a fatty material that covers, insulates, and protects the brain and spinal cord nerves.

So, the correct answer is, ‘Nerve cell’.
Additional Information: Even though a very complex nervous system, nervous tissue consists of only two basic types of nerve cells: neurons and glial cells. They express electrical signals, which are called nerve impulses. Neurons are protected by Glial cells. They provide nutrients and other resources for the neurons.
The neurons are categorized according to the direction they bring nerve impulses in.
- Sensory neurons carry nerve impulses from the tissues and organs to the brain and spinal cord.
- The motor neurons bring nerve impulses to the muscles and glands from the brain and spinal cord.
- Interneurons bring back and forth nerve impulses between the sensory and motor neurons.
Note: Neurons are skilled in passing on information throughout the body. Neurons are equipped with a membrane for transmitting information to other cells. The neuron cell body includes the nucleus and other organelles of the cell. Dendrites detach from the body of the cell and receive nerve impulses from the neurons. The axon is a long line of the cell body transmitting nerve impulses to other cells. In the end, the axon branches out forming axon terminals. These are the points of communication between the neuron and other cells.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




