
What is Lucas reagent? Distinguish primary, secondary and tertiary alcohols using Lucas reagent.
Answer
594.9k+ views
Hint: Lucas reagent is a solution of a transition metal chloride in an inorganic acid. Lucas reagent will give a unimolecular nucleophilic substitution reaction with alcohols in which the different types of alcohols will react differently.
Complete step by step solution:
- Solution of anhydrous Zinc chloride in concentrated hydrochloric acid is known as Lucas reagent.
- Lucas reagent simply substitutes –Cl group in place of –OH group. It is a kind of \[{S_N}1\] reaction. So, carbocation is formed during the reaction. Let’s see how all types of alcohols react with Lucas reagent.
- Below is the reaction of primary alcohol Propan-1-ol with Lucas reagent. Here, primary cation is formed as hydroxyl group leaves after getting protonated by acid in the form of water. It does not give a\[{S_N}1\] reaction at room temperature. So, the solution remains the same and it is clear.
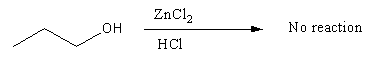
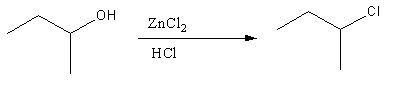
- Secondary alcohol forms secondary cation after the hydroxyl group is removed, it takes some minutes to react with chloride ions present in the solution to give \[{S_N}1\] reaction. It is shown in the reaction. As the reaction occurs, Chloroalkane is the product and we can see the solution becoming hazy.
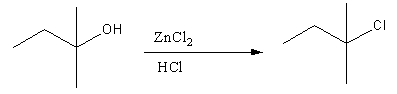
- Tertiary alcohols form tertiary cation by the reaction with Lucas reagent and as tertiary cations are most stable, it gives substitution reaction immediately and gives chloroalkane. Formation of products makes solutions hazy.
- So, we can conclude that tertiary alcohols immediately react with Lucas reagent, secondary alcohols take some minutes to react and primary alcohols do not react with Lucas reagent at room temperatures.
Additional Information:
- Lucas reagent can only distinguish small chain alcohols.
- Mixture of anhydrous Zinc chloride and concentrated hydrochloric acid is taken in equimolar proportions as Lucas reagent .
Note:
Note that here \[{S_N}1\] reaction occurs. Considering it as \[{S_N}2\] reaction will lead to wrong conclusions. In Lucas reagent, we cannot use any other acid. We need to use hydrochloric acid only.
Complete step by step solution:
- Solution of anhydrous Zinc chloride in concentrated hydrochloric acid is known as Lucas reagent.
- Lucas reagent simply substitutes –Cl group in place of –OH group. It is a kind of \[{S_N}1\] reaction. So, carbocation is formed during the reaction. Let’s see how all types of alcohols react with Lucas reagent.
- Below is the reaction of primary alcohol Propan-1-ol with Lucas reagent. Here, primary cation is formed as hydroxyl group leaves after getting protonated by acid in the form of water. It does not give a\[{S_N}1\] reaction at room temperature. So, the solution remains the same and it is clear.
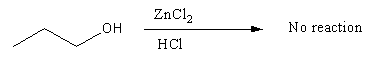
- Secondary alcohol forms secondary cation after the hydroxyl group is removed, it takes some minutes to react with chloride ions present in the solution to give \[{S_N}1\] reaction. It is shown in the reaction. As the reaction occurs, Chloroalkane is the product and we can see the solution becoming hazy.

- Tertiary alcohols form tertiary cation by the reaction with Lucas reagent and as tertiary cations are most stable, it gives substitution reaction immediately and gives chloroalkane. Formation of products makes solutions hazy.

- So, we can conclude that tertiary alcohols immediately react with Lucas reagent, secondary alcohols take some minutes to react and primary alcohols do not react with Lucas reagent at room temperatures.
Additional Information:
- Lucas reagent can only distinguish small chain alcohols.
- Mixture of anhydrous Zinc chloride and concentrated hydrochloric acid is taken in equimolar proportions as Lucas reagent .
Note:
Note that here \[{S_N}1\] reaction occurs. Considering it as \[{S_N}2\] reaction will lead to wrong conclusions. In Lucas reagent, we cannot use any other acid. We need to use hydrochloric acid only.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




