
\[M{a_2}{b_2}{c_2}\] has how many geometrical isomers?
(A) 5
(B) 4
(C) 3
(D) 2
Answer
565.2k+ views
Hint:. Geometrical isomers are the compounds in which the ligands occupy different positions around the metal ion or atom. By arranging the ligands adjacent and opposite to one another, we can determine how many geometrical isomers are possible.
Complete step by step answer:
Let us first understand what an isomer is. Isomers are compounds that have the same molecular formula but different structures and therefore they have different chemical and physical properties. The phenomenon of the existence of such a compound is called isomerism.
Isomerism can be classified into two types:
- Structural isomerism
- Stereoisomerism
When the atoms in the molecule and the functional groups are arranged in different ways, it is known as structural isomerism. Structural isomerism is also known as constitutional isomerism.
- Stereoisomerism is present in the compounds having the same chemical formula but different orientation of the atoms. Geometrical isomerism will come under stereoisomerism. Geometrical isomerism is due to the ligands occupying different positions around the central metal ions. When the same type of ligands occupies at the adjacent position around the central metal ions they are known as cis isomers. When the same type of ligands occupy at the opposite position, they are known as the trans isomers. Geometrical isomerism is also known as Cis-trans isomerism.
In \[M{a_2}{b_2}{c_2}\] compound, there are a total five possible geometrical isomers.
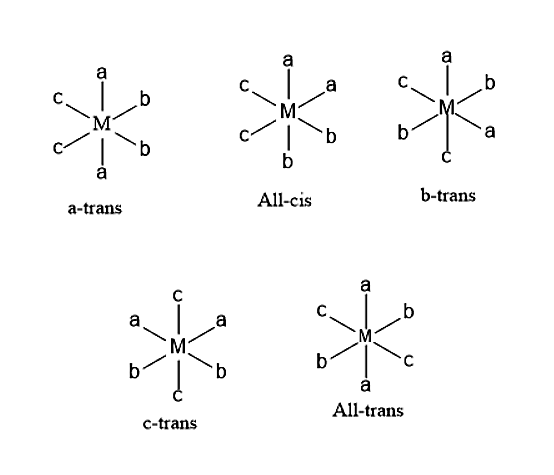
- Let us consider an example of \[{[Co{(N{H_3})_2}C{l_2}{(N{O_2})_2}]^ - }\], it forms five isomers namely,
- cis-diammine-cis-dichloro-trans-di-N-nitritocobaltate (III) ion.
- cis-diammine-cis-dichloro-cis-di-N-nitritocobaltate (III) ion.
- cis-diammine-trans-dichloro-cis-di-N-nitritocobaltate (III) ion.
- trans-diammine-cis-dichloro-cis-di-N-nitritocobaltate (III) ion.
- trans-diammine-trans-dichloro-trans-di-N-hexanitritocobaltate (III) ion.
So, the correct answer is “Option A”.
Additional information: Types of geometrical isomerism that can occur in complexes with coordination number 4:
- \[M{a_2}{b_2}\]
- \[M{a_2}bc\]
- \[Mabcd\]
- \[[M{(ab)_2}]\]
Types of geometrical isomerism that can occur in complexes with coordination number 6:
- \[M{a_3}{b_3}\]
- \[M{a_4}{b_2}\] or \[M{a_2}{b_4}\] or \[M{a_4}bc\]
- \[[Mabcdef]\]
- \[[M{(aa)_2}{b_2}]\]
Note: - Geometrical isomers are not possible in the compounds having coordination number two or three. Because in compounds with coordination number 2 or 3, all the ligands present in the compound will be adjacent to one another.
- Geometrical isomerism will be possible for the compounds with Coordination number 4 or above. But compounds with coordination number 4 can adopt either square planar or tetrahedral structure. In square planar complexes, geometrical isomerism can take place. In tetrahedral complexes, it is not possible since all ligands will be arranged adjacent to one another.
Complete step by step answer:
Let us first understand what an isomer is. Isomers are compounds that have the same molecular formula but different structures and therefore they have different chemical and physical properties. The phenomenon of the existence of such a compound is called isomerism.
Isomerism can be classified into two types:
- Structural isomerism
- Stereoisomerism
When the atoms in the molecule and the functional groups are arranged in different ways, it is known as structural isomerism. Structural isomerism is also known as constitutional isomerism.
- Stereoisomerism is present in the compounds having the same chemical formula but different orientation of the atoms. Geometrical isomerism will come under stereoisomerism. Geometrical isomerism is due to the ligands occupying different positions around the central metal ions. When the same type of ligands occupies at the adjacent position around the central metal ions they are known as cis isomers. When the same type of ligands occupy at the opposite position, they are known as the trans isomers. Geometrical isomerism is also known as Cis-trans isomerism.
In \[M{a_2}{b_2}{c_2}\] compound, there are a total five possible geometrical isomers.

- Let us consider an example of \[{[Co{(N{H_3})_2}C{l_2}{(N{O_2})_2}]^ - }\], it forms five isomers namely,
- cis-diammine-cis-dichloro-trans-di-N-nitritocobaltate (III) ion.
- cis-diammine-cis-dichloro-cis-di-N-nitritocobaltate (III) ion.
- cis-diammine-trans-dichloro-cis-di-N-nitritocobaltate (III) ion.
- trans-diammine-cis-dichloro-cis-di-N-nitritocobaltate (III) ion.
- trans-diammine-trans-dichloro-trans-di-N-hexanitritocobaltate (III) ion.
So, the correct answer is “Option A”.
Additional information: Types of geometrical isomerism that can occur in complexes with coordination number 4:
- \[M{a_2}{b_2}\]
- \[M{a_2}bc\]
- \[Mabcd\]
- \[[M{(ab)_2}]\]
Types of geometrical isomerism that can occur in complexes with coordination number 6:
- \[M{a_3}{b_3}\]
- \[M{a_4}{b_2}\] or \[M{a_2}{b_4}\] or \[M{a_4}bc\]
- \[[Mabcdef]\]
- \[[M{(aa)_2}{b_2}]\]
Note: - Geometrical isomers are not possible in the compounds having coordination number two or three. Because in compounds with coordination number 2 or 3, all the ligands present in the compound will be adjacent to one another.
- Geometrical isomerism will be possible for the compounds with Coordination number 4 or above. But compounds with coordination number 4 can adopt either square planar or tetrahedral structure. In square planar complexes, geometrical isomerism can take place. In tetrahedral complexes, it is not possible since all ligands will be arranged adjacent to one another.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




