
What is the main function of RNA interference?
Answer
581.4k+ views
Hint: The word interference means interfering or causing a disturbance. RNA interference is utilized in producing several pest- resistant plants. One such plant is the tobacco plant which has been made resistant to the nematode Meloidogyne incognita through this method.
Complete answer:
The function of RNA interference is to silence or deactivate specific genes and it is a natural regulatory or defense system occurring within all eukaryotic cells. The process is initiated by the presence of short segments of double-stranded RNA (dsRNA). This dsRNA is further processed by the DICER enzyme into short interfering RNA (siRNA).
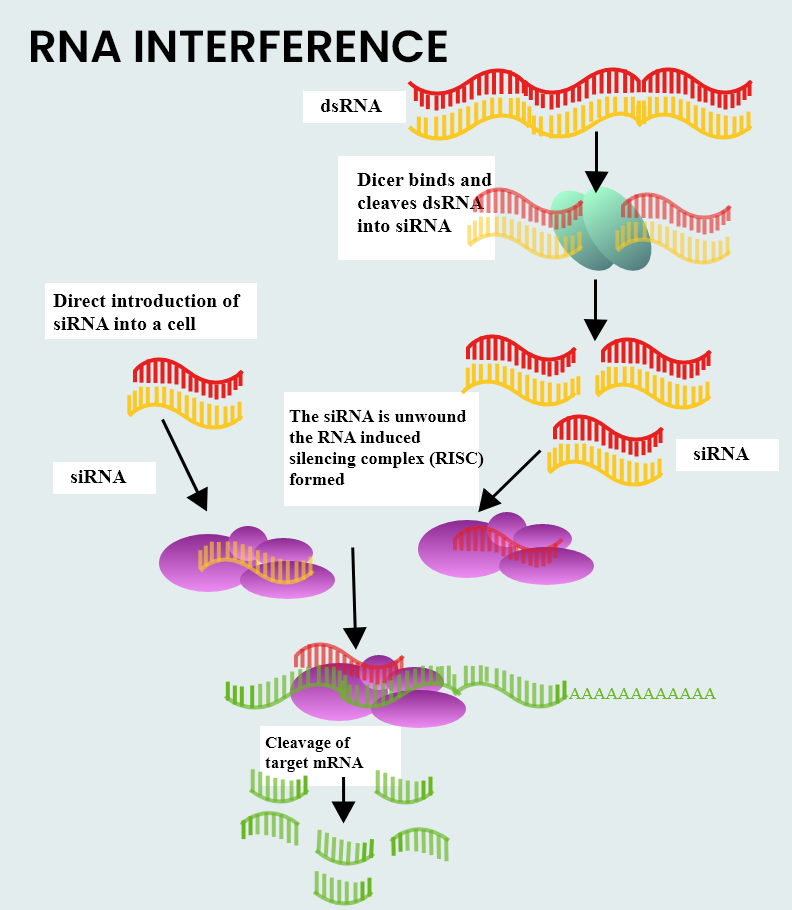
This siRNA now binds to an enzyme-containing molecule called RNA-induced silencing complex (RISC). This siRNA-RISC complex binds to the target messenger RNA (mRNA) and cleaves it. Now the cleaved mRNA is non- functional or silenced. Thus, translation of mRNA into proteins will not occur.
Additional information: RNA interference was discovered by American scientists Andrew Fire and Craig Mello who were awarded the 2006 Nobel Prize for Medicine. They experimentally showed the working of RNA interference in the cells of a nematode called Caenorhabditis elegans. These days microRNAs are used along with siRNA. These are formed by RNAs in the nucleus which were folded and processed and sent into the cytoplasm to go bind with DICER.
Note:
- The tobacco plant was made nematode-resistant by using the vector Agrobacterium tumefaciens.
- The enzyme DICER is a type III endoribonuclease.
- RNA interference is a quick method to silence translation and thus is used for many experiments these days like determining the function of a gene.
Complete answer:
The function of RNA interference is to silence or deactivate specific genes and it is a natural regulatory or defense system occurring within all eukaryotic cells. The process is initiated by the presence of short segments of double-stranded RNA (dsRNA). This dsRNA is further processed by the DICER enzyme into short interfering RNA (siRNA).

This siRNA now binds to an enzyme-containing molecule called RNA-induced silencing complex (RISC). This siRNA-RISC complex binds to the target messenger RNA (mRNA) and cleaves it. Now the cleaved mRNA is non- functional or silenced. Thus, translation of mRNA into proteins will not occur.
Additional information: RNA interference was discovered by American scientists Andrew Fire and Craig Mello who were awarded the 2006 Nobel Prize for Medicine. They experimentally showed the working of RNA interference in the cells of a nematode called Caenorhabditis elegans. These days microRNAs are used along with siRNA. These are formed by RNAs in the nucleus which were folded and processed and sent into the cytoplasm to go bind with DICER.
Note:
- The tobacco plant was made nematode-resistant by using the vector Agrobacterium tumefaciens.
- The enzyme DICER is a type III endoribonuclease.
- RNA interference is a quick method to silence translation and thus is used for many experiments these days like determining the function of a gene.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




