
How to make anhydride from carboxylic acid?
Answer
538.2k+ views
Hint: When a water molecule is removed from any acid molecule, the product that we get is known as an anhydride. In organic acid anhydride, there are two acyl groups (R-C=O) bonded to the same oxygen atom. Its generic structure is
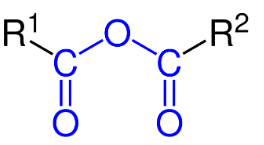
Complete step-by-step answer: The anhydride obtained from carboxylic acid is one of the most common types of organic acid anhydride. It is also known as carboxylic anhydride. The molecular formula of carboxylic anhydride is ${{(RC(O))}_{2}}O$.
Formation of acid anhydrides from carboxylic acid occurs when the carboxylic acid reacts with an acid chloride in the presence of a base.
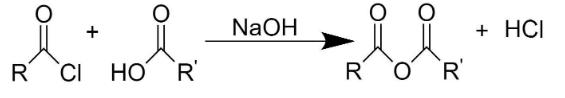
Mechanism of synthesis of carboxylic anhydride from acid chloride:
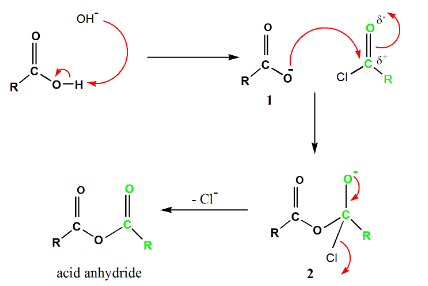
- In the carboxylic acid synthesis, addition-elimination mechanism is followed.
- Chloride anion $(C{{l}^{-}})$ acts as a leaving group.
- First, a proton is extracted by the base from carboxylic acid and forms carboxylate anion.
- The negatively charged oxygen of the carboxylate anion attacks the carbonyl carbon of acyl chloride, which is electrophilic in nature, and forms a tetrahedral intermediate.
- Lastly, the tetrahedral intermediate eliminates the chloride anion to form acid anhydride.
Hence by adding acid anhydride to a carboxylic acid, in the presence of a strong base, acid anhydride can be obtained.
Note: While naming the acid anhydrides, it is important to note that in an unsymmetrical acid anhydride, both of the carboxylic acids reacted must be named before adding the word anhydride. Whereas in symmetrical acid anhydride, simply renaming the word "acid" to "anhydride" of the parent carboxylic acid would suffice.

Complete step-by-step answer: The anhydride obtained from carboxylic acid is one of the most common types of organic acid anhydride. It is also known as carboxylic anhydride. The molecular formula of carboxylic anhydride is ${{(RC(O))}_{2}}O$.
Formation of acid anhydrides from carboxylic acid occurs when the carboxylic acid reacts with an acid chloride in the presence of a base.

Mechanism of synthesis of carboxylic anhydride from acid chloride:

- In the carboxylic acid synthesis, addition-elimination mechanism is followed.
- Chloride anion $(C{{l}^{-}})$ acts as a leaving group.
- First, a proton is extracted by the base from carboxylic acid and forms carboxylate anion.
- The negatively charged oxygen of the carboxylate anion attacks the carbonyl carbon of acyl chloride, which is electrophilic in nature, and forms a tetrahedral intermediate.
- Lastly, the tetrahedral intermediate eliminates the chloride anion to form acid anhydride.
Hence by adding acid anhydride to a carboxylic acid, in the presence of a strong base, acid anhydride can be obtained.
Note: While naming the acid anhydrides, it is important to note that in an unsymmetrical acid anhydride, both of the carboxylic acids reacted must be named before adding the word anhydride. Whereas in symmetrical acid anhydride, simply renaming the word "acid" to "anhydride" of the parent carboxylic acid would suffice.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE

In a human foetus the limbs and digits develop after class 12 biology CBSE

AABbCc genotype forms how many types of gametes a 4 class 12 biology CBSE

The correct structure of ethylenediaminetetraacetic class 12 chemistry CBSE




