
Maltose on treatment with dilute HCl gives:
(A) D-Galactose
(B) D-Glucose
(C) D-Glucose and D-Fructose
(D) D-Fructose
Answer
578.4k+ views
Hint: Reaction with dilute HCl is hydrolysis reaction so hydrolysis of maltose should be done. Hydrolysis is done in the presence of water or dilute acid.
Complete answer:
Reaction of Maltose to glucose is:
${C_{12}}{H_{22}}{O_{11}} + {H_2}O\xrightarrow{{maltose}}2{C_6}{H_{12}}{O_6}$
Maltose ${C_{12}}{H_{22}}{O_{11}}$ is a disaccharide. Disaccharides are carbohydrates which on hydrolysis give two same or different monosaccharides. They are made up of two molecules of monosaccharides linked to each other by condensation reaction. During condensation reaction one molecule of water is eliminated.
Monosaccharides units are linked to each other through oxygen atoms by a bond called glycosidic linkage.
One mole of maltose on hydrolysis gives two moles of $\alpha - D - $ glucose.
Maltose is composed of two $\alpha - D - $ glucose units which are condensed together through ${C_1}$ of one unit and ${C_4}$ of other units. Both glucose units are in pyranose form.
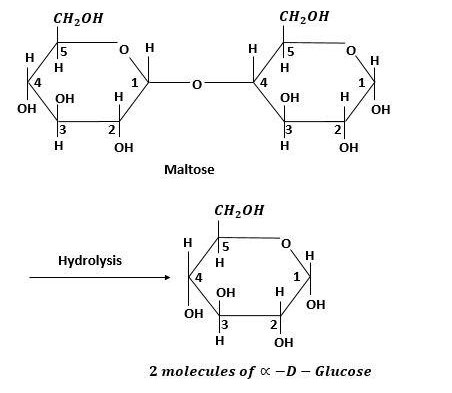
In hydrolysis it breaks at ${C_1}$ and ${C_4}$ positions and forms $\alpha - D - $ glucose.
Additional information: Condensation reaction: It is a reaction in which two molecules combine to form a larger molecule while leaving water or other smaller molecule as a byproduct.
Hydrolysis: It is the chemical breakdown of a compound due to reaction with water.
Monosaccharides: They are simple sugars which contain one oxygen and two hydrogen atoms for each carbon atom present in the compound.
Note: In organic chemistry, reaction with mineral acids like dilute ${H_2}S{O_4}$, dilute HCl is called hydrolysis reaction. Reaction with concentrated ${H_2}S{O_4}$ is called dehydration reaction. They do not form sulphates or chlorides.
Complete answer:
Reaction of Maltose to glucose is:
${C_{12}}{H_{22}}{O_{11}} + {H_2}O\xrightarrow{{maltose}}2{C_6}{H_{12}}{O_6}$
Maltose ${C_{12}}{H_{22}}{O_{11}}$ is a disaccharide. Disaccharides are carbohydrates which on hydrolysis give two same or different monosaccharides. They are made up of two molecules of monosaccharides linked to each other by condensation reaction. During condensation reaction one molecule of water is eliminated.
Monosaccharides units are linked to each other through oxygen atoms by a bond called glycosidic linkage.
One mole of maltose on hydrolysis gives two moles of $\alpha - D - $ glucose.
Maltose is composed of two $\alpha - D - $ glucose units which are condensed together through ${C_1}$ of one unit and ${C_4}$ of other units. Both glucose units are in pyranose form.

In hydrolysis it breaks at ${C_1}$ and ${C_4}$ positions and forms $\alpha - D - $ glucose.
Additional information: Condensation reaction: It is a reaction in which two molecules combine to form a larger molecule while leaving water or other smaller molecule as a byproduct.
Hydrolysis: It is the chemical breakdown of a compound due to reaction with water.
Monosaccharides: They are simple sugars which contain one oxygen and two hydrogen atoms for each carbon atom present in the compound.
Note: In organic chemistry, reaction with mineral acids like dilute ${H_2}S{O_4}$, dilute HCl is called hydrolysis reaction. Reaction with concentrated ${H_2}S{O_4}$ is called dehydration reaction. They do not form sulphates or chlorides.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

What is a transformer Explain the principle construction class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE




