
Mango is a monocot plant.
A. True
B. False
Answer
525.1k+ views
Hint: Dicot plants are the angiosperm with two cotyledons in their seeds that is a characteristic feature of dicot plants.
Complete answer:
Angiosperms or flowering plants are divided on the basis of the nature of the embryo in the seed into Monocotyledonous and Dicotyledonous plants. Dicots consist of plants having seeds with two cotyledons However, monocots involve the plants having seeds with only one cotyledon. Examples of the dicot plants are mango, neem, sunflower, apple, plums, etc.
Characteristic of the dicot plants –
- Dicot plants have an embryo with two cotyledons. The Embryo axis has two ends, one which forms the shoot tip known as plumule and the lower tip that forms the root tip called as radical.
- Cotyledons usually have a swollen appearance which acts as a food reserve for the developing plantlet.
- Dicot's plants have three furrows or pores in its pollen.
- Leaf veins in dicots generally have various auxiliary veins that reticulate between the major veins.
- Dicots have tap root systems with primary roots, which are thick for long extension and to penetrate deeply.
- During secondary growth, the diameter of the dicot stem increases and produces wood and bark.
So, the correct answer is ‘false’.
Note: In leaf veins, reticulate venation is the characteristic feature of the dicot plants however parallel venation is of monocots. But due to exception, some of the dicot plants also show parallel venation such as Calophyllum, Corymbium and some of the monocot’s plants show reticulate venation for example Alocasia, Smilax, etc.
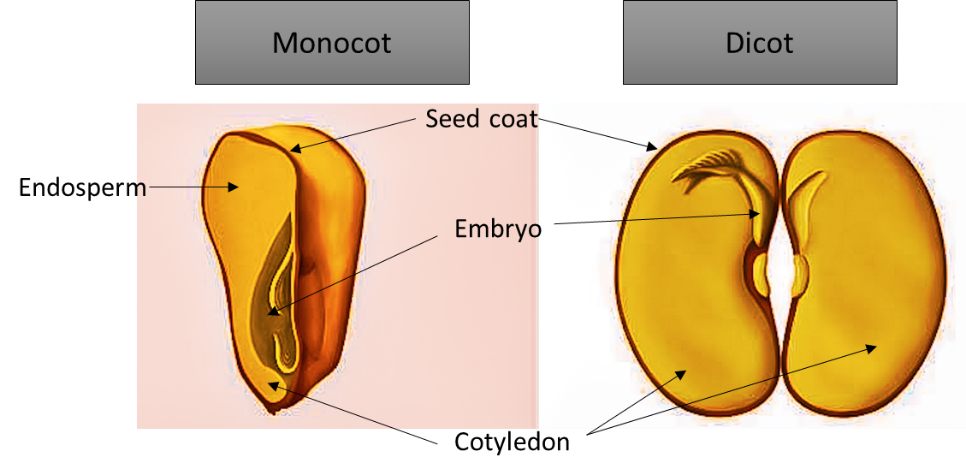
Figure: Difference between monocot and dicot seeds
Complete answer:
Angiosperms or flowering plants are divided on the basis of the nature of the embryo in the seed into Monocotyledonous and Dicotyledonous plants. Dicots consist of plants having seeds with two cotyledons However, monocots involve the plants having seeds with only one cotyledon. Examples of the dicot plants are mango, neem, sunflower, apple, plums, etc.
Characteristic of the dicot plants –
- Dicot plants have an embryo with two cotyledons. The Embryo axis has two ends, one which forms the shoot tip known as plumule and the lower tip that forms the root tip called as radical.
- Cotyledons usually have a swollen appearance which acts as a food reserve for the developing plantlet.
- Dicot's plants have three furrows or pores in its pollen.
- Leaf veins in dicots generally have various auxiliary veins that reticulate between the major veins.
- Dicots have tap root systems with primary roots, which are thick for long extension and to penetrate deeply.
- During secondary growth, the diameter of the dicot stem increases and produces wood and bark.
So, the correct answer is ‘false’.
Note: In leaf veins, reticulate venation is the characteristic feature of the dicot plants however parallel venation is of monocots. But due to exception, some of the dicot plants also show parallel venation such as Calophyllum, Corymbium and some of the monocot’s plants show reticulate venation for example Alocasia, Smilax, etc.

Figure: Difference between monocot and dicot seeds
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




