
Map Question on the given outline map of India Mark and Label the following
1.Arid Soil
2.Laterite Soil
3.Mountain Soil/Forest Soil
4.Alluvial soil
5.Black soil
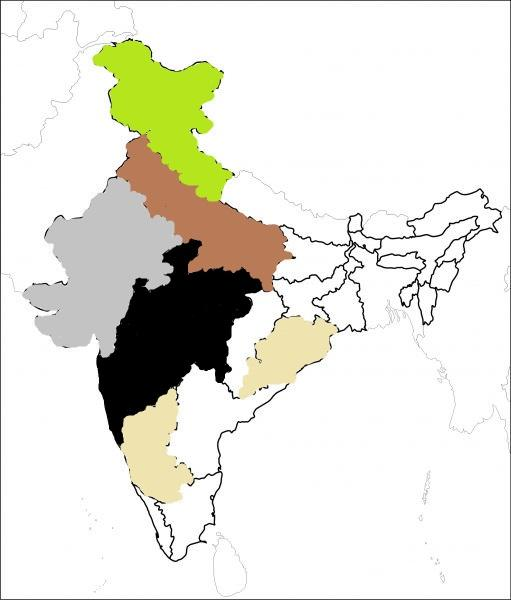
Arid Soil Laterite Soil Mountain Soil Alluvial Soil Black Soil

| Arid Soil | |
| Laterite Soil | |
| Mountain Soil | |
| Alluvial Soil | |
| Black Soil |
Answer
560.4k+ views
Hint:Soil is that layer of weathered rock fragments and the decaying matters of plant and animal products which gives conditions for giving life to plants. India has eight different kinds of soils found in different climatic and physiographic locations.
Complete answer:
1. Arid Soil: Arid or desert soils are sandy and gravelly soils having low organic matter. These soils are developed under the arid and semi-arid conditions and are deposited mainly by wind action. Arid soils are mostly found in states such as Rajasthan and Gujarat.
2.Laterite Soil: Laterite soils are those soils that are an end product of weathering due to heavy rainfall. The Laterite soils are distributed across states like Orissa and Karnataka.
Mountain Soil: Mountain soils are those heterogeneous soils found in the valley and hilly slopes of the Himalayas.
3.Alluvial Soils: Alluvial soils are those soils which deposit from the rivers and are considered to be the most fertile among the soils. Most of the Indo-Gangetic plains such as Haryana, Uttar Pradesh and Punjab have covers of alluvial soil.
4.Black Soil: Black soil as its name and colour suggests, derives from its parent material which is the volcanic rocks that were formed in the Deccan Plateau and distributed in states like Maharashtra and Madhya Pradesh.
Note: As a natural resource, soil has and continues to be of immense value to humans. The nature and fertility of the soil determines the agricultural productivity which ultimately depends on the productivity of the soil and the level of development for the cultivating communities.
Complete answer:
1. Arid Soil: Arid or desert soils are sandy and gravelly soils having low organic matter. These soils are developed under the arid and semi-arid conditions and are deposited mainly by wind action. Arid soils are mostly found in states such as Rajasthan and Gujarat.
2.Laterite Soil: Laterite soils are those soils that are an end product of weathering due to heavy rainfall. The Laterite soils are distributed across states like Orissa and Karnataka.
Mountain Soil: Mountain soils are those heterogeneous soils found in the valley and hilly slopes of the Himalayas.
3.Alluvial Soils: Alluvial soils are those soils which deposit from the rivers and are considered to be the most fertile among the soils. Most of the Indo-Gangetic plains such as Haryana, Uttar Pradesh and Punjab have covers of alluvial soil.
4.Black Soil: Black soil as its name and colour suggests, derives from its parent material which is the volcanic rocks that were formed in the Deccan Plateau and distributed in states like Maharashtra and Madhya Pradesh.
Note: As a natural resource, soil has and continues to be of immense value to humans. The nature and fertility of the soil determines the agricultural productivity which ultimately depends on the productivity of the soil and the level of development for the cultivating communities.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 10 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 General Knowledge: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
What is the median of the first 10 natural numbers class 10 maths CBSE

Which women's tennis player has 24 Grand Slam singles titles?

Who is the Brand Ambassador of Incredible India?

Why is there a time difference of about 5 hours between class 10 social science CBSE

Write a letter to the principal requesting him to grant class 10 english CBSE

A moving boat is observed from the top of a 150 m high class 10 maths CBSE




