
Difference between mass and weight?
Answer
530.5k+ views
Hint: The quantity of matter in the body is termed as mass but the implied force by Earth into the center of the rigid body is called weight.
Complete step by step answer:
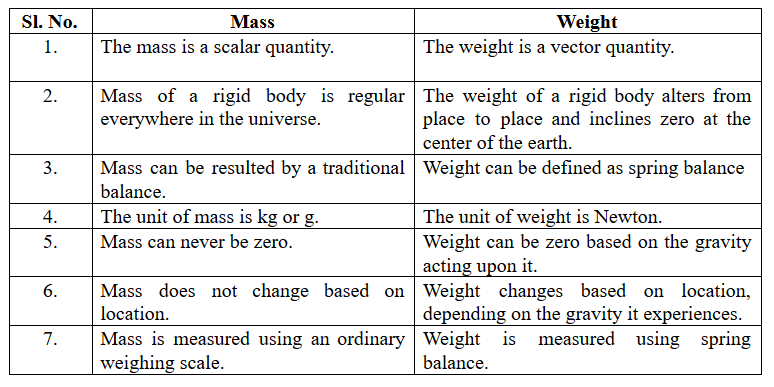
The difference between mass and weight of the rigid body is given as below –
Additional information:
The mass of an object is an elemental feature of the object. It is an analytical quota of its inertia. It is a principle part of the bulk of matter in the object. All mechanical capacities can be explained in terms of mass, length and time. The symbol of mass is m and the SI unit of mass is kilogram (kg).
At the normal speed which is impending the speed of light, the mass of the rigid body is normally premeditated to the unchanging property of an object is called the expansion of relativistic mass.
The weight of an object is explained as the force of gravity on the object and may be calculated as the mass times the acceleration of gravity. The standard unit of weight is newton (N). According to second law of newton, weight is expressed as –
$W=mg$ ……………………………………… (1)
Where W = Weight of the object.
m = Mass of the object.
g = Acceleration of gravity.
Note: Always remember that the main difference between the mass and weight of rigid bodies is implied force through the earth surface. The term weight and mass are used interchangeably in daily life, but their meanings are different. Don’t get confused with the daily life terms. For example, a person of mass 50 kg may weigh differently based on location.
Complete step by step answer:
The difference between mass and weight of the rigid body is given as below –

Additional information:
The mass of an object is an elemental feature of the object. It is an analytical quota of its inertia. It is a principle part of the bulk of matter in the object. All mechanical capacities can be explained in terms of mass, length and time. The symbol of mass is m and the SI unit of mass is kilogram (kg).
At the normal speed which is impending the speed of light, the mass of the rigid body is normally premeditated to the unchanging property of an object is called the expansion of relativistic mass.
The weight of an object is explained as the force of gravity on the object and may be calculated as the mass times the acceleration of gravity. The standard unit of weight is newton (N). According to second law of newton, weight is expressed as –
$W=mg$ ……………………………………… (1)
Where W = Weight of the object.
m = Mass of the object.
g = Acceleration of gravity.
Note: Always remember that the main difference between the mass and weight of rigid bodies is implied force through the earth surface. The term weight and mass are used interchangeably in daily life, but their meanings are different. Don’t get confused with the daily life terms. For example, a person of mass 50 kg may weigh differently based on location.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 10 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 General Knowledge: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
What is the median of the first 10 natural numbers class 10 maths CBSE

Which women's tennis player has 24 Grand Slam singles titles?

Who is the Brand Ambassador of Incredible India?

Why is there a time difference of about 5 hours between class 10 social science CBSE

Write a letter to the principal requesting him to grant class 10 english CBSE

A moving boat is observed from the top of a 150 m high class 10 maths CBSE




