
What do you mean by the chain reaction in nuclear fission?
Answer
502.8k+ views
Hint: Nuclear fission is a reaction in which radioactive atoms are split into pieces that cause subsequent reactions with the help of neutrons. These kinds of reactions take place in nuclear power plants to generate electricity.
Complete answer:
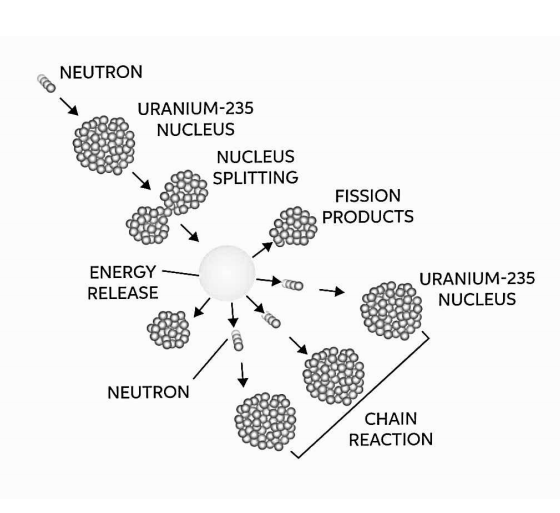
A nuclear fission chain reaction is a self-propagating series of fission processes in which neutrons generated during fission cause at least one subsequent nucleus to fission. Only in the right multiplying environment and under the right conditions can the chain reaction happen.
Additional Information:-
Only in the right multiplying environment and under the right conditions can the chain reaction happen. It goes without saying that if one neutron triggers two more fissions, the quantity of neutrons in the multiplication system will grow over time, as will the reactor power (reaction rate). In order to stabilise such a multiplication environment, the system's non-fission neutron absorption must be increased (e.g. to insert control rods). Furthermore, this multiplication environment (the nuclear reactor) operates like an exponential system, which means that the power gain is exponential rather than linear.
On the other hand, if one neutron produces less than one further fission, the number of neutrons in the multiplication system, as well as the reactor's power, diminishes with time (reaction rate). The system's non-fission neutron absorption must be minimised in order to keep the chain reaction running (e.g. to withdraw control rods).
Note:
The fission process can yield two, three, or more free neutrons, which can then cause further fissions, and so on. The fission chain reaction is a sequence of fission events that is important in nuclear reactor physics.
Complete answer:
A nuclear fission chain reaction is a self-propagating series of fission processes in which neutrons generated during fission cause at least one subsequent nucleus to fission. Only in the right multiplying environment and under the right conditions can the chain reaction happen.

Additional Information:-
Only in the right multiplying environment and under the right conditions can the chain reaction happen. It goes without saying that if one neutron triggers two more fissions, the quantity of neutrons in the multiplication system will grow over time, as will the reactor power (reaction rate). In order to stabilise such a multiplication environment, the system's non-fission neutron absorption must be increased (e.g. to insert control rods). Furthermore, this multiplication environment (the nuclear reactor) operates like an exponential system, which means that the power gain is exponential rather than linear.
On the other hand, if one neutron produces less than one further fission, the number of neutrons in the multiplication system, as well as the reactor's power, diminishes with time (reaction rate). The system's non-fission neutron absorption must be minimised in order to keep the chain reaction running (e.g. to withdraw control rods).
Note:
The fission process can yield two, three, or more free neutrons, which can then cause further fissions, and so on. The fission chain reaction is a sequence of fission events that is important in nuclear reactor physics.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE

In a human foetus the limbs and digits develop after class 12 biology CBSE

AABbCc genotype forms how many types of gametes a 4 class 12 biology CBSE

The correct structure of ethylenediaminetetraacetic class 12 chemistry CBSE




