
What is meant by a distance of distinct vision from a normal human eye? Give its value in cm.
Answer
585.3k+ views
Hint: Human eye has a special type of lens which is convex in nature. This is called eye lens. The special feature of this lens is that it can adjust its focal length as per the location of the object. Irrespective of some defect, a normal human eye has a limit of distance between which one can see a particular object. We’ll now understand about this limit.
Complete step by step answer:
Our eye lens works in such a way that it focuses on the object so that maximum intensity of light reflected from that object falls on our eye. After focusing onto an object, it creates an image on the retina of our eye after which the brain translates the image.
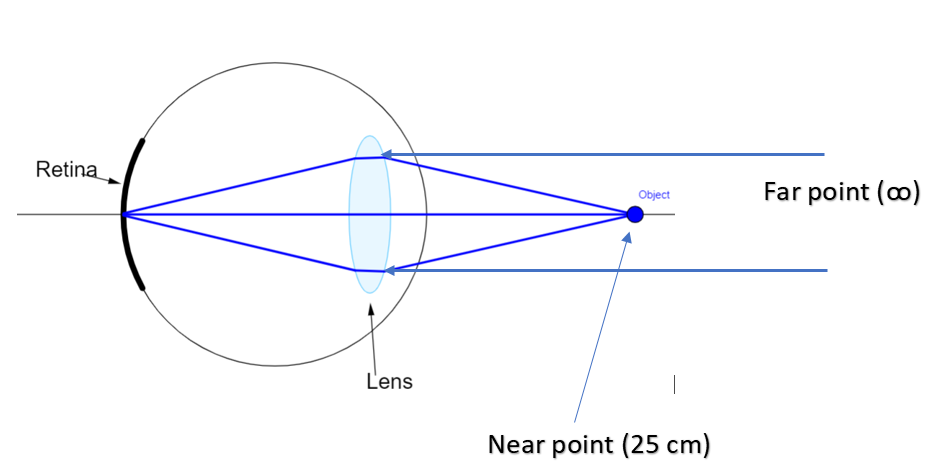
But this lens has to get contracted to focus on nearby objects. This contraction has a limit called limit of human vision or near point of human eye. It may be defined as a point before which if an object is placed, the eye can’t see anything. For a normal human eye, its value is 25 cm.
Also, a normal human eye can see up to any distance. Thus the far point of the normal human eye is infinity.
By the term infinite, what could be understood? Well it’s something very far or very large. But what about the length of Titanic in comparison to the needle? It’s also very large. In optics, usually the object is considered to be at infinity if the distance of the object from the lens is much greater than the size of lens or we can say if the rays coming towards the lens are almost parallel, we can say that the object is at infinity.
As we can see the sun, moon and the stars, it means that the far point (or the maximum human limit) of the human eye is infinity.
Note:
One might get confused that if the human eye can see up to any distance possible, then why aren't we able to see Pluto or distant planets or galaxies? This is because we’re able to see only that object from which light comes directly or indirectly in our eye. The light coming from these planets is so less intense that we need special apparatus to see them.
Complete step by step answer:
Our eye lens works in such a way that it focuses on the object so that maximum intensity of light reflected from that object falls on our eye. After focusing onto an object, it creates an image on the retina of our eye after which the brain translates the image.
But this lens has to get contracted to focus on nearby objects. This contraction has a limit called limit of human vision or near point of human eye. It may be defined as a point before which if an object is placed, the eye can’t see anything. For a normal human eye, its value is 25 cm.
Also, a normal human eye can see up to any distance. Thus the far point of the normal human eye is infinity.
By the term infinite, what could be understood? Well it’s something very far or very large. But what about the length of Titanic in comparison to the needle? It’s also very large. In optics, usually the object is considered to be at infinity if the distance of the object from the lens is much greater than the size of lens or we can say if the rays coming towards the lens are almost parallel, we can say that the object is at infinity.
As we can see the sun, moon and the stars, it means that the far point (or the maximum human limit) of the human eye is infinity.

Note:
One might get confused that if the human eye can see up to any distance possible, then why aren't we able to see Pluto or distant planets or galaxies? This is because we’re able to see only that object from which light comes directly or indirectly in our eye. The light coming from these planets is so less intense that we need special apparatus to see them.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

What is a transformer Explain the principle construction class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE




