
What is meant by ‘Dispersion of light’?
Answer
549.9k+ views
Hint: White light consists of waves of different wavelengths. The angle of refraction of a light wave depends on the wavelength of the waves. When light passes through a prism, the different wavelengths refract at different angles such that light appears to be splitting into its colours.
Complete answer:
Dispersion of light is the phenomenon of splitting of white light into its constituent colours. Sun emits electromagnetic waves, which have a wide range of wavelengths. The arrangement of the waves in the order of their wavelengths is called electromagnetic spectrum. The waves with wavelengths, which fall in the visible region of the spectrum is light.
Hence, light consists of electromagnetic waves of different wavelengths. Each wavelength imparts a specific colour. The spectrum of the visible light is called VIBGYOR. As shown in the figure below:
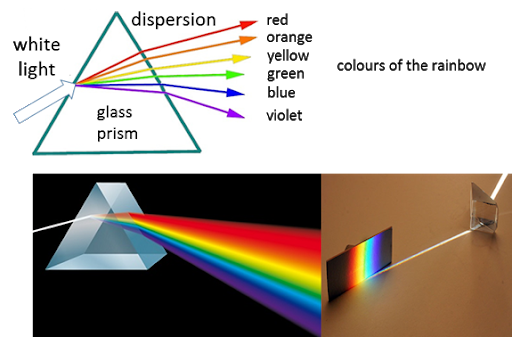
Which means the light mainly consists of seven colours and that are violet, indigo, blue, green, yellow, orange and red. Light of each colour has a different wavelength. We know that when light passes through from medium to a different medium, it refracts at the interface of the two mediums. That deviates from the direction of the incident or we say that the light appears to bend. The extent of bending of light depends on the wavelength of the light. Light of different wavelengths refract by different angles. Therefore, When white light from air is passed through the prism, the light refracts. Since light consists of different wavelengths, the waves of different colors refract at different angles. Thus, the light appears to be splitting into its constituent colours when it comes out of the prism.
Note: When we talk about the refractive index of a medium, it is not the same for all the wavelengths of light. This is because the refractive index depends on the wavelength of light. Considered a glass. We know that the refractive index of glass is 1.5. However, this value of the refractive index of the glass is an average value.
Complete answer:
Dispersion of light is the phenomenon of splitting of white light into its constituent colours. Sun emits electromagnetic waves, which have a wide range of wavelengths. The arrangement of the waves in the order of their wavelengths is called electromagnetic spectrum. The waves with wavelengths, which fall in the visible region of the spectrum is light.
Hence, light consists of electromagnetic waves of different wavelengths. Each wavelength imparts a specific colour. The spectrum of the visible light is called VIBGYOR. As shown in the figure below:

Which means the light mainly consists of seven colours and that are violet, indigo, blue, green, yellow, orange and red. Light of each colour has a different wavelength. We know that when light passes through from medium to a different medium, it refracts at the interface of the two mediums. That deviates from the direction of the incident or we say that the light appears to bend. The extent of bending of light depends on the wavelength of the light. Light of different wavelengths refract by different angles. Therefore, When white light from air is passed through the prism, the light refracts. Since light consists of different wavelengths, the waves of different colors refract at different angles. Thus, the light appears to be splitting into its constituent colours when it comes out of the prism.
Note: When we talk about the refractive index of a medium, it is not the same for all the wavelengths of light. This is because the refractive index depends on the wavelength of light. Considered a glass. We know that the refractive index of glass is 1.5. However, this value of the refractive index of the glass is an average value.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




