
What is meant by ketal? Give an example of reaction (with mechanism) showing its formation.
Answer
563.4k+ views
Hint: Ketals are a group of organic compounds. Ketal is a functional group that is derived from a ketone. Ketal is also referred to as an acetal derivative of ketone. Ketal is prepared by the reaction of ketone with alcohols under anhydrous condition in presence of acid catalyst.
Complete solution:
We know that ketals are a group of organic compounds. As the name suggests ketal is a combination of ketone and acetal. Ketal is a functional group that is derived from a ketone. Ketal is also referred to as an acetal derivative of ketone.
Ketal is a functional group which is derived from ketone by replacing the carbonyl group with two alkoxy groups.
Ketal is prepared by the reaction of ketone with alcohols like methyl alcohol or ethyl alcohol under anhydrous condition. Ketone reacts with alcohol in presence of acid catalyst.
The reaction of ketone with alcohol is as follows:
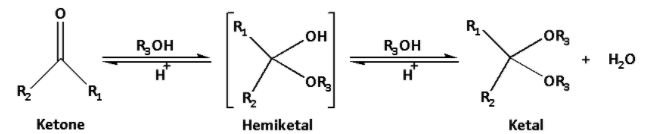
The mechanism of ketal formation involves two steps.
In the first step, the carbonyl group of ketone gets protonated in the presence of acid and thus, it becomes more electrophilic. The first alcohol molecule acts as a nucleophile and attacks the protonated carbonyl group. This leads to the formation of an oxonium ion. The oxonium ion is then deprotonated by the acid and hemiketal is produced.
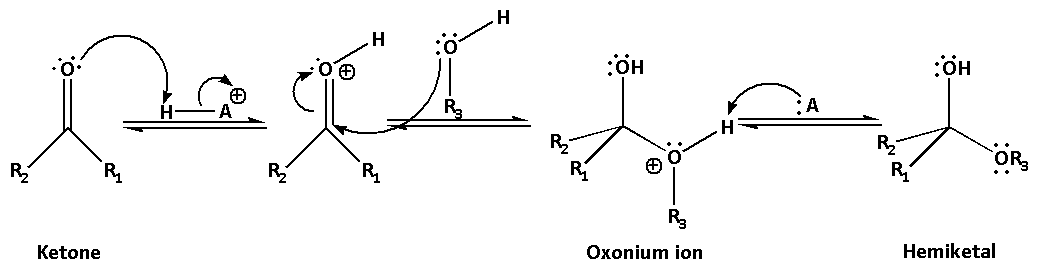
In the second step, the hemiketal gets protonated in the presence of acid and results in formation of water as a leaving group. When the water molecule leaves, the carbon-oxygen bond is regenerated and thus, attack of nucleophile becomes easier. The second molecule of alcohol then gets added to the hemiketal and leads to the formation of oxonium ion. The oxonium ion is then deprotonated to produce a ketal.
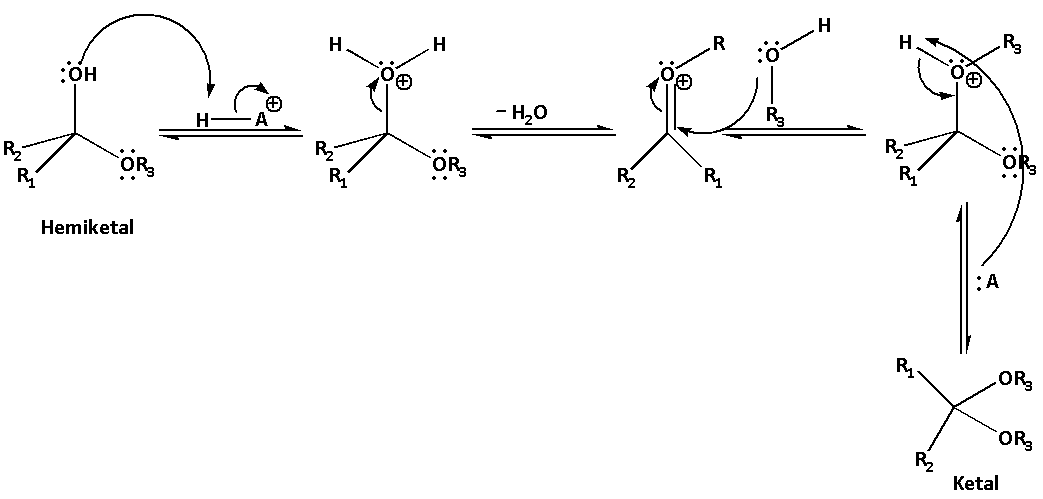 Thus, the reaction proceeds through formation of a hemiketal intermediate.
Thus, the reaction proceeds through formation of a hemiketal intermediate.
Note: Some ketals are cyclic in nature and are known as cyclic ketals. Cyclic acetals are produced by the reaction of ketones with diols in presence of acid catalyst. Cyclic acetals are more stable than ketals. This is because of the presence of chelate effect derived from hydroxyl groups of ketal that are connected to each other in diol.
Complete solution:
We know that ketals are a group of organic compounds. As the name suggests ketal is a combination of ketone and acetal. Ketal is a functional group that is derived from a ketone. Ketal is also referred to as an acetal derivative of ketone.
Ketal is a functional group which is derived from ketone by replacing the carbonyl group with two alkoxy groups.
Ketal is prepared by the reaction of ketone with alcohols like methyl alcohol or ethyl alcohol under anhydrous condition. Ketone reacts with alcohol in presence of acid catalyst.
The reaction of ketone with alcohol is as follows:

The mechanism of ketal formation involves two steps.
In the first step, the carbonyl group of ketone gets protonated in the presence of acid and thus, it becomes more electrophilic. The first alcohol molecule acts as a nucleophile and attacks the protonated carbonyl group. This leads to the formation of an oxonium ion. The oxonium ion is then deprotonated by the acid and hemiketal is produced.

In the second step, the hemiketal gets protonated in the presence of acid and results in formation of water as a leaving group. When the water molecule leaves, the carbon-oxygen bond is regenerated and thus, attack of nucleophile becomes easier. The second molecule of alcohol then gets added to the hemiketal and leads to the formation of oxonium ion. The oxonium ion is then deprotonated to produce a ketal.

Note: Some ketals are cyclic in nature and are known as cyclic ketals. Cyclic acetals are produced by the reaction of ketones with diols in presence of acid catalyst. Cyclic acetals are more stable than ketals. This is because of the presence of chelate effect derived from hydroxyl groups of ketal that are connected to each other in diol.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

What is a transformer Explain the principle construction class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE




