
What is meant by latent heat? How will the state of matter transform if latent heat is given off?
Answer
553.2k+ views
Hint: Latent heat is the heat that is required to convert a solid into a liquid or liquid into gas. It is the heat energy released or absorbed during the phase change of the substance without a change in temperature of the substance i.e. temperature remains constant.
Complete answer:
Latent heat is defined as the heat needed to change the state of matter of a substance. It is the heat supplied from the surroundings to the substance to convert a solid into a liquid or to a vapor (gas) or a liquid into a gas. It is the heat given off to the surroundings from the substance to convert a liquid into a solid or to liquefy a gas into a liquid state. The figure below shows the temperature versus heat supplied graph.
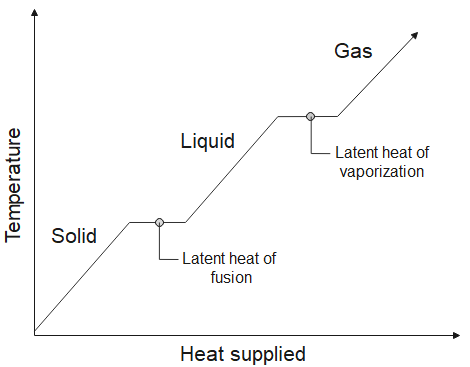
There are two types latent heat,
1. Latent heat of Fusion – It is the heat absorbed when solid melts into liquid (For example, ice melts into water, heat is absorbed) or the heat released when liquid turns into solid (For example, water freezes into ice, heat is released). The temperature of the substance is constant during the entire process.
2. Latent heat of vaporization– It is the heat absorbed when liquid turns into gas (For example, water vaporizes into water vapor, heat is absorbed) or the heat released when gas turns into liquid (For example, water vapor condenses into water, heat is released). The temperature of the substance is constant during the entire process.
Latent heat L is given by,
$L=\dfrac{Q}{m}$
Where, Q is the heat energy released or absorbed during the phase change of the substance and m is the mass of the substance.
If latent heat is given off, the substance in liquid state will be converted into solid state and the substance in gas or vapor state will be converted into liquid state. Here, the heat released is given off from the internal energy of the substance to its surroundings, therefore the internal energy decreases.
Note:
Latent heat is heat energy released or absorbed per unit mass of the substance, its unit is Joules or calories i.e. amount of heat per unit mass of the substance that is undergoing the phase change with temperature of substance remaining constant during the process.
Complete answer:
Latent heat is defined as the heat needed to change the state of matter of a substance. It is the heat supplied from the surroundings to the substance to convert a solid into a liquid or to a vapor (gas) or a liquid into a gas. It is the heat given off to the surroundings from the substance to convert a liquid into a solid or to liquefy a gas into a liquid state. The figure below shows the temperature versus heat supplied graph.

There are two types latent heat,
1. Latent heat of Fusion – It is the heat absorbed when solid melts into liquid (For example, ice melts into water, heat is absorbed) or the heat released when liquid turns into solid (For example, water freezes into ice, heat is released). The temperature of the substance is constant during the entire process.
2. Latent heat of vaporization– It is the heat absorbed when liquid turns into gas (For example, water vaporizes into water vapor, heat is absorbed) or the heat released when gas turns into liquid (For example, water vapor condenses into water, heat is released). The temperature of the substance is constant during the entire process.
Latent heat L is given by,
$L=\dfrac{Q}{m}$
Where, Q is the heat energy released or absorbed during the phase change of the substance and m is the mass of the substance.
If latent heat is given off, the substance in liquid state will be converted into solid state and the substance in gas or vapor state will be converted into liquid state. Here, the heat released is given off from the internal energy of the substance to its surroundings, therefore the internal energy decreases.
Note:
Latent heat is heat energy released or absorbed per unit mass of the substance, its unit is Joules or calories i.e. amount of heat per unit mass of the substance that is undergoing the phase change with temperature of substance remaining constant during the process.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

10 examples of friction in our daily life




