
What is meant by the 'angle of incidence ' and the 'angle of refraction ' for a ray of light? Draw a labelled ray diagram to show the angle of incidence and the angle of refraction for a refracted ray of light.
Answer
516.9k+ views
Hint: If a ray of light moves from a denser medium to a rarer medium, the light ray will bend apart from the normal. If a ray of light moves from a rarer medium to a thicker medium, the light ray will turn towards the normal; the angle of refraction is smaller than the angle of incidence.
Complete step-by-step solution:
Refraction is the turning of a wave when it crosses from one medium to another. When the light goes from air into glass, the light slows down and adjusts direction slightly. When light crosses from a less dense material to a denser material, the refracted light twists towards the perpendicular line. If the light wave nears the boundary perpendicularly, the light ray does not refract despite the change in speed.
A light ray refracts whenever it moves at an angle into a means of the various refractive index—this change in speed results in a change in direction. As an example, consider air going into the water. The speed of light reduces as it remains to travel at various angles.
When light moves from denser to rarer, its speed increments. However, when light moves from rarer to denser, its speed decrements.
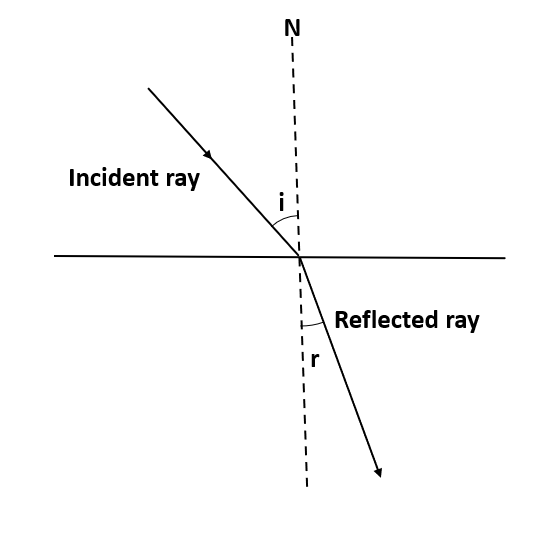
The angle among the incident ray and perpendicular line at the incidence point is called the angle of incidence (i).
The angle between the refracted ray and perpendicular line at the point of refraction is called the angle of refraction (r).
Note:Refraction is described as turning the wave when it joins a medium where its speed is changed. Refraction of light is one such process. According to refraction laws, the incident ray, the refracted ray, and the perpendicular line are all in a similar plane. The ratio between the sine of the incidence angle and the sine of the refraction angle is equal to a constant. Flickering of stars at night and the creation of mirages are the results of refraction, while the configuration of a rainbow is an example of refraction of light.
Complete step-by-step solution:
Refraction is the turning of a wave when it crosses from one medium to another. When the light goes from air into glass, the light slows down and adjusts direction slightly. When light crosses from a less dense material to a denser material, the refracted light twists towards the perpendicular line. If the light wave nears the boundary perpendicularly, the light ray does not refract despite the change in speed.
A light ray refracts whenever it moves at an angle into a means of the various refractive index—this change in speed results in a change in direction. As an example, consider air going into the water. The speed of light reduces as it remains to travel at various angles.
When light moves from denser to rarer, its speed increments. However, when light moves from rarer to denser, its speed decrements.
The angle among the incident ray and perpendicular line at the incidence point is called the angle of incidence (i).
The angle between the refracted ray and perpendicular line at the point of refraction is called the angle of refraction (r).

Note:Refraction is described as turning the wave when it joins a medium where its speed is changed. Refraction of light is one such process. According to refraction laws, the incident ray, the refracted ray, and the perpendicular line are all in a similar plane. The ratio between the sine of the incidence angle and the sine of the refraction angle is equal to a constant. Flickering of stars at night and the creation of mirages are the results of refraction, while the configuration of a rainbow is an example of refraction of light.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




