
What is meant by the following term? Give an example of the reaction.
2,4-DNP derivative
Answer
493.2k+ views
Hint: 2,4-DNP is the abbreviated name of 2,4- dinitrophenyl hydrazine. 2,4-DNP is also known as Brady’s reagent. A derivative is a substance that is formed when the main reagent (as in this case it is 2,4-DNP) reacts with some chemical compound. To attain a derivative a molecule has to be eliminated that eventually forms the product. The reaction must be an Elimination reaction.
Complete answer:
We’ve seen the definition of a derivative. Let’s understand the formation of the 2,4-DNP derivative.
The 2,4-DNP derivative is formed when 2,4-Dinitrophenyl hydrazine reacts with a carbonyl compound namely an aldehyde or a ketone in a weakly acidic medium. It leads to the formation of a 2,4-dinitrophenyl hydrazone.
In simple words, we can say that it is substituted hydrazine.
The reaction for the formation of the 2,4-DNP derivative is as follows:
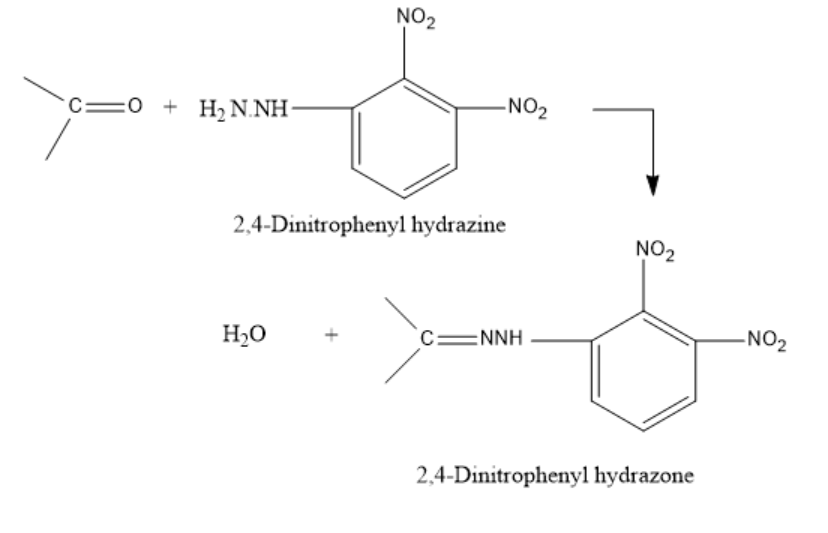
The groups attached to the carbonyl carbon can be both alkyl groups (ketones) or one alkyl and one hydrogen (aldehydes).
2,4-DNP is used as a test to find aldehydes or ketones. It forms bright orange colour crystals called 2,4-dinitrophenyl hydrazone on reaction with carbonyl compounds. If 2,4-dinitrophenyl hydrazine is formed as a precipitate, we can say that there is a presence of a carbonyl compound. The crystals are filtered and purified by recrystallization.
2,4-DNP derivatives have different melting points. They are compared to the melting points of 2,4 DNP to identify the presence of carbonyl compounds.
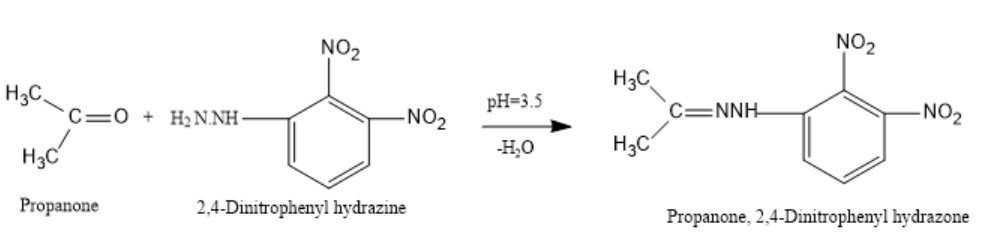
Let us now see a reaction for the formation of 2,4-DNP derivative:
If Propanone reacts with 2,4-dinitrophenylhydrazine in a weakly acidic medium of pH-3.5 then, Propanone,2,4-dinitrophenylhydrazone will be prepared.
Note:
2,4-Dinitrophenyl hydrazine derivative distinguishes between aldehyde and ketone by the presence of a hydrogen bond in aldehyde. Ketones do not contain a hydrogen bond. The hydrogen bond present oxidizes the aldehydes, as they are fast reducing agents.
Complete answer:
We’ve seen the definition of a derivative. Let’s understand the formation of the 2,4-DNP derivative.
The 2,4-DNP derivative is formed when 2,4-Dinitrophenyl hydrazine reacts with a carbonyl compound namely an aldehyde or a ketone in a weakly acidic medium. It leads to the formation of a 2,4-dinitrophenyl hydrazone.
In simple words, we can say that it is substituted hydrazine.
The reaction for the formation of the 2,4-DNP derivative is as follows:

The groups attached to the carbonyl carbon can be both alkyl groups (ketones) or one alkyl and one hydrogen (aldehydes).
2,4-DNP is used as a test to find aldehydes or ketones. It forms bright orange colour crystals called 2,4-dinitrophenyl hydrazone on reaction with carbonyl compounds. If 2,4-dinitrophenyl hydrazine is formed as a precipitate, we can say that there is a presence of a carbonyl compound. The crystals are filtered and purified by recrystallization.
2,4-DNP derivatives have different melting points. They are compared to the melting points of 2,4 DNP to identify the presence of carbonyl compounds.
Let us now see a reaction for the formation of 2,4-DNP derivative:
If Propanone reacts with 2,4-dinitrophenylhydrazine in a weakly acidic medium of pH-3.5 then, Propanone,2,4-dinitrophenylhydrazone will be prepared.

Note:
2,4-Dinitrophenyl hydrazine derivative distinguishes between aldehyde and ketone by the presence of a hydrogen bond in aldehyde. Ketones do not contain a hydrogen bond. The hydrogen bond present oxidizes the aldehydes, as they are fast reducing agents.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




