
What is menstruation? Why does it occur?
Answer
571.8k+ views
Hint: Menstruation Is also known as the periods.It is a regular secretion of blood and tissues into the vagina from the inner lining of the uterus.
Complete Answer:
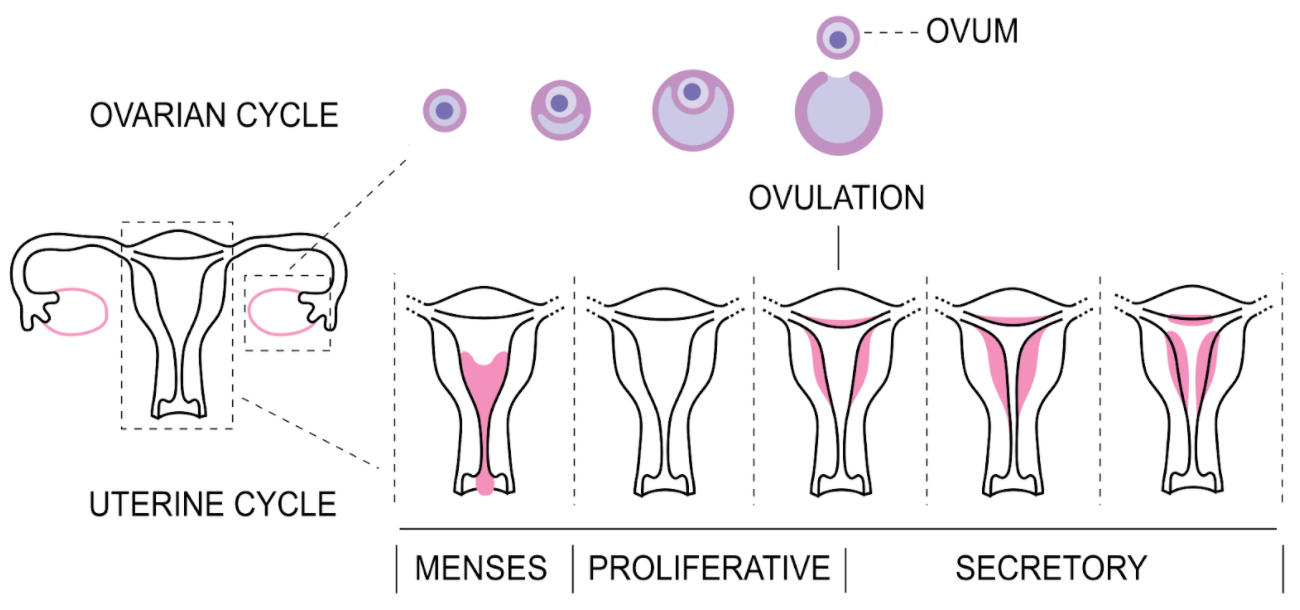
- The first period usually begins at the age of puberty that is from 12 to 15 years of age . The first period in the females is known as minarc. The length of time is normally 28 days from the first day of the cycle and the first day of the next period.
- Owing to changes in hormones in the body, a phase occurs. Chemical messengers are hormones. The female hormones oestrogen and progesterone are released by the ovaries. These hormones cause the uterine lining (or the womb) to build up.
- For a fertilised egg to adhere to and begin to grow, the built-up lining is ready. If no fertilised egg is present, the lining breaks down and bleeds. Then the same phase occurs all over again. This process is called menstruation.
- Usually it takes about a month to make up the padding, then break it down. That is why most women and girls have their cycles only once a month.
- Ovulation is the release of the ovaries from an egg. The same hormones that cause the lining of the uterus to build up also cause one of the ovaries to leave an egg. The egg passes to the uterus through a thin tube called a fallopian tube.
- When a sperm cell fertilises the egg, it sticks itself to the wall of the uterus, where it grows into a baby over time. If the egg is not fertilised, the lining of the uterus breaks down, causing a period of bleeding.
A menstrual cycle is divided into four phases:
1. Menstrual phase
2. Follicular phase
3. Ovulation phase
4. Luteal phase
The menstrual cycle is regulated by the complex interaction of hormones that is luteinizing hormone, follicle stimulating hormone and the female sex hormones estrogen and progesterone.
Note: PMS (premenstrual syndrome) is when a girl has symptoms that occur before or after her time that are emotional and physical. Moodiness, depression, anxiety, bloating, and acne may contain such symptoms. Following the first few days of a cycle, the symptoms go away.
Complete Answer:
- The first period usually begins at the age of puberty that is from 12 to 15 years of age . The first period in the females is known as minarc. The length of time is normally 28 days from the first day of the cycle and the first day of the next period.
- Owing to changes in hormones in the body, a phase occurs. Chemical messengers are hormones. The female hormones oestrogen and progesterone are released by the ovaries. These hormones cause the uterine lining (or the womb) to build up.
- For a fertilised egg to adhere to and begin to grow, the built-up lining is ready. If no fertilised egg is present, the lining breaks down and bleeds. Then the same phase occurs all over again. This process is called menstruation.
- Usually it takes about a month to make up the padding, then break it down. That is why most women and girls have their cycles only once a month.
- Ovulation is the release of the ovaries from an egg. The same hormones that cause the lining of the uterus to build up also cause one of the ovaries to leave an egg. The egg passes to the uterus through a thin tube called a fallopian tube.
- When a sperm cell fertilises the egg, it sticks itself to the wall of the uterus, where it grows into a baby over time. If the egg is not fertilised, the lining of the uterus breaks down, causing a period of bleeding.
A menstrual cycle is divided into four phases:
1. Menstrual phase
2. Follicular phase
3. Ovulation phase
4. Luteal phase
The menstrual cycle is regulated by the complex interaction of hormones that is luteinizing hormone, follicle stimulating hormone and the female sex hormones estrogen and progesterone.

Note: PMS (premenstrual syndrome) is when a girl has symptoms that occur before or after her time that are emotional and physical. Moodiness, depression, anxiety, bloating, and acne may contain such symptoms. Following the first few days of a cycle, the symptoms go away.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE

Give 10 examples of unisexual and bisexual flowers




