
Mention the function of trophoblast in the human embryo.
Answer
574.8k+ views
Hint: An embryo is the early development stage of an animal when it is in the egg or within the uterus of the mother. During conception, it is the unborn child which is at the end of the 7th week. It is created by the first mitotic division when the fertilization of a human whose side is with the human sperm is completed.
Complete answer:
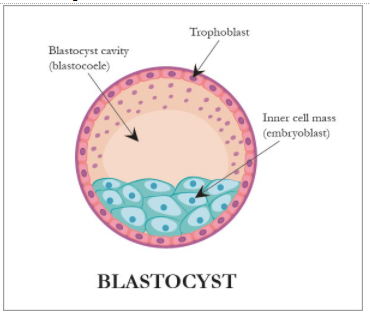
The trophoblast is the cells that form the outer layer of blastocyst. They are present for four days of post-fertilization in human beings. They provide nutrients to the embryo and develop into a large part of the placenta which is formed during the first stage of pregnancy. The cells are forced to differentiate from the fertilized egg to become an extraembryonic structure. They do not directly contribute to the embryo. The trophoblast is contiguous with the ectoderm of the embryo after gastrulation. This is referred to as trophectoderm. The cells in the human embryo lost their totipotency during the first differentiation. They became no longer totipotent stem cells as they cannot form trophoblast and become important stem cells. They play an important role in embryo implantation and interaction with the decidualized maternal uterus. The placental villi consist of mesenchymal cells. They are directly connected to the fetus circulation with the umbilical cord.
Additional Information:
The trophoblast differentiates into two cells within 6 days after fertilization. The cytotrophoblast is the inner layer which is a single-celled of the trophoblast. The syncytiotrophoblast is the outer layer which is a thick layer that lacks cell boundaries. It grows into the endometrial stroma which secretes hcG to maintain progesterone and sustain a pregnancy. The intermediate pro4 blast is the implantation site. It is an anchor placenta. It is located in the villi and chorion. The trophic blast facilitates the exchange of nutrients, wastage, and gases between the maternal and fetal systems. The extravillous trophoblast penetrates the uterus and outgrows the placenta. It is important for physically attaching the present to the mother. It allows the altering of the vasculature in the uterus. Some proper blast replaces the endothelial cells in the uterine spiral arteries which are independent of maternal vasoconstriction. In short, the foetus receives a continuous supply of blood and is not subjected to fluctuations in oxygen by the placenta which can cause damage.
Note: The first stage of the embryo of humans is similar to that of birds and fishes. Disc theory was generated by a German scientist Ernest Haeckel. The theory was known as recapitulation as according to the scientist the embryonic development of an organism is recapitulated at their initial revolutionary steps. The heartbeats 54 million x before the baby is born and starts beating at 3 weeks and one day after fertilization.
Complete answer:
The trophoblast is the cells that form the outer layer of blastocyst. They are present for four days of post-fertilization in human beings. They provide nutrients to the embryo and develop into a large part of the placenta which is formed during the first stage of pregnancy. The cells are forced to differentiate from the fertilized egg to become an extraembryonic structure. They do not directly contribute to the embryo. The trophoblast is contiguous with the ectoderm of the embryo after gastrulation. This is referred to as trophectoderm. The cells in the human embryo lost their totipotency during the first differentiation. They became no longer totipotent stem cells as they cannot form trophoblast and become important stem cells. They play an important role in embryo implantation and interaction with the decidualized maternal uterus. The placental villi consist of mesenchymal cells. They are directly connected to the fetus circulation with the umbilical cord.
Additional Information:
The trophoblast differentiates into two cells within 6 days after fertilization. The cytotrophoblast is the inner layer which is a single-celled of the trophoblast. The syncytiotrophoblast is the outer layer which is a thick layer that lacks cell boundaries. It grows into the endometrial stroma which secretes hcG to maintain progesterone and sustain a pregnancy. The intermediate pro4 blast is the implantation site. It is an anchor placenta. It is located in the villi and chorion. The trophic blast facilitates the exchange of nutrients, wastage, and gases between the maternal and fetal systems. The extravillous trophoblast penetrates the uterus and outgrows the placenta. It is important for physically attaching the present to the mother. It allows the altering of the vasculature in the uterus. Some proper blast replaces the endothelial cells in the uterine spiral arteries which are independent of maternal vasoconstriction. In short, the foetus receives a continuous supply of blood and is not subjected to fluctuations in oxygen by the placenta which can cause damage.

Note: The first stage of the embryo of humans is similar to that of birds and fishes. Disc theory was generated by a German scientist Ernest Haeckel. The theory was known as recapitulation as according to the scientist the embryonic development of an organism is recapitulated at their initial revolutionary steps. The heartbeats 54 million x before the baby is born and starts beating at 3 weeks and one day after fertilization.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




