
Micropropagation is a technique
(a)For the production of many plants that are clones of each other
(b)For the production of haploid plants
(c)For the production of somatic hybrids
(d)For the production of somaclonal plants
Answer
588.6k+ views
Hint: It is a plant tissue culture that rapidly multiplies stock plant material to produce many progeny plants. This is the only viable method to produce genetically modified cells or cells after protoplast fusion.
Complete answer:
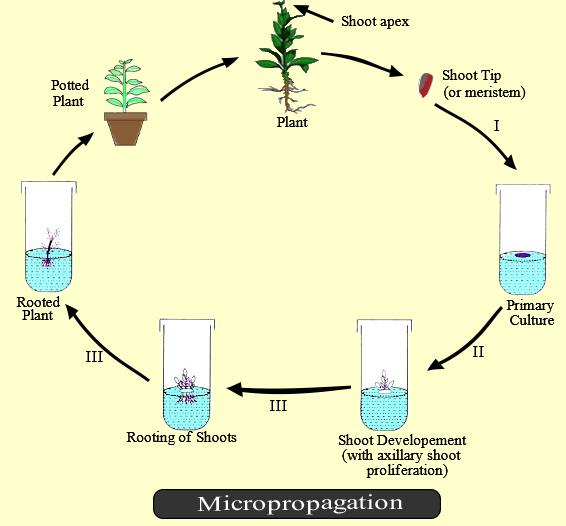
A tissue culture technique for plant propagation in which tissue is taken from a plant and grown in a laboratory to produce genetically identical plantlets or clones to the parent of a plant, this method is known as micropropagation.
Additional Information:
There are 5 different Methods of Micropropagation which are –
In the Meristem Culture method of micropropagation, subtending leaf primordial and a meristem is placed into their respective growing media culture and allowed to grow. After some weeks, an elongated rooted plantlet is produced. Once they reach a considerable height, these plantlets are transferred into the soil. In this method, a disease-free plant is often produced and may be successfully used for the rapid multiplication of varied herbaceous plants.
In the Callus Culture method, selected plant tissue is placed in an artificial growing medium culture until the callus is formed. After the assembly of callus, they're transferred into a medium containing plant growth regulators for the induction of adventitious organs.
In the Suspension Culture method of micropropagation, cells or groups of cells are dispersed and allowed to grow in an aerated and sterile liquid culture medium.
In embryo culture method, the embryo is extracted and placed into a medium with proper nutrients in aseptic conditions.
In the Protoplast Culture method, the plant cell is isolated and cultured in an appropriate medium to reform the cell wall and callus. Later, under suitable conditions, the cell develops a cell wall followed by an increase in cell division and cellular differentiation and grows into a new plant.
So, the correct answer is ‘for the production of many plants that are clones of each other’.
Note: Micropropagation techniques require intensive labour and this often limits their commercial application. Automation can reduce the labour required. The main disadvantage of this method includes the production of infected progeny from infected plant samples.
Complete answer:
A tissue culture technique for plant propagation in which tissue is taken from a plant and grown in a laboratory to produce genetically identical plantlets or clones to the parent of a plant, this method is known as micropropagation.
Additional Information:
There are 5 different Methods of Micropropagation which are –
In the Meristem Culture method of micropropagation, subtending leaf primordial and a meristem is placed into their respective growing media culture and allowed to grow. After some weeks, an elongated rooted plantlet is produced. Once they reach a considerable height, these plantlets are transferred into the soil. In this method, a disease-free plant is often produced and may be successfully used for the rapid multiplication of varied herbaceous plants.
In the Callus Culture method, selected plant tissue is placed in an artificial growing medium culture until the callus is formed. After the assembly of callus, they're transferred into a medium containing plant growth regulators for the induction of adventitious organs.
In the Suspension Culture method of micropropagation, cells or groups of cells are dispersed and allowed to grow in an aerated and sterile liquid culture medium.
In embryo culture method, the embryo is extracted and placed into a medium with proper nutrients in aseptic conditions.
In the Protoplast Culture method, the plant cell is isolated and cultured in an appropriate medium to reform the cell wall and callus. Later, under suitable conditions, the cell develops a cell wall followed by an increase in cell division and cellular differentiation and grows into a new plant.
So, the correct answer is ‘for the production of many plants that are clones of each other’.
Note: Micropropagation techniques require intensive labour and this often limits their commercial application. Automation can reduce the labour required. The main disadvantage of this method includes the production of infected progeny from infected plant samples.

Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




