
What is the minimum and maximum distance between the convex lens and the object for the magnification of a real image to be greater than 1?
(A). O and \[\text{f}\]
(B). \[\text{f}\] and \[\text{2f}\]
(C). \[\text{f}\]and \[\infty \]
(D). \[\text{2f}\] and \[\infty \]
Answer
573.3k+ views
Hint: Convex lenses form two types of images for different positions of the object behind the lens; real image is always inverted but it can be diminished, enlarged or of the same size of the object. It is formed on the other side of the lens from the object. While a virtual image is always erect, enlarged formed on the same side of the lens as the object.
Formula Used:
\[\text{m=}\dfrac{{{\text{h}}_{\text{i}}}}{{{\text{h}}_{\text{o}}}}\]
\[\text{m = }\dfrac{\text{v}}{\text{u}}\]
Complete answer:
A convex lens can form real images as well as virtual images for different positions of the object. Some characteristics of a convex lens are-
Radius of curvature\[\text{(}{{\text{R}}_{\text{1}}}\text{, }{{\text{R}}_{\text{2}}}\text{)}\] is the radius of the sphere of which the lens is a part of. There are two radii of curvature in a lens
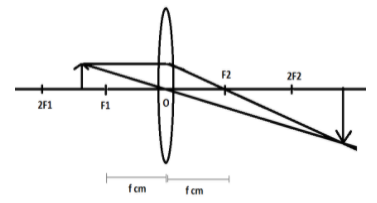
Focus\[({{\text{F}}_{\text{1}}}\text{, }{{\text{F}}_{\text{2}}}\text{)}\] is a point on the axis of the lens where light rays parallel to the axis converge after refraction from the lens.
The distance between the centre of lens and focus is called the Focal Length \[\text{(}{{\text{f}}_{1}}\text{ cm corresponding to }{{\text{F}}_{1}}\text{, }{{\text{f}}_{2}}\text{ cm corresponding to }{{\text{F}}_{2}}\text{)}\]. It is\[(+)\]for a convex lens while \[(-)\] for a concave lens.
Magnification is the ratio of image height\[\text{(}{{\text{h}}_{\text{i}}}\text{)}\]to object height \[\text{(}{{\text{h}}_{\text{o}}}\text{)}\]
\[\text{m=}\dfrac{{{\text{h}}_{\text{i}}}}{{{\text{h}}_{\text{o}}}}\] or \[\text{m = }\dfrac{\text{v}}{\text{u}}\]
When the object is kept at focus, the image formed is real, inverted and enlarged. The position of the image is at infinity. This means that object distance is equal to\[\text{f}\].
A convex lens always forms a real, inverted and enlarged image when the object kept between \[{{\text{f}}_{{}}}\text{ and 2}{{\text{f}}_{{}}}\]. So, the maximum distance, the object can shift while still forming an enlarged image is \[\text{2f}\]
Therefore, the minimum distance between the convex lens and the object for the magnification of a real image to be greater than 1 is \[\text{f}\] and the maximum distance is \[\text{2f}\] .
The correct option is (B).
Note:
According to sign conventions, the magnification of a real image is \[(-)\] while for a virtual image it is \[(+)\]. Also all lengths behind the lens are \[(-)\]while the lengths in front of the lens are\[(+)\]. The object distance is always \[(-)\]but image distance is \[(-)\]for real images and \[(+)\] for virtual images.
Formula Used:
\[\text{m=}\dfrac{{{\text{h}}_{\text{i}}}}{{{\text{h}}_{\text{o}}}}\]
\[\text{m = }\dfrac{\text{v}}{\text{u}}\]
Complete answer:
A convex lens can form real images as well as virtual images for different positions of the object. Some characteristics of a convex lens are-
Radius of curvature\[\text{(}{{\text{R}}_{\text{1}}}\text{, }{{\text{R}}_{\text{2}}}\text{)}\] is the radius of the sphere of which the lens is a part of. There are two radii of curvature in a lens
Focus\[({{\text{F}}_{\text{1}}}\text{, }{{\text{F}}_{\text{2}}}\text{)}\] is a point on the axis of the lens where light rays parallel to the axis converge after refraction from the lens.
The distance between the centre of lens and focus is called the Focal Length \[\text{(}{{\text{f}}_{1}}\text{ cm corresponding to }{{\text{F}}_{1}}\text{, }{{\text{f}}_{2}}\text{ cm corresponding to }{{\text{F}}_{2}}\text{)}\]. It is\[(+)\]for a convex lens while \[(-)\] for a concave lens.
Magnification is the ratio of image height\[\text{(}{{\text{h}}_{\text{i}}}\text{)}\]to object height \[\text{(}{{\text{h}}_{\text{o}}}\text{)}\]
\[\text{m=}\dfrac{{{\text{h}}_{\text{i}}}}{{{\text{h}}_{\text{o}}}}\] or \[\text{m = }\dfrac{\text{v}}{\text{u}}\]
When the object is kept at focus, the image formed is real, inverted and enlarged. The position of the image is at infinity. This means that object distance is equal to\[\text{f}\].
A convex lens always forms a real, inverted and enlarged image when the object kept between \[{{\text{f}}_{{}}}\text{ and 2}{{\text{f}}_{{}}}\]. So, the maximum distance, the object can shift while still forming an enlarged image is \[\text{2f}\]
Therefore, the minimum distance between the convex lens and the object for the magnification of a real image to be greater than 1 is \[\text{f}\] and the maximum distance is \[\text{2f}\] .
The correct option is (B).

Note:
According to sign conventions, the magnification of a real image is \[(-)\] while for a virtual image it is \[(+)\]. Also all lengths behind the lens are \[(-)\]while the lengths in front of the lens are\[(+)\]. The object distance is always \[(-)\]but image distance is \[(-)\]for real images and \[(+)\] for virtual images.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




