
How many minimum carbons required for chain isomerism and position isomerism in alkenes?
Answer
587.7k+ views
Hint: The minimum number of carbon atoms to form an alkene only is 2. Now form an alkene with 2 carbon atoms and check if the isomerism is possible or not. If the previous compound does not satisfy the requirements, form an alkene with 3 carbon atoms and continue till the above isomerism requirements are fulfilled. Chain isomerism and position isomerism are types of structural isomerism.
Complete step-by-step answer:
The word “isomer” is derived from the Greek words "isos" and "mers". "Isos" means equal and "mers" means parts, so "isomers" means equal parts.
Isomerism is the phenomenon in which two or more compounds have the same chemical formula but differ in chemical structures. Chemical compounds that have identical chemical formulas but differ in properties and the arrangement of atoms in the molecule are called isomers i.e. they exhibit isomerism.
Isomerism is of two types namely, Structural isomerism and stereoisomerism.
In structural isomerism the functional groups and the atoms in the molecules of these isomers are bonded in different ways. Structural isomers have different IUPAC names although their chemical formulae are the same.
The types of structural isomerism are:
- Chain
- Positional
- Functional
- Metamerism
- Tautomerism
- Ring - chain
We will now draw a 2-carbon alkene compound.
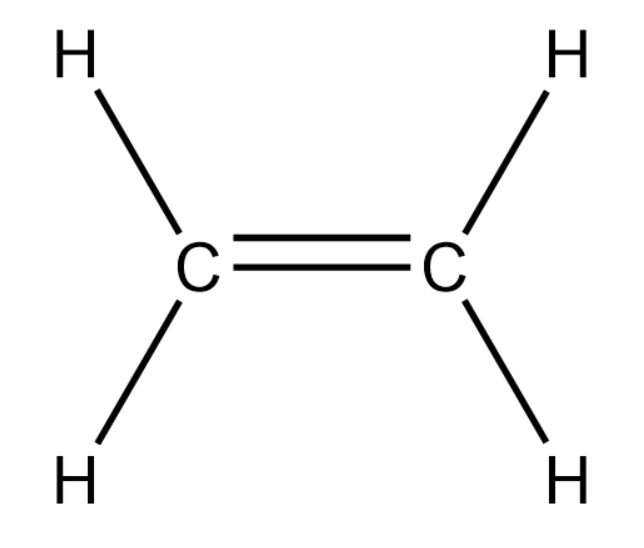
In the above compound we cannot find chain as well as position isomerism.
We will now draw a 3-carbon alkene compound.
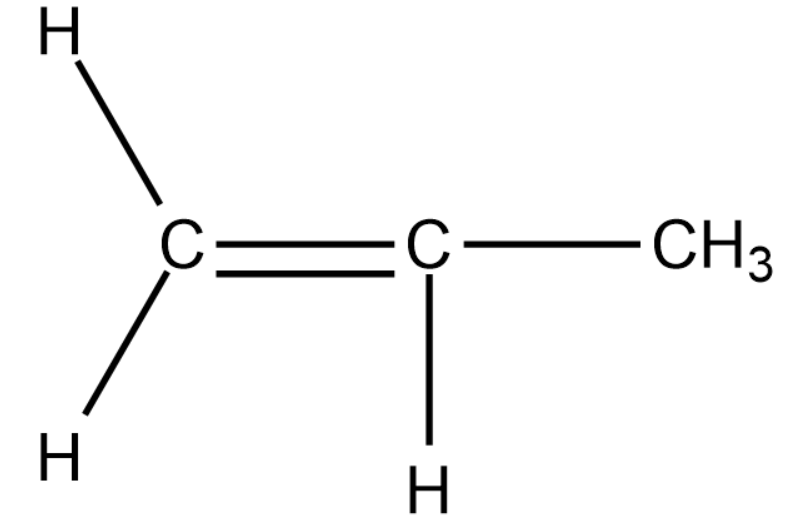
In the above compound as well, we cannot find chain or position isomerism.
We will now draw a 4-carbon alkene compound.
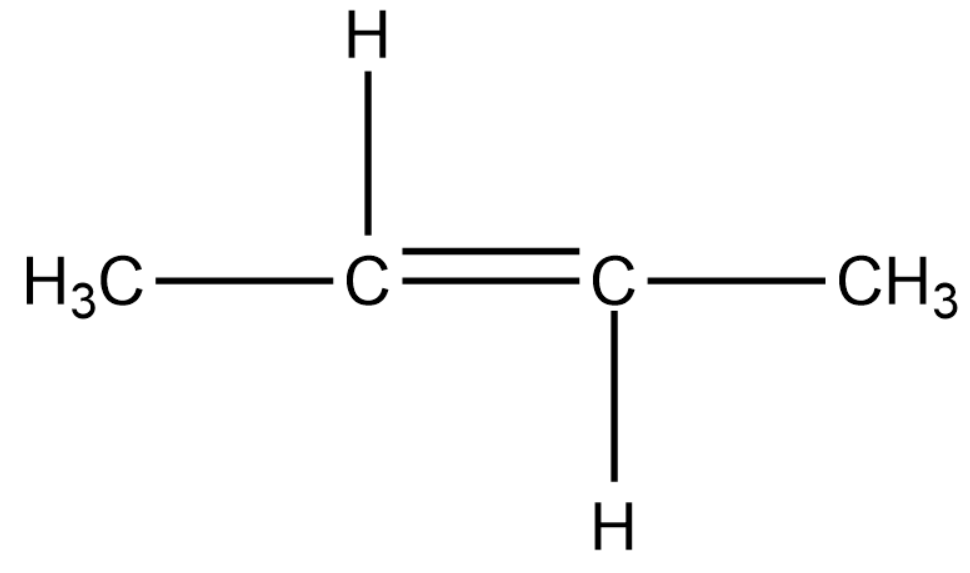
In the above compound we can shift the double bond to the terminal carbon. This compound shows position isomerism. The methyl groups can be replaced by the hydrogen atom, thus showing chain isomerism.
Chain isomers:
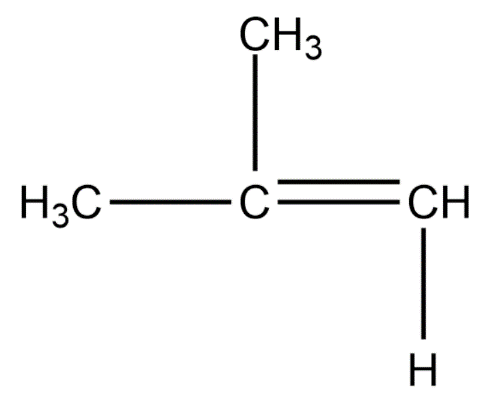
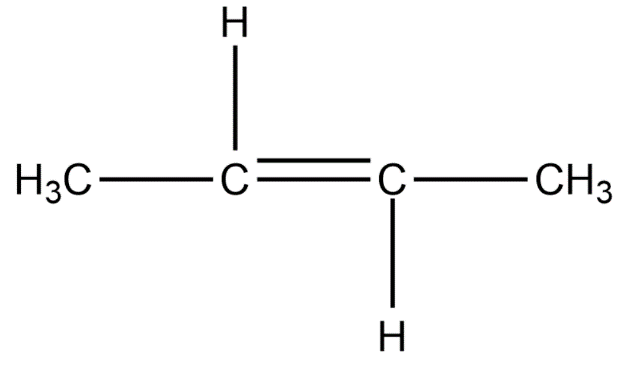
Position isomers:
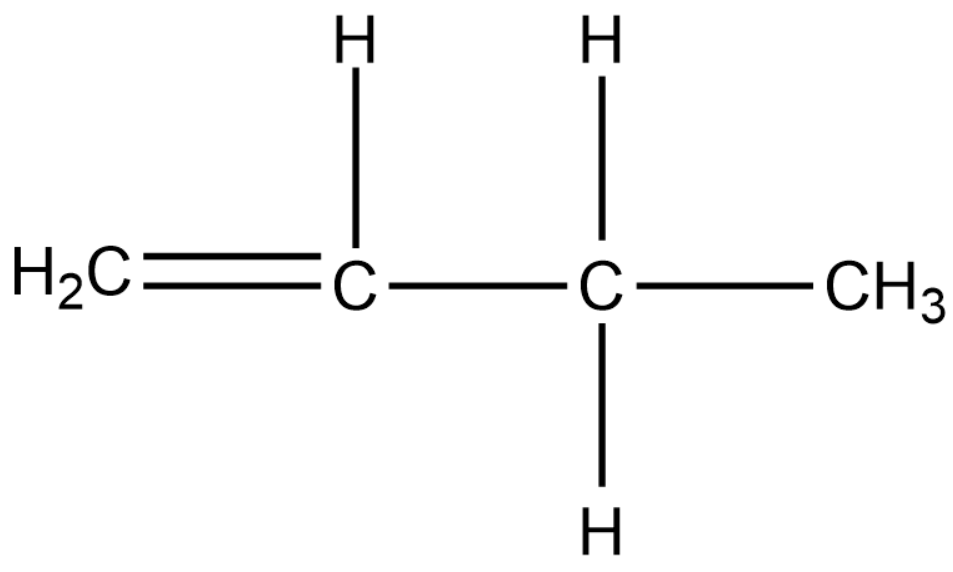
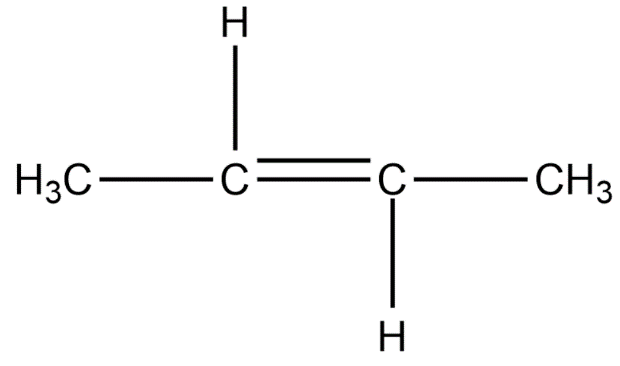
Therefore, the minimum number of carbon atoms required for chain and position isomerism in alkenes is 4.
Note: In the above question we found chain isomerism and position isomerism for alkenes with a 4-carbon system. However, we can find position isomers for alkenes with a 3-carbon system provided there is a substituent functional group like a halogen atom( F, Cl, Br, I).
Complete step-by-step answer:
The word “isomer” is derived from the Greek words "isos" and "mers". "Isos" means equal and "mers" means parts, so "isomers" means equal parts.
Isomerism is the phenomenon in which two or more compounds have the same chemical formula but differ in chemical structures. Chemical compounds that have identical chemical formulas but differ in properties and the arrangement of atoms in the molecule are called isomers i.e. they exhibit isomerism.
Isomerism is of two types namely, Structural isomerism and stereoisomerism.
In structural isomerism the functional groups and the atoms in the molecules of these isomers are bonded in different ways. Structural isomers have different IUPAC names although their chemical formulae are the same.
The types of structural isomerism are:
- Chain
- Positional
- Functional
- Metamerism
- Tautomerism
- Ring - chain
We will now draw a 2-carbon alkene compound.

In the above compound we cannot find chain as well as position isomerism.
We will now draw a 3-carbon alkene compound.

In the above compound as well, we cannot find chain or position isomerism.
We will now draw a 4-carbon alkene compound.

In the above compound we can shift the double bond to the terminal carbon. This compound shows position isomerism. The methyl groups can be replaced by the hydrogen atom, thus showing chain isomerism.
Chain isomers:


Position isomers:


Therefore, the minimum number of carbon atoms required for chain and position isomerism in alkenes is 4.
Note: In the above question we found chain isomerism and position isomerism for alkenes with a 4-carbon system. However, we can find position isomers for alkenes with a 3-carbon system provided there is a substituent functional group like a halogen atom( F, Cl, Br, I).
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




